Abstract
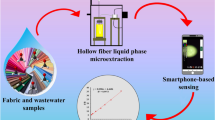
A novel, cost-effective platform using a biodegradable sensor and a simple heat control unit was proposed for multi-sample formaldehyde (FA) assay in one run based on pervaporation. The biodegradable sensor was a composite starch gel attached to paper and immobilized with a mixture of color agents of modified 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazol (AHMT). The sensor was situated on the cap of a vial that served for pervaporation. Two types of heat control units were specially designed using the concepts of aluminum block and water bath heating. With these two designs, multi-sample assays together with standard calibration could be performed in the same run under the same conditions. An FA solution was placed in the vial of the pervaporation unit. After a heating period, FA vapor would change the color of the sensor to purple due to the reaction between AHMT and FA. As a result, the color intensity was proportional to the FA concentration. The change of the color (green or G intensity) was monitored using a smartphone camera and image processing software. Factors affecting the sensitivity of the assay, pervaporation time, pervaporation temperature, FA solution volume, and humidity, were studied. Under the chosen condition, the developed procedure, with a calibration of G intensity = 7.93[FA] + 198, R2 = 0.98, was applied to analyze real samples of seafood and mushrooms available in local markets in Thailand. As there were 24 pervaporation units in the proposed platform, 5 working standards and 9 samples with duplicates could be included in a 1-run assay either in the laboratory or on-site. The developed assay offers green chemical analysis with a simple, cost-effective approach. This serves the UN-SDGs of #2, #3, #7, #10, and #12.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
World Health Organization, Iarc. Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 88, 1 (2006)
P. Verma, V.K. Gupta, Talanta 30, 443 (1983)
S. Viegas, C. Ladeira, C. Nunes, J. Malta-Vacas, M. Gomes, M. Brito, P. Mendonça, J. Prista, J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 5, 1 (2010)
V. Yurayart, W. Sanitchua, Thai J. Toxicol. 32, 53 (2017)
T.S. Yeh, T.C. Lin, C.C. Chen, H.M. Wen, J. Food Drug Anal. 21, 190 (2013)
W. Claeys, C. Vleminckx, A. Dubois, A. Huyghebaert, M. Höfte, P. Daenens, B. Schiffer, Food Addit. Contam. 26, 1265 (2009)
I. Ueta, S. Mochizuki, S. Kawakubo, T. Kuwabara, Y. Saito, Anal. Sci. 31, 99 (2015)
J. Li, J. Zhu, L. Ye, Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 16, 127 (2007)
H. Wang, J. Ding, X. Du, X. Sun, L. Chen, Q. Zeng, Y. Xu, X. Zhang, Q. Zhao, L. Ding, Food Chem. 131, 380 (2012)
H.C. Hu, Y.X. Tian, X.S. Chai, Anal. Sci. 28, 689 (2012)
M. Hladová, J. Martinka, P. Rantuch, A. Nečas, Res. Pap. Fac. Mater. Sci. Technol. Slovak Univ. Technol. 27, 105 (2019)
Q. Li, P. Sritharathikhun, S. Motomizu, Anal. Sci. 23, 413 (2007)
F. Nowshad, M.N. Islam, M.S. Khan, Agric. Food Secur. 7, 1 (2018)
S. Teerasong, N. Amornthammarong, K. Grudpan, N. Teshima, T. Sakai, D. Nacapricha, N. Ratanawimarnwong, Anal. Sci. 26, 629 (2010)
X.L. Guo, Y. Chen, H.L. Jiang, X.B. Qiu, D.L. Yu, Sensors (Switzerland) 2018, 18 (2018)
Y. Sekine, R. Katori, Y. Tsuda, T. Kitahara, Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom) 37, 1647 (2016)
S.H. Jung, J.W. Kim, I.G. Jeon, Y.H. Lee, Aquaculture 194, 253 (2001)
K. Murai, M. Okano, H. Kuramitz, N. Hata, T. Kawakami, S. Taguchi, Anal. Sci. 24, 1455 (2008)
U. Pongkitdachoti, F. Unob, Anal. Methods 14, 926 (2022)
C. Yeerum, P. Issarangkura Na Ayutthaya, K. Kesonkan, K. Kiwfo, P. Boochathum, K. Grudpan, M. Vongboot, Molecules 2022, 27 (2022)
K. Rovina, J.M. Vonnie, S.N. Shaeera, S.X. Yi, N.F.A. Halid, Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 27, 100310 (2020)
O. Bunkoed, F. Davis, P. Kanatharana, P. Thavarungkul, S.P.J. Higson, Anal. Chim. Acta 659, 251 (2010)
W. Wongniramaikul, W. Limsakul, A. Choodum, Food Chem. 249, 154 (2018)
P. Jaikang, P. Paengnakorn, K. Grudpan, Microchem. J. 152, 104283 (2020)
Y. Ai and J. L. Jane, Starch – Stärke, 2015, 67, 213.
H.J. Chung, Q. Liu, L. Lee, D. Wei, Food Hydrocoll. 25, 968 (2011)
R. Thakur, P. Pristijono, C.J. Scarlett, M. Bowyer, S.P. Singh, Q.V. Vuong, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 132, 1079 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge to the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, Petchra Pra Jom Klao Ph.D. Research Scholarship from King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi (C. Yeerum), the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) Distinguished Research Professor Award Grant (DPG6080002 to K. Grudpan), and Chiang Mai University (through CMU Presidential Scholarship (Contact no. 20/2022) and Center of Excellence for Innovation in Analytical Science and Technology for Biodiversity-based Economic and Society (I-ANALY-S-T_B.BES-CMU)). We are grateful to Asst. Siripat Suteerapataranon for useful discussion and language editing, as well as Dr. Piyanat Issarangkura Na Ayutthaya for useful discussions.
Funding
Petchra Pra Jom Klao Ph.D. Research Scholarship from King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi (C. Yeerum) and the TRF Distinguished Research Professor Award Grant (DPG6080002 to K. Grudpan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yeerum, C., Kiwfo, K., Kesonkan, K. et al. Cost-effective formaldehyde assay platform for multi-sample analysis in one run based on pervaporation coupled with a biodegradable sensor and a simple heat control unit. ANAL. SCI. 39, 653–662 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-022-00220-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44211-022-00220-5