Abstract
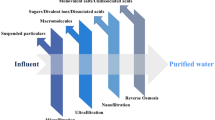
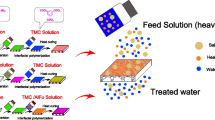
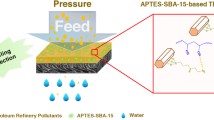
One of the most daunting challenges faced by the planet is a reliable and accessible supply of water in sufficient quantity. The membrane technology has emerged as a cost-effective alternative for water purification. One such pressure-driven membrane separation process is nanofiltration (NF), where the interfacial polymerization (IP) is predominantly used to prepare the thin polyamide selective layer. Over the last decade, a wide variety of novel/modified IP techniques have been explored to improve the performance of the polyamide (PA) thin-film composite and thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane in both pressure-driven and osmotic driven applications. This paper explores different IP fabrication techniques viz. support-free IP technique, filtration-assisted IP technique, reverse IP technique, electrospray-based IP technique, etc. The thickness of the PA layer can be precisely monitored by many of these modified IP techniques. The incorporation of nanoparticles on the PA layer and membrane matrix could enhance the fouling resistance, increase the rejection efficiency and improve the water permeability. The efficiency of these membranes has been explored for the separation/removal of emerging contaminants, divalent/multi-valent ions, low molecular weight organics, micropollutants, and inorganic salts. Several advantages of these IP techniques are discussed in detail; however, the various associated challenges must be overcome before these techniques can be transferred from lab-scale to commercial applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
M. V. Fanucchi, Drinking water and sanitation, in International Encyclopedia of Public Health (Second Edition), S. R. Quah, Ed., ed Oxford: Academic Press, 2017, pp. 350–360.
P. O. Ukaogo, U. Ewuzie, and C. V. Onwuka, 21 - Environmental pollution: causes, effects, and the remedies, in Microorganisms for Sustainable Environment and Health, P. Chowdhary, A. Raj, D. Verma, and Y. Akhter, Eds., ed: Elsevier, 2020, pp. 419–429.
C. Postigo, D. E. Martinez, S. Grondona, and K. S. B. Miglioranza, Groundwater pollution: sources, mechanisms, and prevention, in Encyclopedia of the Anthropocene, D. A. Dellasala and M. I. Goldstein, Eds., ed Oxford: Elsevier, 2018, pp. 87–96.
D.M. Warsinger, S. Chakraborty, E.W. Tow, M.H. Plumlee, C. Bellona, S. Loutatidou et al., A review of polymeric membranes and processes for potable water reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 81, 209–237 (2018)
M. T. Amin, A. A. Alazba, and U. Manzoor, A review of removal of pollutants from water/wastewater using different types of nanomaterials, Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 2014, p. 825910, 2014.
Z. Yang, Y. Zhou, Z. Feng, X. Rui, T. Zhang, Z. Zhang, A review on reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes for water purification. Polymers 11, 1252 (2019)
K. Yamjala, M.S. Nainar, N.R. Ramisetti, Methods for the analysis of azo dyes employed in food industry – a review. Food Chem. 192, 813–824 (2016)
R.P. Lively, D.S. Sholl, From water to organics in membrane separations. Nat. Mater. 16, 276–279 (2017)
Z.-G. Wen, J.-H. Di, X.-Y. Zhang, Uncertainty analysis of primary water pollutant control in China’s pulp and paper industry. J. Environ. Manage. 169, 67–77 (2016)
S. Bhattacharyya, P. Das, and S. Datta, Removal of ranitidine from pharmaceutical waste water using activated carbon (AC) prepared from waste lemon peel, in Waste Water Recycling and Management, Singapore, 2019, pp. 123–141.
A. Moslehyani, A. F. Ismail, T. Matsuura, M. A. Rahman, and P. S. Goh, Chapter 3 - Recent progresses of ultrafiltration (UF) membranes and processes in water treatment, in Membrane Separation Principles and Applications, A. F. Ismail, M. A. Rahman, M. H. D. Othman, and T. Matsuura, Eds., ed: Elsevier, 2019, pp. 85–110.
D. Zhao, S. Yu, A review of recent advance in fouling mitigation of NF/RO membranes in water treatment: pretreatment, membrane modification, and chemical cleaning. Desalin. Water Treat. 55, 870–891 (2015)
A.W. Mohammad, Y.H. Teow, W.L. Ang, Y.T. Chung, D.L. Oatley-Radcliffe, N. Hilal, Nanofiltration membranes review: recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 356, 226–254 (2015)
T. A. Siddique, N. K. Dutta, and N. Roy Choudhury, Nanofiltration for arsenic removal: challenges, recent developments, and perspectives, Nanomaterials (Basel), vol. 10, Jul 6 2020.
M. Park and S. A. Snyder, Chapter 6 - Attenuation of contaminants of emerging concerns by nanofiltration membrane: rejection mechanism and application in water reuse, in Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Water and Wastewater, A. J. Hernández-Maldonado and L. Blaney, Eds., ed: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2020, pp. 177–206.
D. Askenaizer, Drinking water quality and treatment, in Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology (Third Edition), R. A. Meyers, Ed., ed New York: Academic Press, 2003, pp. 651–671.
B. Van der Bruggen, M. Mänttäri, M. Nyström, Drawbacks of applying nanofiltration and how to avoid them: a review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 63, 251–263 (2008)
M.A. Abdel-Fatah, Nanofiltration systems and applications in wastewater treatment: review article. Ain Shams Engineering Journal 9, 3077–3092 (2018)
R. Epsztein, E. Shaulsky, N. Dizge, D.M. Warsinger, M. Elimelech, Role of ionic charge density in donnan exclusion of monovalent anions by nanofiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 4108–4116 (2018)
Y. Liu, J. Zhu, J. Zheng, X. Gao, M. Tian, X. Wang, et al., Porous organic polymer embedded thin-film nanocomposite membranes for enhanced nanofiltration performance, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 602, p. 117982, 2020.
W. Lin, M. Li, Y. Wang, X. Wang, K. Xue, K. **ao, et al., Quantifying the dynamic evolution of organic, inorganic and biological synergistic fouling during nanofiltration using statistical approaches, Environment International, vol. 133, p. 105201, 2019.
J. Glater, The early history of reverse osmosis membrane development. Desalination 117, 297–309 (1998)
S. Loeb and S. Sourirajan, Sea water demineralization by means of an osmotic membrane, in Saline Water Conversion—II. vol. 38, ed: AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY, 1963, pp. 117–132.
Y. Yu, Q.-Y. Wu, H.-Q. Liang, L. Gu, and Z.-K. Xu, Preparation and characterization of cellulose triacetate membranes via thermally induced phase separation, Journal of Applied Polymer Science, vol. 134, 2017.
R.W. Holloway, A. Achilli, T.Y. Cath, The osmotic membrane bioreactor: a critical review. Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. 1, 581–605 (2015)
E. Shaulsky, V. Karanikola, A.P. Straub, A. Deshmukh, I. Zucker, M. Elimelech, Asymmetric membranes for membrane distillation and thermo-osmotic energy conversion. Desalination 452, 141–148 (2019)
H. Strathmann, Membrane technology and applications, 2nd ed., Richard W. Baker John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., UK (2004), Journal of Membrane Science - J MEMBRANE SCI, vol. 246, pp. 113–114, 2005.
N.L. Le, S.P. Nunes, Materials and membrane technologies for water and energy sustainability. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 7, 1–28 (2016)
G.M. Geise, H.-S. Lee, D.J. Miller, B.D. Freeman, J.E. McGrath, D.R. Paul, Water purification by membranes: the role of polymer science. J. Polym. Sci., Part B: Polym. Phys. 48, 1685–1718 (2010)
W.J. Lau, S. Gray, T. Matsuura, D. Emadzadeh, J.P. Chen, A.F. Ismail, A review on polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes: history, applications, challenges and approaches. Water Res 80, 306–324 (2015)
J.M. Gohil, A.K. Suresh, Chlorine attack on reverse osmosis membranes: mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Membr. Sci. 541, 108–126 (2017)
F. Yan, H. Chen, Y. Lü, Z. Lü, S. Yu, M. Liu et al., Improving the water permeability and antifouling property of thin-film composite polyamide nanofiltration membrane by modifying the active layer with triethanolamine. J. Membr. Sci. 513, 108–116 (2016)
B. Khorshidi, A. Bhinder, T. Thundat, D. Pernitsky, M. Sadrzadeh, Develo** high throughput thin film composite polyamide membranes for forward osmosis treatment of SAGD produced water. J. Membr. Sci. 511, 29–39 (2016)
M. Simcik, M.C. Ruzicka, M. Karaszova, Z. Sedlakova, J. Vejrazka, M. Vesely et al., Polyamide thin-film composite membranes for potential raw biogas purification: experiments and modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 167, 163–173 (2016)
M.J.T. Raaijmakers, N.E. Benes, Current trends in interfacial polymerization chemistry. Prog. Polym. Sci. 63, 86–142 (2016)
C. Yu, H. Li, X. Zhang, Z. Lü, S. Yu, M. Liu et al., Polyamide thin-film composite membrane fabricated through interfacial polymerization coupled with surface amidation for improved reverse osmosis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 566, 87–95 (2018)
P. Karami, B. Khorshidi, M. McGregor, J. T. Peichel, J. B. P. Soares, and M. Sadrzadeh, Thermally stable thin film composite polymeric membranes for water treatment: a review, Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 250, p. 119447, 2020.
W. J. Lau and A. Ismail, Progress in Interfacial Polymerization Technique on Composite Membrane Preparation, 2011.
M. Q. Seah, W. J. Lau, P. S. Goh, H. H. Tseng, R. A. Wahab, and A. F. Ismail, Progress of interfacial polymerization techniques for polyamide thin film (nano)composite membrane fabrication: a comprehensive review, Polymers (Basel). 12 (2020)
S. Nagandran, P. S. Goh, A. F. Ismail, T.-W. Wong, and W. R. Binti Wan Dagang, The recent progress in modification of polymeric membranes using organic macromolecules for water treatment. Symmetry 12 (2020)
F. Liu, L. Wang, D. Li, Q. Liu, B. Deng, A review: the effect of the microporous support during interfacial polymerization on the morphology and performances of a thin film composite membrane for liquid purification. RSC Adv. 9, 35417–35428 (2019)
A. Giwa, M. Ahmed, S.W. Hasan, Polymers for membrane filtration in water purification, in Polymeric Materials for Clean Water, R. ed. by Ed. Das (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2019), pp. 167–190
R. Castro-Muñoz, L.L. González-Melgoza, O. García-Depraect, Ongoing progress on novel nanocomposite membranes for the separation of heavy metals from contaminated water. Chemosphere 270, 129421 (2021)
A. Rabajczyk, M. Zielecka, K. Cygańczuk, Ł. Pastuszka, and L. Jurecki, Nanometals-containing polymeric membranes for purification processes. Materials (Basel, Switzerland) 14, 513 (2021)
K.C. Khulbe, T. Matsuura, Synthetic membrane characterisation – a review: part I. Membr. Technol. 2017, 7–12 (2017)
M. Khajouei, M. Peyravi, M. Jahanshahi, The potential of nanoparticles for upgrading thin film nanocomposite membranes – a review. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 3, 2–12 (2017)
A. Giwa, N. Akther, V. Dufour, S.W. Hasan, A critical review on recent polymeric and nano-enhanced membranes for reverse osmosis. RSC Adv. 6, 8134–8163 (2016)
S. Kheirieh, M. Asghari, and M. Afsari, Application and modification of polysulfone membranes. Rev. Chem. Eng. 34 (2017)
B. Hu, L. Miao, Y. Zhao, and C. Lü, Azide-assisted crosslinked quaternized polysulfone with reduced graphene oxide for highly stable anion exchange membranes. J Membr. Sci 530 (2017)
Y. Zhao, L. Dai, Q. Zhang, S. Zhou, S. Zhang, Chlorine-resistant sulfochlorinated and sulfonated polysulfone for reverse osmosis membranes by coating method. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 541, 434–443 (2019)
I.L. Alsvik, M.-B. Hägg, Preparation of thin film composite membranes with polyamide film on hydrophilic supports. J. Membr. Sci. 428, 225–231 (2013)
L.D. Ti**g, M. Yao, J. Ren, C.-H. Park, C.S. Kim, H.K. Shon, Nanofibers for water and wastewater treatment: recent advances and developments, in Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies. ed. by X.-T. Bui, C. Chiemchaisri, T. Fujioka, S. Varjani (Springer Singapore, Singapore, 2019), pp. 431–468
M. Kadhom, B. Deng, Synthesis of high-performance thin film composite (TFC) membranes by controlling the preparation conditions: technical notes. J. Water Process Eng. 30, 100542 (2019)
X. Li, Q. Li, W. Fang, R. Wang, W.B. Krantz, Effects of the support on the characteristics and permselectivity of thin film composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 580, 12–23 (2019)
S.S. Shenvi, A.M. Isloor, A.F. Ismail, A review on RO membrane technology: developments and challenges. Desalination 368, 10–26 (2015)
W. J. Lau, S. Gray, T. Matsuura, D. Emadzadeh, J. Paul Chen, and A. F. Ismail, A review on polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes: history, applications, challenges and approaches, Water Research, vol. 80, pp. 306–324, 2015.
G.S. Lai, W.J. Lau, P.S. Goh, M. Karaman, M. Gürsoy, A.F. Ismail, Development of thin film nanocomposite membrane incorporated with plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition-modified hydrous manganese oxide for nanofiltration process. Compos. Part B: Eng. 176, 107328 (2019)
K.C. Wong, P.S. Goh, A.F. Ismail, Thin film nanocomposite: the next generation selective membrane for CO2 removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 15726–15748 (2016)
Q. Kong, H. Xu, C. Liu, G. Yang, M. Ding, W. Yang et al., Fabrication of high performance TFN membrane containing NH2-SWCNTs via interfacial regulation. RSC Adv. 10, 25186–25199 (2020)
Z. Yang, H. Guo, Z.-K. Yao, Y. Mei, C.Y. Tang, Hydrophilic silver nanoparticles induce selective nanochannels in thin film nanocomposite polyamide membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 5301–5308 (2019)
D.L. Zhao, S. Japip, Y. Zhang, M. Weber, C. Maletzko, T.-S. Chung, Emerging thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes for reverse osmosis: a review. Water Res. 173, 115557 (2020)
D.L. Zhao, T.-S. Chung, Applications of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in membrane technologies: a review. Water Res. 147, 43–49 (2018)
Y. He, D.L. Zhao, T.-S. Chung, Na+ functionalized carbon quantum dot incorporated thin-film nanocomposite membranes for selenium and arsenic removal. J. Membr. Sci. 564, 483–491 (2018)
Y. Mutharasi, N.J. Kaleekkal, T. Arumugham, F. Banat, M.S.R.S. Kapavarapu, Antifouling and photocatalytic properties of 2-D Zn/Al layered double hydroxide tailored low-pressure membranes. Chem. Eng. Process - Process Intensif. 158, 108191 (2020)
P. Lu, W. Li, S. Yang, Y. Liu, Q. Wang, Y. Li, Layered double hydroxide-modified thin–film composite membranes with remarkably enhanced chlorine resistance and anti-fouling capacity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 220, 231–237 (2019)
S.-Y. Kwak, S.H. Kim, S.S. Kim, Hybrid organic/inorganic reverse osmosis (RO) membrane for bactericidal anti-fouling. 1. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticle self-assembled aromatic polyamide thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 2388–2394 (2001)
M. Fathizadeh, A. Aroujalian, A. Raisi, Effect of added NaX nano-zeolite into polyamide as a top thin layer of membrane on water flux and salt rejection in a reverse osmosis process. J. Membr. Sci. 375, 88–95 (2011)
H. Huang, X. Qu, X. Ji, X. Gao, L. Zhang, H. Chen et al., Acid and multivalent ion resistance of thin film nanocomposite RO membranes loaded with silicalite-1 nanozeolites. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 11343–11349 (2013)
M. Majumder, N. Chopra, R. Andrews, B.J. Hinds, Enhanced flow in carbon nanotubes. Nature 438, 44–44 (2005)
Ihsanullah. Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: developments, challenges, and prospects for the future. Sep. Purif. Technol. 209, 307–337 (2019)
E. Mahmoudi, L.Y. Ng, W.L. Ang, Y.T. Chung, R. Rohani, A.W. Mohammad, Enhancing morphology and separation performance of polyamide 6,6 membranes by minimal incorporation of silver decorated graphene oxide nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 9, 1216 (2019)
M.H. Tajuddin, N. Yusof, N. Abdullah, M.N.Z. Abidin, W.N.W. Salleh, A.F. Ismail et al., Incorporation of layered double hydroxide nanofillers in polyamide nanofiltration membrane for high performance of salts rejections. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 97, 1–11 (2019)
M. Wu, J. Yuan, H. Wu, Y. Su, H. Yang, X. You et al., Ultrathin nanofiltration membrane with polydopamine-covalent organic framework interlayer for enhanced permeability and structural stability. J. Membr. Sci. 576, 131–141 (2019)
Z. Zhang, G. Kang, H. Yu, Y. **, Y. Cao, Fabrication of a highly permeable composite nanofiltration membrane via interfacial polymerization by adding a novel acyl chloride monomer with an anhydride group. J. Membr. Sci. 570–571, 403–409 (2019)
T.H. Lee, J.Y. Oh, S.P. Hong, J.M. Lee, S.M. Roh, S.H. Kim et al., ZIF-8 particle size effects on reverse osmosis performance of polyamide thin-film nanocomposite membranes: importance of particle deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 570–571, 23–33 (2019)
W. Yan, M. Shi, Z. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Liu, S. Zhao et al., Amino-modified hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres-incorporated reverse osmosis membrane with high performance. J. Membr. Sci. 581, 168–177 (2019)
G.S. Lai, W.J. Lau, P.S. Goh, A.F. Ismail, N. Yusof, Y.H. Tan, Graphene oxide incorporated thin film nanocomposite nanofiltration membrane for enhanced salt removal performance. Desalination 387, 14–24 (2016)
M.R. Esfahani, S.A. Aktij, Z. Dabaghian, M.D. Firouzjaei, A. Rahimpour, J. Eke et al., Nanocomposite membranes for water separation and purification: fabrication, modification, and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 213, 465–499 (2019)
M. Q. Seah, W. J. Lau, P. S. Goh, H.-H. Tseng, R. A. Wahab, and A. F. Ismail, Progress of interfacial polymerization techniques for polyamide thin film (nano)composite membrane fabrication: a comprehensive review. Polymers 12 (2020)
Z. Zhang, Y. Qin, G. Kang, H. Yu, Y. **, and Y. Cao, Tailoring the internal void structure of polyamide films to achieve highly permeable reverse osmosis membranes for water desalination, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 595, p. 117518, 2020.
A. Saeedi-Jurkuyeh, A. J. Jafari, R. R. Kalantary, and A. Esrafili, A novel synthetic thin-film nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane modified by graphene oxide and polyethylene glycol for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions, Reactive and Functional Polymers, vol. 146, p. 104397, 2020.
Y. Zhang, H. Ruan, C. Guo, J. Liao, J. Shen, and C. Gao, Thin-film nanocomposite reverse osmosis membranes with enhanced antibacterial resistance by incorporating p-aminophenol-modified graphene oxide, Separation and Purification Technology, vol. 234, p. 116017, 2020.
Z.-C. Ng, C.-Y. Chong, W.-J. Lau, M. Karaman, A.F. Ismail, Boron removal and antifouling properties of thin-film nanocomposite membrane incorporating PECVD-modified titanate nanotubes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 94, 2772–2782 (2019)
Q.-F. An, W.-D. Sun, Q. Zhao, Y.-L. Ji, and C.-J. Gao, Study on a novel nanofiltration membrane prepared by interfacial polymerization with zwitterionic amine monomers, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 431, pp. 171–179, 2013/03/15/ 2013.
K. C. Khulbe and T. Matsuura, Thin film composite and/or thin film nanocomposite hollow fiber membrane for water treatment, pervaporation, and gas/vapor separation, Polymers, vol. 10, 2018.
W. Zhao, H. Liu, N. Meng, M. Jian, H. Wang, X. Zhang, Graphene oxide incorporated thin film nanocomposite membrane at low concentration monomers. J. Membr. Sci. 565, 380–389 (2018)
C.Y. Chong, W.J. Lau, N. Yusof, G.S. Lai, N.H. Othman, T. Matsuura et al., Studies on the properties of RO membranes for salt and boron removal: influence of thermal treatment methods and rinsing treatments. Desalination 428, 218–226 (2018)
S. Gholami, J. López, A. Rezvani, V. Vatanpour, and J. L. Cortina, Fabrication of thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes incorporated with aromatic amine-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Rejection performance of inorganic pollutants from groundwater with improved acid and chlorine resistance, Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 384, p. 123348, 2020.
S.W. Lin, A.V. Martínez-Ayala, S. Pérez-Sicairos, R.M. Félix-Navarro, Preparation and characterization of low-pressure and high MgSO4 rejection thin-film composite NF membranes via interfacial polymerization process. Polym. Bull. 76, 5619–5632 (2019)
W. Shao, C. Liu, H. Ma, Z. Hong, Q. **e, Y. Lu, Fabrication of pH-sensitive thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes with enhanced performance by incorporating amine-functionalized graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 487, 1209–1221 (2019)
G.S. Lai, W.J. Lau, P.S. Goh, A.F. Ismail, Y.H. Tan, C.Y. Chong et al., Tailor-made thin film nanocomposite membrane incorporated with graphene oxide using novel interfacial polymerization technique for enhanced water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 344, 524–534 (2018)
J. Zhu, S. Yuan, A. Uliana, J. Hou, J. Li, X. Li et al., High-flux thin film composite membranes for nanofiltration mediated by a rapid co-deposition of polydopamine/piperazine. J. Membr. Sci. 554, 97–108 (2018)
Y. Pan, R. Xu, Z. Lü, S. Yu, M. Liu, C. Gao, Enhanced both perm-selectivity and fouling resistance of poly(piperazine-amide) nanofiltration membrane by incorporating sericin as a co-reactant of aqueous phase. J. Membr. Sci. 523, 282–290 (2017)
J. Yin, G. Zhu, B. Deng, Graphene oxide (GO) enhanced polyamide (PA) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for water purification. Desalination 379, 93–101 (2016)
Z. Wang, Z. Wang, S. Lin, H. **, S. Gao, Y. Zhu et al., Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination. Nat. Commun. 9, 2004 (2018)
M.-B. Wu, Y. Lv, H.-C. Yang, L.-F. Liu, X. Zhang, Z.-K. Xu, Thin film composite membranes combining carbon nanotube intermediate layer and microfiltration support for high nanofiltration performances. J. Membr. Sci. 515, 238–244 (2016)
S. Al Aani, A. Haroutounian, C. J. Wright, and N. Hilal, Thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes modified with polydopamine coated metals/carbon-nanostructures for desalination applications, Desalination, vol. 427, pp. 60–74, 2018.
G.S. Lai, W.J. Lau, P.S. Goh, Y.H. Tan, B.C. Ng, A.F. Ismail, A novel interfacial polymerization approach towards synthesis of graphene oxide-incorporated thin film nanocomposite membrane with improved surface properties. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 75–87 (2019)
J. Zhu, J. Hou, S. Yuan, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, R. Zhang et al., MOF-positioned polyamide membranes with a fishnet-like structure for elevated nanofiltration performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 7, 16313–16322 (2019)
Y. Ren, J. Zhu, S. Cong, J. Wang, B. Van der Bruggen, J. Liu et al., High flux thin film nanocomposite membranes based on porous organic polymers for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 585, 19–28 (2019)
M. Wu, T. Ma, Y. Su, H. Wu, X. You, Z. Jiang et al., Fabrication of composite nanofiltration membrane by incorporating attapulgite nanorods during interfacial polymerization for high water flux and antifouling property. J. Membr. Sci. 544, 79–87 (2017)
L. Shen, W.-S. Hung, J. Zuo, X. Zhang, J.-Y. Lai, Y. Wang, High-performance thin-film composite polyamide membranes developed with green ultrasound-assisted interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 570–571, 112–119 (2019)
L. Shen, W.-s. Hung, J. Zuo, L. Tian, M. Yi, C. Ding, et al., Effect of ultrasonication parameters on forward osmosis performance of thin film composite polyamide membranes prepared with ultrasound-assisted interfacial polymerization, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 599, p. 117834, 2020.
T.J. Mason, Ultrasound in synthetic organic chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 26, 443–451 (1997)
K. Suslick and G. Price, Application of ultrasound to materials chemistry, Annual Review of Materials Science, vol. 29, pp. 295–326, 08/01 1999.
T. Tsuru, S. Sasaki, T. Kamada, T. Shintani, T. Ohara, H. Nagasawa et al., Multilayered polyamide membranes by spray-assisted 2-step interfacial polymerization for increased performance of trimesoyl chloride (TMC)/m-phenylenediamine (MPD)-derived polyamide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 446, 504–512 (2013)
L. Shan, J. Gu, H. Fan, S. Ji, G. Zhang, Microphase diffusion-controlled interfacial polymerization for an ultrahigh permeability nanofiltration membrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 44820–44827 (2017)
J.B. Morales-Cuevas, S. Pérez-Sicairos, S.W. Lin, M.I. Salazar-Gastélum, Evaluation of a modified spray-applied interfacial polymerization method for preparation of nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 136, 48129 (2019)
A. Jaworek, A.T. Sobczyk, Electrospraying route to nanotechnology: an overview. J. Electrostat. 66, 197–219 (2008)
M. Yanilmaz, Y. Lu, M. Dirican, K. Fu, X. Zhang, Nanoparticle-on-nanofiber hybrid membrane separators for lithium-ion batteries via combining electrospraying and electrospinning techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 456, 57–65 (2014)
X.-H. Ma, Z. Yang, Z.-K. Yao, H. Guo, Z.-L. Xu, C.Y. Tang, Interfacial polymerization with electrosprayed microdroplets: toward controllable and ultrathin polyamide membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 5, 117–122 (2018)
S. Yang, J. Wang, L. Fang, H. Lin, F. Liu, and C. Y. Tang, Electrosprayed polyamide nanofiltration membrane with intercalated structure for controllable structure manipulation and enhanced separation performance, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 602, p. 117971, 2020.
J. Chen, J. Zhang, X. Wu, X. Cui, W. Li, H. Zhang et al., Accurately controlling the hierarchical nanostructure of polyamide membranes via electrostatic atomization-assisted interfacial polymerization. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 8, 9160–9167 (2020)
Q. An, W.-S. Hung, S.-C. Lo, Y.-H. Li, M. De Guzman, C.-C. Hu et al., Comparison between free volume characteristics of composite membranes fabricated through static and dynamic interfacial polymerization processes. Macromolecules 45, 3428–3435 (2012)
S. O. Mbam, S. E. Nwonu, O. A. Orelaja, U. S. Nwigwe, and X.-F. Gou, Thin-film coating; historical evolution, conventional deposition technologies, stress-state micro/nano-level measurement/models and prospects projection: a critical review, Materials Research Express, vol. 6, p. 122001, 2019.
M.F. Jimenez-Solomon, Q. Song, K.E. Jelfs, M. Munoz-Ibanez, A.G. Livingston, Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization. Nat Mater 15, 760–767 (Jul 2016)
E. P. Chan, J.-H. Lee, J. Y. Chung, and C. M. Stafford, An automated spin-assisted approach for molecular layer-by-layer assembly of crosslinked polymer thin films, Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 83, p. 114102, 2012.
X. Kang, X. Liu, J. Liu, Y. Wen, J. Qi, and X. Li, Spin-assisted interfacial polymerization strategy for graphene oxide-polyamide composite nanofiltration membrane with high performance, Applied Surface Science, vol. 508, p. 145198, 2020.
S. Kaur, S. Sundarrajan, R. Gopal, S. Ramakrishna, Formation and characterization of polyamide composite electrospun nanofibrous membranes for salt separation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 124, E205–E215 (2012)
H. Mahdavi, M. Moslehi, A new thin film composite nanofiltration membrane based on PET nanofiber support and polyamide top layer: preparation and characterization. J. Polym. Res. 23, 257 (2016)
O. Qanati, A. Ahmadi, M. S. Seyed dorraji, M. H. Rasoulifard, and V. Vatanpour, Thin-film nanofiltration membrane with monomers of 1,2,4,5-benzene tetracarbonyl chloride and ethylene diamine on electrospun support: preparation, morphology and chlorine resistance properties, Polymer Bulletin, vol. 75, pp. 3407–3425, 2018.
X. Wang, T.-M. Yeh, Z. Wang, R. Yang, R. Wang, H. Ma et al., Nanofiltration membranes prepared by interfacial polymerization on thin-film nanofibrous composite scaffold. Polymer 55, 1358–1366 (2014)
H. Yan, X. Miao, J. Xu, G. Pan, Y. Zhang, Y. Shi et al., The porous structure of the fully-aromatic polyamide film in reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 475, 504–510 (2015)
K. Shen, C. Cheng, T. Zhang, and X. Wang, High performance polyamide composite nanofiltration membranes via reverse interfacial polymerization with the synergistic interaction of gelatin interlayer and trimesoyl chloride, Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 588, p. 117192, 2019.
J.S. Trivedi, D.V. Bhalani, G.R. Bhadu, S.K. Jewrajka, Multifunctional amines enable the formation of polyamide nanofilm composite ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes with modulated charge and performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 6, 20242–20253 (2018)
S. Karan, Z. Jiang, A.G. Livingston, Sub–10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science 348, 1347 (2015)
Y. Cui, X.-Y. Liu, T.-S. Chung, Ultrathin polyamide membranes fabricated from free-standing interfacial polymerization: synthesis, modifications, and post-treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 56, 513–523 (2017)
Z.-Y. Ma, X. Zhang, C. Liu, S.-N. Dong, J. Yang, G.-P. Wu et al., Polyamide nanofilms synthesized via controlled interfacial polymerization on a “jelly” surface. Chem. Commun. 56, 7249–7252 (2020)
C. Jiang, L. Zhang, P. Li, H. Sun, Y. Hou, Q.J. Niu, Ultrathin film composite membranes fabricated by novel in situ free interfacial polymerization for desalination. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12, 25304–25315 (2020)
R. Zhang, S. Yu, W. Shi, J. Zhu, B. Van der Bruggen, Support membrane pore blockage (SMPB): an important phenomenon during the fabrication of thin film composite membrane via interfacial polymerization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 215, 670–680 (2019)
J. Zhu, J. Hou, R. Zhang, S. Yuan, J. Li, M. Tian et al., Rapid water transport through controllable, ultrathin polyamide nanofilms for high-performance nanofiltration. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 6, 15701–15709 (2018)
S.-J. Park and J.-H. Lee, Fabrication of high-performance reverse osmosis membranes via dual-layer slot coating with tailoring interfacial adhesion," Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 614, p. 118449, 2020.
G.S. Lai, W.J. Lau, S.R. Gray, T. Matsuura, R.J. Gohari, M.N. Subramanian et al., A practical approach to synthesize polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes with improved separation properties for water/wastewater treatment. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 4, 4134–4144 (2016)
J. Nambikkattu, J. Jose, and N. Jacob Kaleekkal, Tailoring the performance of thin-film composite membrane using ZIF-8 for wastewater treatment, Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021/03/13/ 2021.
C. Jarusutthirak, S. Mattaraj, R. Jiraratananon, Influence of inorganic scalants and natural organic matter on nanofiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 287, 138–145 (2007)
A.J.C. Semiao, G. Gazzola, O. Habimana, R. Heffernan, C. Murphy, E. Casey, Understanding the mechanisms of biofouling on nanofiltration membranes: effect of the biofilm structure on solute removal. Procedia Engineering 44, 1557–1560 (2012)
D. Pichardo-Romero, Z. Garcia-Arce, A. Zavala-Ramírez, and R. Castro-Muñoz, Current advances in biofouling mitigation in membranes for water treatment: an overview, Processes, vol. 8, p. 182, 02/05 2020.
S. Chellam, C. Serra, M. Wiesner, Estimating costs for integrated membrane systems. Journal American Water Works Association - J AMER WATER WORK ASSN 90, 96–104 (1998)
J. Nambikkattu, N.J. Kaleekkal, J.P. Jacob, Metal ferrite incorporated polysulfone thin-film nanocomposite membranes for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 11915–11927 (2021)
Funding
The authors declare the partial financial support from DST-SERB project under start-up research grant (SRG/2019/000028) to Dr. Noel Jacob Kaleekkal by the Department of Science and Technology- Science and Engineering Research Board, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhaskar, V.V., Kaleekkal, N.J. Next-generation thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes for water remediation: a review. emergent mater. 5, 1373–1390 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00273-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00273-8