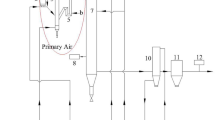
Abstract
In this study, coal slime was mainly utilized to conduct experiments on a 30 kW preheating combustion test rig to analyze the conversion pathway of sulfur during the experiment, aiming at reducing slime pollution, controlling sulfur emission reasonably, and providing theoretical support for the preheating combustion technology. The results showed that after the coal slime was preheated, a large number of elements were released. The maximum release rates for H and S were 94.0% and 73.3%, respectively. The released S was converted into the sulfur-containing gases like H2S, COS, CS2, and the rest existed in the solid in the five forms of mercaptan, thiophene, sulfoxide, sulfone, and sulfate. Besides, during the combustion process, the gas was oxidized continuously and finally converted into SO2, leaving only the sulfate in the fly ash. In the preheating combustion process, 26.7% of the S was released from the coal, 73.3% of the S was retained in the semi-coke, and the final SO2 emission concentration of combustion was 959 ppm.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, J.M., and Li, C.M. 2010. Current situation, problems and suggestions of comprehensive utilization of coal slime in China. Energy of China 32 (10): 38–40.
National Energy Administration. Notice of the National Energy Administration on Printing and Distributing the Action Plan for Clean and Efficient Utilization of Coal (2015–2020). Available at: http://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/auto85/201505/t20150505_1917.htm. Accessed 12 Dec 2021.
Si, Y.C., and Du, M.L. 2017. Research progress of slime utilization. Guangdong Chemical Industry 44 (04): 79–80.
Cheng, C., and He, P. 2012. Status and analysis of utilization of coal slurry. New Technology and New Process 9: 66–69.
Yi, S. 1992. Coal-burning sludge technology and pollution control at home and abroad. Coal Processing and Comprehensive Utilization 6: 32–36.
Yao, W.J. 2015. Analysis on processing and utilization of coal slime. Energy and Energy conservation 115 (04): 176–178.
Zhou, B.W. 2017. A study on the preparation of briquette made of coal slime and sludge and the effect of sulfur fixation. Liaoning, China: Liaoning University of Engineering and Technology.
Zhou, K., Lin, Q.Z., Hu, H.W. 2018. Ignition and combustion behaviors of single coal slime particles in CO2/O2 atmosphere. Combustion & Flame 194: 250–263.
Tang, Y.L. 2020. Research on evaluation of replacement strategy for coal-fired boilers in industrial enterprises. Nan**g, China: Nan**g University of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
Ouyang, Z., Liu, W., Man, C.B., et al. 2018. Experimental study on combustion, flame and NOX emission of pulverized coal preheated by a preheating burner. Fuel Processing Technology 179: 197–202.
Yao, Y., Zhu, J.G., Lv, Q.G., et al. 2015. Experimental study on preheated combustion of pulverized semi-coke. Journal of Thermal Science 24 (04): 370–377.
Zhu, S.J., Lv, Q.G., Zhu, J.G. 2019. Experimental investigation of NOX emissions during pulverized char combustion in oxygen-enriched air preheated with a circulating fluidized bed. Journal of the Energy Institute 92 (5): 1388–1398.
Zhang, Y., Zhu, J.G., Lv, Q.G., et al. 2019. Experiment on preheating characteristics of bituminous coal by circulating fluidized bed. China Powder Science and Technology 25 (06): 7–11.
Ma, L.L., Qin, Z.H., Zhang, L., et al. 2014. Peak fitting methods and parameter settings in XPS analysis for organic sulfur in coal. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology 42 (03): 277–283.
Li, D., Zhang, C., **a, J., et al. 2013. Evolution of organic sulfur in the thermal upgrading process of Shengli lignite. Energy and Fuels 27 (6): 3446–3453.
Zhang, L.J., Li, Z.H., He, W.J., et al. 2018. Study on the change of organic sulfur forms in coal during low-temperature oxidation process. Fuel 222: 350–361.
Ouyang, Z.Q., Zhu, J.G., Lyu, Q.G. 2013. Experimental study on preheating and combustion characteristics of pulverized anthracite coal. Fuel 113 (2): 122–127.
Liu, F.R., **e, L.L., Guo, H.Q., et al. 2014. Sulfur release and transformation behaviors of sulfur-containing model compounds during pyrolysis under oxidative atmosphere. Fuel 115: 596–599.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the high-efficiency and low-nitrogen combustion technology and demonstration of coal-fired industrial boilers (XDA20140100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
we don’t have any conflict with other organizations.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Lv, Q. et al. Experimental study on conversion path of sulfur in coal slime preheating combustion. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 4, 63–68 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-022-00094-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-022-00094-3