Abstract
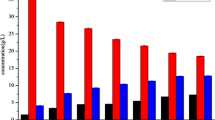
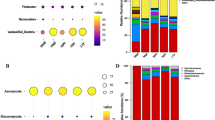
Chinese rice wine (CRW) is the oldest kind of wine in China and is mainly fermented by wheat Qu and yeast with rice, millet, etc. This gives CRW a unique quality, but the flavor components are complex. Its formation is related to microorganisms, but the link between CRW and microorganisms is poorly understood. Here, we used two kinds of sorghum (JZ22 and JB3, of which JZ22 has a higher tannin content) as the raw materials to brew and determined the structural and functional dynamics of the microbiota by metagenomics and flavor analyses. We detected 106 (JZ22) and 109 (JB3) volatile flavor compounds and 8 organic acids. By correlation analysis, we established 687 (JZ22) and 496 (JB3) correlations between the major flavor compounds and microbes. In JZ22, Blautia, Collinsella, Bifidobacterium, Faecalibacterium and Prevotella had the most correlations with flavor production. In JB3, the top 5 genera were Stenotrophomonas, Bdellovibrio, Solibacillus, Sulfuritalea and Achromobacter. In addition, more esters were detected, and more microorganisms correlated with ester generation in JZ22. This study provides a new idea for the micro ecological diversity of CRW fermented with sorghum. This is of significance for improving the quality and broadening the CRW varieties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Chinese rice wine (CRW), a traditional alcohol drink, is fermented from rice with wheat Qu and yeast. It is one of the oldest drinks in the world, along with beer and wine1. CRW is also called “liquid cake” because of its abundant nutrition and pleasant aroma2. Sorghum is a kind of natural and high-nutrition functional food that is rich in dietary fiber, protein, fat, folic acid, ferrum and other microelements. Sorghum is the main raw material for producing spirits. Chinese liquor brewed with sorghum, such as Maotai-flavored liquor, has long enjoyed a good reputation. However, with the changes in China’s policies on the liquor industry and the increase in people’s living standards, high-nutrition, low-alcohol CRWis becoming increasingly popular with consumers. Brewing CRW with sorghum not only increases the value of sorghum but also combines these two nutritious foods together.
Flavor differences can be caused by many factors, such as the raw ingredients used in the fermentation, fermentation conditions, distillation practices, and aging processes3. ** sequence42.
Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered with a 97% similarity cutoff using UPARSE (version 7.1 http://drive5.com/uparse/), and chimeric sequences were identified and removed using UCHIME. The taxonomy of each 16 S rRNA gene sequence was analyzed by an RDP Classifier algorithm (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/) against the Silva (SSU123) 16 S rRNA database using a confidence threshold of 70%. The taxonomy of each ITS gene sequwence was analyzed by Unite (Release 6.0 http://unite.ut.ee/index.php)43.
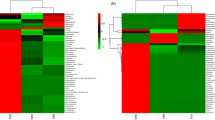
Alpha rarefaction was performed in QIIME (version 1.7.0) using the Chao1 estimates of species abundance44, while observed species estimation of the amount of unique OTUs found in each sample and Shannon index45 were calculated. Cluster analysis was preceded by NMDS46. For the QIIME calculation, the beta diversity of the unweighted and weighted UniFrac distances was used for the UPGMA clustering and principal coordinate analysis47. To identify the differences in the bacterial communities between the two groups, similarities were analyzed using the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity distance matrices.
The metagenomic functional composition prediction analysis for all biofilm samples from 16 S data in the latest Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database was performed using PICRUSt pipeline as described by Langille et al.48.
To associate the microbiota and flavour compounds, the significance of correlations between the microbial genera and flavour were tested(pearson correlation). The p values were adjusted by FDR using Benjamini–Hochberg method, the cutoff of adjusted p value was set as 0.05. The association network was constructed by using all significant associations, and it was displayed using R language programming.
References
Xu, E. et al. Characterization of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Chinese Rice Wine Fermented from Enzymatic Extruded Rice. Journal of Food Science. 80, 1476–1489 (2015).
Fu, J. Introduction to yellow rice wine in China from ancient time to present day. Liquor-Making Science & Technology. 113–116 (2011).
Fan, W. & Qian, M. Characterization of aroma compounds of chinese “Wuliangye” and “Jiannanchun” liquors by aroma extract dilution analysis. J Agric Food Chem. 54, 2695–2704 (2006).
**ong, R. Preliminary study on the selection criteria of raw materials for the Chinese Rice Wine (Zhejiang A&F University, Zhejiang, Linan, 2015).
Chen, S., Luo, T., Xu, Y., Fan, W. & Zhao, G. Effects of yeast strains and raw materials on β-phonylethanol production in Chinese rice wines. China Brewing. 28, 23–26 (2009).
Cui, L. Biosynthetic Pathways and Steps of Pyrazine Compounds in Maotai-flavor Liquor. Liquor Making. 34, 39–40 (2007).
Zhang, CL. The relationship between quality, microorganism and aroma components of Luzhou Laojiao Daqu. (Jiangnan Universty. Jiangsu, Wuxi, 2012).
Fujii, T. et al. Molecular cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of the yeast alcohol acetyltransferase gene. Applied & Environmental Microbiology. 60, 2786–2792 (1994).
Beaumont, M. Flavouring composition prepared by fermentation with Bacillus spp. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 75, 189–196 (2002).
Wei, Z., Tabrizi, M., Robert, N. M. J. & Zhong, H. Daqu - A Traditional Chinese Liquor Fermentation Starter. Journal of the Institute of Brewing. 117, 82–90 (2011).
De, F., Genovese, A., Ferranti, P., Gilbert, J. & Ercolini, D. Metatranscriptomics reveals temperature-driven functional changes in microbiome impacting cheese maturation rate. Scientific Reports. 6, 2045–2322 (2016).
Liu, S. P. et al. Bacterial succession and the dynamics of volatile compounds during the fermentation of Chinese rice wine from Shaoxing region. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 31, 1907–1921 (2015).
Wang, P. X. et al. Changes in flavour characteristics and bacterial diversity during the traditional fermentation of Chinese rice wines from Shaoxing region. Food Control. 44, 58–63 (2014).
Lv, Y. et al. Characterization of microbial communities in Chinese rice wine collected at Yichang city and Suzhou city in China. Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology. 27, 1409–1418 (2017).
Guo, X., Hu, P., Xu, Y. & Zhao, G. Research on the Volatile Flavoring Substances in Yellow Rice Wine. Liquor-making Science & Technology. 5 (2004).
Cui, Y., Cao, X., Wang, C. & Zhou, G. Research progress of 4-Vinylguaiacol and 4-Ethylguaiacol in fermentation industry. China Brewing. 28, 14–17 (2009).
Mason, D. & Braunwald, E. The Effects of Nitroglycerin and Amyl Nitrite on Arteriolar and Venous Tone in the Human Forearm. Circulation. 32, 755 (1965).
Luo, T., Fan, W. & Xu, Y. Characterization of volatile and semi-volatile compounds in Chinese rice wines by headspace solid phase microextraction followed by gas. Journal of the Institute of Brewing. 114, 172–179 (2008).
Yu, L., Ding, F. & Ye, H. Analysis of characteristic flavour compounds in Chinese rice wines and representative fungi in wheat Qu samples from different regions. Journal of the Institute of Brewing. 118, 114–119 (2012).
Lv, X. C. et al. Bacterial community dynamics during the traditional brewing of Wuyi Hong Qu glutinous rice wine as determined by culture-independent methods. Food Control. 34, 300–306 (2013).
Jiménez, N., Curiel, J., Reverón, I., Rivas, B. & Muñoz, R. Uncovering the Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 Gallate Decarboxylase Involved in Tannin Degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 79, 4253–4263 (2013).
Chowdhury, S., Khanna, S., Verma, S. & Tripathi, A. Molecular diversity of tannic acid degrading bacteria isolated from tannery soil. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 97, 1210–1219 (2004).
Kasai, D., Masai, E., Miyauchi, K., Katayama, Y. & Fukuda, M. Characterization of the Gallate Dioxygenase Gene: Three Distinct Ring Cleavage Dioxygenases Are Involved in Syringate Degradation by Sphingomonas paucimobilis SYK-6†. Journal of Bacteriology. 187, 5067–5074 (2005).
Nogales, J. et al. Unravelling the gallic acid degradation pathway in bacteria: the gal cluster from Pseudomonas putida. Molecular Microbiology. 79, 359–374 (2011).
Luan, J. Research on the Flavor in Rice Wine. China Brewing 21, 21–24 (2002).
Li, H., et al. Integrated Electromicrobial Conversion of CO2 to Higher Alcohols. Science. 335 (2012).
Chen, H., Wu, Z. & **e, G. Detection of Organic Acids in Rancid Yellow Rice Wine in Storage. Liquor-Making Science & Technology. 2, 78–81 (2017).
Liu, J. J. et al. Research and Application on L-Malic Acid. Chian Food Additives. 3, 53–56 (2003).
Feng, A., Zhao, W., Bai, W. & Pang, J. Determination of organic acids in different rice wine. China Brewing. 29, 144–146 (2010).
Erikax, B. & Bernardoa, L. Characterization of Cladosporium Rot in Grapevines,a Problem of Growing Importance in Chile. Plant Disease. 92, 1635–1642 (2008).
Takada, T., Kurakawa, T., Tsuji, H. & Nomoto, K. Fusicatenibacter saccharivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human faeces. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology. 63, 3691–3696 (2013).
**a, R. & Che, B. Determination of Isoamyl nitrite by gas chromatography. Chinese Journal of Medicine. 41, 48–48 (2006).
Palleroni, N. & Bradbury, J. Stenotrophomonas, a new bacterial genus for Xanthomonas maltophilia (Hugh 1980) Swings et al. 1983. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 43 (1993).
Pontesucre, A. ABC transporters in microorganisms: research, innovation and value as targets against drug resistance. (ed. Ponte-Sucre, A) Ch. 2, 35–36 (Caister Academic, 2009).
Ter Beek, J., Guskov, A. & Slotboom, D. J. Structural diversity of ABC transporters. Journal of General Physiology. 143, 419–435 (2014).
Song, Z., Du, H., Zhang, Y. & Xu, Y. Unraveling Core Functional Microbiota in Traditional Solid-State Fermentation by High-Throughput Amplicons and Metatranscriptomics Sequencing. Frontiers in Microbiology. 8 (2017).
Guan, B., Ding, Y., **e, L. & Long, Y. The Modification of the DNS Method for the Determination of Reducing Sugar. Journal of Wuxi University of Light Industry. 18 (1999).
Ye, F., Chen, X. & Ni, X. Study of Analytical Method for Organic acids in Yellow Rice Wines by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Liquor Making. 40, 80–85 (2013).
Zhang, X. L., Tian, X. Q., Ma, L. Y. & Yang, Q. Biodiversity of the Symbiotic Bacteria Associated with Toxic Marine Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Journal of Biosciences & Medicines. 3, 23–28 (2015).
Buee, M. et al. 454 Pyrosequencing analyses of forest soils reveal an unexpectedly high fungal diversity. New Phytologist. 184, 449–456 (2009).
Ren, G., Ren, W., Teng, Y. & Li, Z. Evident bacterial community changes but only slight degradation when polluted with pyrene in a red soil. Frontiers in Microbiology. 6 (2015).
Magoč, T. & Salzberg, S. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27, 2957–2963 (2011).
Kõljalg, U. et al. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Molecular Ecology. 22, 5271–5277 (2013).
Caporaso, J. G. et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods. 7, 335–336 (2010).
Kemp, P. & Aller, J. Bacterial diversity in aquatic and other environments: what 16 S rDNA libraries can tell us. Fems Microbiology Ecology. 47, 161–177 (2004).
Werley, H., Devine, E., Zorn, C., Ryan, P. & Westra, B. The NMDS: Abstraction tool for standardized, comparable, essential data. American Journal of Public Health. 81, 421–426 (1991).
Lozupone, C., Lladser, M., Knights, D., Stombaugh, J. & Knight, R. UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. Isme Journal. 5 (2011).
Langille, M. G. I. et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16 S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nature Biotechnology. 31, 814–821 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Key R&D Program of China(2016YFD0400500) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31400161). We are also grateful to all wine producers that collaborate with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L.X., X.L. and Q.R. designed the research; X.L. and Z.P.L. analyzed the results; H.J.W. and Z.W.W. performed the experiments; J.L.X. and F.P.Z. participated in writing the manuscript and revision; Q.R. supervised the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Wu, H., Wang, Z. et al. Microbial dynamics and metabolite changes in Chinese Rice Wine fermentation from sorghum with different tannin content. Sci Rep 8, 4639 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23013-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23013-1
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The initial composition and structure of microbial community determined the yield and quality of Baijiu during the spontaneous fermentation
International Microbiology (2023)
-
Microbial succession and exploration of higher alcohols-producing core bacteria in northern Huangjiu fermentation
AMB Express (2022)
-
Metabolite-based cell sorting workflow for identifying microbes producing carbonyls in tobacco leaves
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2022)
-
Global cocoa fermentation microbiome: revealing new taxa and microbial functions by next generation sequencing technologies
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (2021)
-
Bacterial succession and the dynamics of flavor compounds in the Huangjiu fermented from corn
Archives of Microbiology (2020)