Abstract
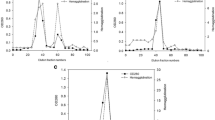
Chitinases are found in species from all kingdoms, including Kingdom Animalia. We purified chitinase, poly [1,4-(N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminide)] glycanohydrolase, by cation exchange chromatography on SP-Sepharose from the integument of a lepidopteran, the Mediterranean flour moth, Ephestia kuehniella Zeller, and further characterized it. Ephestia kuehniella chitinase has similar properties to other insect chitinases, with respect to the molecular mass. Its molecular mass was 79.7 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The optimum pH and temperature for activity were 6 and 40 °C, respectively. The purified enzyme exhibited stability at a pH range from 4.5 to 8.0 and showed high sensitivity to Co2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, Hg2+ and Ag+. The Km and Vmax values of E. kuehniella chitinase were, respectively, 3.98 mg/mL and 7.11 μmol/min/mg for colloidal chitin. In comparison to the values determined for the substrate affinity, the enzyme had a 2.36-fold higher affinity for Carboxymethyl-Chitin-Remazol Brilliant Violet (CM-Chitin-RBV) as a soluble substrate. We examined the antibacterial effect of E. kuehniella chitinase on the growth of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. The enzyme inhibited the growth of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus thuringiensis and Escherichia coli, where the average diameter of inhibition zone was 20, 23 and 19 mm, respectively. The antimicrobial effect and chitinase activity strengthen the hypothesis that the enzyme could be used in biological control against plant pests.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Abdel-Banat B. M. A., Kameyama Y, Yoshioka T. and Koga D. (1999) Purification and characterization of a 54 kDa chitinase from Bombyx mori. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 29, 537–547.
Abdel-Banat B. M. A., Zhou W., Karasuda S. and Koga D. (2002) Analysis of hydrolytic activity of a 65-kDa chitinase from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry 66, 1119–1122.
Arakane Y and Muthukrishnan S. (2010) Insect chitinase and chitinase-like proteins. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 67, 201–216.
Arakane Y, Zhu Q., Matsumiya M., Muthukrishnan S. and Kramer K. J. (2003) Properties of catalytic, linker and chitin-binding domains of insect chitinase. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 33, 631–648.
Bhattacharya D., Nagpure A. and Gupta R. K. (2007) Bacterial chitinases: Properties and potential. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 27, 21–28.
Bradford M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry 72, 248–254.
Cantarel B. L., Coutinho P. M., Rancurel C, Bernard T., Lombard V. and Henrissat B. (2009) The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Research 37, D233–D238.
Das S., Van Dellen K, Bulik D., Magnelli P., Cui J., Head J., Robbins P. W. and Samuelson J. (2006) The cyst wall of Entamoeba invadens contains chitosan (deacetylated chitin). Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 148, 86–92.
Ehrlich H., Krautter M., Hanke T, Simon P., Knieb C, Heinemann S. and Worch H. (2007a) First evidence of the presence of chitin in skeletons of marine sponges. Part II. Glass sponges (Hexactinellida: Porifera). journal of Experimental Zoology Part B 308, 473–483.
Ehrlich H, Maldonado M., Spindler K.-d., Eckert C., Hanke T, Born R., Goebel C., Simon P., Heinemann S. and Worch H. (2007b) First evidence of chitin as a component of the skeletal fibers of marine sponges. Part I. Verongidae (Demospongia: Porifera). Journal of Experimental Zoology Part B 308, 347–356.
Esseling J. J. and Emons A. M. C. (2004) Dissection of Nod factor signalling in legumes: Cell biology, mutants and pharmacological approaches. Journal of Microscopy 214, 104–113.
Fukamizo T. (2000) Chitinolytic enzymes: Catalysis, substrate binding, and their application. Current Protein & Peptide Science 1, 105–124. doi: 10.2174/1389203003381450.
Genta F. A., Blanes L., Cristofoletti P. T, do Lago C. L., Terra W. R. and Ferreira C. (2006) Purification, characterization and molecular cloning of the major chitinase from Tenebrio molitor larval midgut. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 36, 789–800.
Haider S. K, Maity C, Jana A., Pati B. R. and Keshab C. M. (2012) Chitinolytic enzymes from the newly isolated Aeromonas hydrophila SBK1: Study of the mosquitocidal activity. BioControl 57, 441–449.
Hegedus D., Erlandson M., Gillott C. and Toprak U. (2009) New insights into peritrophic matrix synthesis, architecture, and function. Annual Review of Entomology 54, 285–302.
Hunt S. and El Sherief A. (1990) Aperiodic structure in the ‘pen’ chitin of the squid Loligo vulgaris. Tissue and Cell 22, 191–197.
Jagadeeswari S. J. and Panneer Selvam K. (2012) Optimization of chitinase production by soil Streptomyces sp. SJKP9. Journal of Academia and Industrial Research 1, 332–336.
Jeuniaux C. and Voss-Foucart M. F (1991) Chitin biomass and production in the marine environment. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 19, 347–356.
Kabir K. E., Hirowatari D., Watanabe K. and Koga D. (2006a) Purification and characterization of a novel isozyme of chitinase from Bombyx mori. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 70, 252–262. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70.252
Kabir K. E., Sugimoto H, Tado H, Endo K., Yamanaka A., Tanaka S. and Koga D. (2006b) Effect of Bombyx mori chitinase against Japanese pine sawyer (Monochamus alternatus) adults as a biopesticide. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 70, 219–229. doi: 10.1271/bbb.70.219
Khan M. A., Hamid R., Ahmad M., Abdin M. Z. and Javed S. (2010) Optimization of culture media for enhanced chitinase production from a novel strain of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia using response surface methodology. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 20, 1597–1602.
Koga D., Jilka J. and Kramer K. J. (1983) Insect endochitinases: Glycoproteins from moulting fluid, integument and pupal haemolymph of Manduca sexta L. Insect Biochemistry 13, 295–305.
Koga D., Sasaki Y, Uchiumi Y, Hirai N, Arakene Y and Nagamatsu Y (1997) Purification and characterization of Bombyx mori chitinases. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 27, 757–767.
Kondo K., Matsumoto M., Kojo A. and Maeda R. (2002) Purification and characterization of chitinase from pupae of Vieris rapae crucivora (Boisduval). Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan 35, 241–246.
Laemmli U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685.
Lee Y. S., Park I. H., Yoo J. S., Chung S. Y., Lee Y. C, Cho Y S., Ahn S. C, Kim C. M. and Choi Y. L. (2007) Cloning, purification, and characterization of chitinase from Bacillus sp. DAU101. Bioresource Technology 98, 2734–2741.
Linder M. and Teeri T. T. (1997) The roles and function of cellulose-binding domains. Journal of Biotechnology 57, 15–28.
Mathur A., Rawat A., Bhatt G., Baweja S., Ahmad F., Grover A., Madhav K., Dhand M., Mathur D., Verma S. K., Singh S. K. and Dua V. K. (2011) Isolation of Bacillus producing chitinase from soil: Production and purification of chito-oligosaccharides from chitin extracted from fresh water crustaceans and antimicrobial activity of chitinase. Recent Research in Science and Technology 3(11), 01–06.
Merzendorfer H. (2006) Insect chitin synthases: A review. Journal of Comparative Physiology B 176, 1–15.
Merzendorfer H. (2013) Insect-derived chitinases. Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology 136, 19–50.
Milewski S., O’Donnell R. W. and Gooday G. W. (1992) Chemical modification studies of the active centre of Candida albicans chitinase and its inhibition by allosamidin. Journal of General Microbiology 138, 2545–2550.
Miller G. L. (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry 31, 426–428.
Reynolds S. E. and Samuels R. I. (1996) Physiology and biochemistry of insect moulting fluid. Advances in Insect Physiology 26, 157–232.
Roncero C. (2002) The genetic complexity of chitin synthesis in fungi. Current Genetics 41, 367–378.
Ruiz-Herrera J. and Ortiz-Castellanos L. (2010) Analysis of the phylogenetic relationships and evolution of the cell walls from yeasts and fungi. FEMS Yeast Research 10, 225–243.
Samuels R. I. and Paterson I. C. (1995) Cuticle degrading proteases from insect moulting fluid and culture filtrates of entomopathogenic fungi. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 110, 661–669.
Wang S. L., Hsiao W. J. and Chang W. T. (2002) Purification and characterization of an antimicrobial chitinase extracellularly produced by Monascus purpureus CCRC31499 in a shrimp and crab shell powder medium. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 50, 2249–2255.
Weiss I. M., Schönitzer V., Eichner N. and Sumper M. (2006) The chitin synthase involved in marine bivalve mollusk shell formation contains a myosin domain. FEBS Letters 580, 1846–1852.
Zhang H. B., Liu M. Y, Tian Y J. and Hu X. Q. (2011) Comparative characterization of chitinases from silkworm (Bombyx mori) and bollworm (Helicoverpa armígera). Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics 61, 267–275.
Zhang Y, Foster J. M., Nelson L. S., Ma D. and Carlow C. K. S. (2005) The chitin synthase genes chs-1 and chs-2 are essential for C. elegans development and responsible for chitin deposition in the eggshell and pharynx, respectively. Developmental Biology 285, 330–339.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehranian, M., Farshbaf Pourabad, R., Sokhandan-Bashir, N. et al. Purification and characterization of chitinase from the integument of the Mediterranean flour moth, Ephestia kuehniella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and its antibacterial role. Int J Trop Insect Sci 38, 105–116 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758417000364
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758417000364