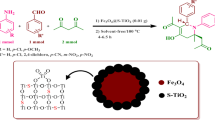
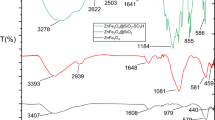
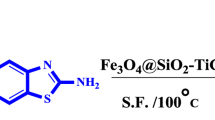
Abstract
Nanostructured catalysts represent a new frontier between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Nanocatalysts and nanocatalysis have received intensive attention over the past two decades, because of high activity and selectivity. Owing to this, in the present research work we utilized nanoparticles to improve the catalytic properties of a material. However, the isolation and recovery of these tiny nanoparticles from the reaction mixture are not easy. To overcome this issue, the use of magnetic nanoparticles has emerged as a viable solution; their insoluble and paramagnetic nature enables easy and efficient separation of the catalysts from the reaction mixture with an external magnet. In the present study, the microwave-assisted, three-component reaction between aryl aldehyde, ammonium acetate, and aryl 1,2 diketone that led to the synthesis of 8-phenyl-7H-acenaphtho[1,2-d]imidazoles in the presence of magnetically recoverable nanocatalyst has been described (CoFe2O4@SiO2–HClO4). Characterization of magnetic nanoparticles was carried out with FT-IR, XRD, SEM-EDX, TEM, TGA-DSC, and VSM techniques. The advantages of the present protocol are a simple method of catalyst preparation, high yield of desired products, short reaction time, and easy magnetic recovery and reusability of catalyst. These features provide attractive objectives for the present study.
Graphical abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MCR:
-
Multicomponent reaction
- MNPs:
-
Magnetic nanoparticles
- NPs:
-
Nanoparticles
- MW:
-
Microwave
- Cat:
-
Catalyst
References
A. Roy, E. Elzaki, V. Tirth, S. Kajoak, H. Osman, A. Algahtani, S. Islam, L. Nahla, F. Mayeen, U. Khandaker, M. Nazmul, I. Talha, B. Emran, M. Bilal, Catalysts 11(12), 1494 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11121494
P. Sekoai, C. Ouma, S. du Preez, P. Modisha, N. Engelbrecht, D. Bessarabov, A. Ghimire, Application of nanoparticles in biofuels: an overview. Fuel 237, 380 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.030
A. Erik, E. Stan, A. Jeroen, W. Gabriel, R. Mohammad, M. Shunsuke, G. Michael, G. Jaime, J. Appl. Phys. 131, 083101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0079016
S. Bharathala, P. Sharma, Biomedical applications of nanoparticles. Nanotechnology in Modern Animal Biotechnology. 113–132 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-818823-1.00008-9
D. Astruc, Chem. Rev. 120(2), 461 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00696
B.K. Yardımcı, Imidazole antifungals: a review of their action mechanisms on cancerous cells. IJSM. 7(3), 139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.21448/ijsm.714310
F. Saccoliti, V. Madia, V. Tudino, A. De Leo, L. Pescatori, A. Messore, R. Di Santo, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 156, 53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.063
A. Siwach, P. Verma, BMC Chem. 15, 12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-020-00730-1
K. Nikolic, D. Agbaba, Cardiovasc. Ther. 30(4), 209 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5922.2011.00269.x
K. Alaoui, N. Dkhireche, M.E. Touhami, Y.E. Kacimi, Review of application of imidazole and imidazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors of metals (2020), pp. 101–131. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-7998-2775-7.ch005
R. Sndaroos, S. Damavandi, Res Chem Intermed 40, 2681–2687 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-013-1121-4
F. Hasanzadeh, F.K. Behbahani, Russ. J. Org. Chem. 56, 1070–1076 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070428020060160
N.S. Fallah, M. Mokhtary, J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 9(4), 531–537 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtusci.2014.12.004
M. Adib, B. Mohammadi, S. Ansari, H.R. Bijanzadeh, L.G. Zhu, Tetrahedron Lett. 52(18), 2299 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2011.01.091
G. Allaedini, M.T. Siti, A. Payam, Int. Nano Lett. 5(4), 183–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-015-0153-8
S. Werner, F. Arthur, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5
A.K. Chakraborti, R. Gulhane, Chem. Commun. 15, 1896–1897 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1039/b304178f
J.B. Howard, E.B. Wilson, J. Chem. Phys. 2, 630 (1934). https://doi.org/10.1038/352139a0
D. Narsimulu, O. Padmaraj, E.S. Srinadhu, N. Satyanarayana, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 17208–17214 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7650-7
J. Hu, Y. Bando, J. Zhan, X. Yuan, T. Sekiguchi, D. Golberg, Adv. Mater. 17, 225 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200401789
D. Hossein, N. Alireza, S. Saeid, IJETR 2(3), 238 (2014)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge SGB Amravati University for providing laboratory facilities for the present research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thakare, N.V., Aswar, A.S. & Salunkhe, N.G. CoFe2O4@SiO2–HClO4 magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis and its application in catalysis. emergent mater. 6, 1285–1297 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00502-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00502-2