Abstract
Background
The selective safety data collection (SSDC) proposed in The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use E19 guideline is a more selective approach to collect safety data of medicinal products with well-characterized safety profiles. There has been no systematic survey of the implementation status of SSDCs.
Methods
A literature search was conducted on clinical trials using SSDC published in The New England Journal of Medicine from February 1, 2016, to December 31, 2019. By reviewing the retrieved texts, protocols, and statistical analysis plans, we identified the method of safety data collection and evaluated whether each trial adopted SSDC.
Results
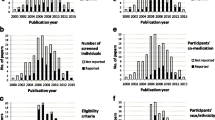
Of the 459 trials of medicinal products searched, 44 clinical trials adopted SSDC. The common objectives of these studies were “to study additional endpoints” (31 trials, 70.5%) and “new indications of approved drugs” (8 trials, 18.2%). Participant number was more than 1000 in 33 trials (75.0%). Most trials adopted SSDC for the entire study population throughout the trial period. Death and serious adverse events (SAEs) were recorded in all trials. Twenty-nine (66.6%) recorded death, SAE, and AE leading to drug discontinuation, which were specified in the E19 draft guideline as the data that should be collected under all circumstances.
Conclusion
There have already been cases where SSDC was used in clinical trials for regulatory application. It is desirable that the E19 guideline will harmonize the method for implementation of SSDC, making SSDC more common as an option for clinical trial design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Food and Drug Administration. Cancer drug and biological products—Clinical data in marketing applications. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/cancer-drug-and-biological-products-clinical-data-marketing-applications. Accessed 21 December 2021.
Sekine N, Aruga A. Selective safety data collection in clinical studies of oncology drugs for marketing approval in the United States. J Regul Sci. 2017;5(2):36–44.
Food and Drug Administration. A determining the extent of safety data collection needed in late-stage premarket and postapproval clinical investigations. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/determining-extent-safety-data-collection-needed-late-stage-premarket-and-postapproval-clinical. Accessed 21 December 2021.
ICH E19 Guideline optimisation of safety data collection. Draft version endorsed on 3 April 2019. Step 2. https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/E19_EWG_Draft_Guideline.pdf. Accessed 21 December 2021.
Hart RG, Sharma M, Mundl H, et al. Rivaroxaban for stroke prevention after embolic stroke of undetermined source. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(23):2191–201.
Holman RR, Bethel MA, Mentz RJ, et al. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(13):1228–39.
Hochhaus A, Larson RA, Guilhot F, et al. Long-term outcomes of imatinib treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(10):917–27.
Chuang-Stein C, Mohberg NR, Musselman DM. Organization and analysis of safety data using a multivariate approach. Stat Med Action. 1992;11(8):1075–89.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Masakazu Fujiwara for his collaboration with this work. We would like to thank executives of the Data Science Expert Committee of the Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association (Tomoko Kato, Hideharu Yamamoto, Naoto Awaji, Yuichi Kawata, Satoru Tsuchiya, and Osamu Komiyama) for their useful advice. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
Funding
This study was funded by the Japan Pharmaceutical Manufacturers Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to writing of the manuscript, data interpretation, and approval of the final version of the manuscript. Y. Yamatani, H. Saeki, R. Tanaka and H. Sakai contributed to the conception of the design of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yuki Yamatani, Hiroyuki Saeki, Risa Tanaka, Takuji Komeda, Yukiko Watabe, and Hironori Sakai are employees of Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., FUJIFILM Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd., Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Eisai Co., Ltd.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamatani, Y., Saeki, H., Tanaka, R. et al. How Many Clinical Trials Exist that Have Adopted Selective Safety Data Collection? NEJM Literature Search Results: The Possibility of Harmonizing the ICH E19 Guideline. Ther Innov Regul Sci 56, 677–684 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43441-022-00414-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43441-022-00414-z