Abstract
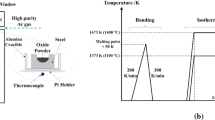
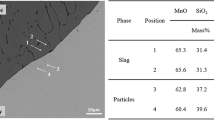
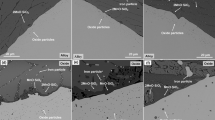
Diffusion couple experiments were performed to study the thermodynamic and kinetic mechanisms of interfacial reactions between the 316L stainless steel and the composite MnO–SiO2 oxide during isothermal heating at 1473 K (1200 °C) for 1, 3, 5, and 10 h and at 1173, 1273, 1373, 1473, and 1573 K (900, 1000, 1100, 1200, and 1300 °C) for 3 h. Compositional variations in the 316L stainless steel and the composite MnO–SiO2 oxide in the vicinity of the steel–oxide interface in each diffusion couple specimen were determined. Before and after isothermal heating, thermodynamic equilibria between the oxide and steel at the interface were estimated in accordance with the calculation of the Gibbs free energy change in the interfacial steel–oxide reactions. The diffusion coefficients of Mn, Cr, and Si in 316L stainless steel under different experimental conditions were quantitatively acquired. The results showed that solid-state interfacial reactions occurred between the Cr in the 316L stainless steel and composite MnO–SiO2 oxide during isothermal heating, which resulted in the depletion of Cr and accumulation of Si and Mn in the steel in the vicinity of the steel–oxide interface. The widths of the Cr-depleted zone, Mn-accumulated zone and Si-accumulated zone all showed increasing trends with increasing isothermal heating temperature and time. The average values of the diffusion coefficients of Mn, Cr, and Si in the steel at 1473 K (1200 °C) were 1.21 × 10–14 ± 2.96 × 10–15, 1.69 × 10–14 ± 2.54 × 10–15, and 1.00 × 10–14 ± 1.96 × 10–15 m2 s−1, respectively, and they continued to increase with increasing isothermal heating temperature.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Kaushik, M. Lowry, H. Yin, H. Pielet, Ironmak. Steelmak. 39 (2012) 284–300.
C. Temmel, B. Karlsson, N.G. Ingesten, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 31 (2008) 466–477.
L.F. Zhang, Steel Res. Int. 77 (2006) 158–169.
Y. Ren, L. Zhang, W. Fang, S. Shao, J. Yang, W. Mao, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 1024–1034.
L. Wang, S. Yang, J. Li, T. Wu, W. Liu, J. **ong, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 99–107.
J.H. Shin, J.H. Park, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51 (2020) 1211–1224.
L.T. Wang, S.H. Peng, Q.Y. Zhang, Z.B. Li, Steel Res. Int. 77 (2006) 25–31.
X. Yin, Y.H. Sun, Y.D. Yang, X.F. Bai, X.X. Deng, M. Barati, A. McLean, Ironmak. Steelmak. 43 (2016) 533–540.
H. Shibata, K. Kimura, T. Tanaka, S.Y. Kitamura, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 1944–1950.
K.H. Kim, S.J. Kim, H. Shibata, S.Y. Kitamura, ISIJ Int. 54 (2014) 2144–2153.
Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, L. Zhang, N. Liu, Y. Ren, Steel Res. Int. 92 (2021) 2000605.
W. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Luo, Y. Ren, X. Sun, Ironmak. Steelmak. 49 (2022) 472–483.
M. Li, H. Matsuura, F. Tsukihashi, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 50 (2019) 863–873.
W. Gan, C. Liu, K. Liao, H. Zhang, H. Ni, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 53 (2022) 485–502.
W. Gan, C. Liu, K. Liao, H. Zhang, H. Ni, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 53 (2022) 2553–2569.
T. Michler, J. Naumann, M. Hock, K. Berreth, M.P. Balogh, E. Sattler, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 628 (2015) 252–261.
C.L. Lai, L.W. Tsay, C. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 584 (2013) 14–20.
S. Guo, E.H. Han, H.T. Wang, Z.M. Zhang, J.Q. Wang, Acta Metall. Sin. 53 (2017) 455–464.
D. **, D.J. Tian, J.H. Li, M. Sakane, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 39 (2016) 850–858.
F. Yan, W. **ong, E. Faierson, G.B. Olson, Scripta Mater. 155 (2018) 104–108.
J. Wang, W. Li, Y. Ren, L. Zhang, Steel Res. Int. 90 (2019) 1800600.
K. Takano, R. Nakao, S. Fukumoto, T. Tsuchiyama, S. Takaki, Tetsu-to-Hagane 89 (2003) 616–622.
Y. Ren, L. Zhang, P.C. Pistorius, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48 (2017) 2281–2292.
M. Hino, K. Ito, Thermodynamic data for steelmaking, Tohoku University Press, Sendai, Japan, 2010.
X.H. Huang, Principles of iron and steel metallurgy, Metallurgical Industry Press, Bei**g, China, 2013.
G. Neumann, C. Tuijn, Self-diffusion and impurity diffusion in pure metals: handbook of experimental data, Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2009.
T. Thorvaldsson, A. Salwén, Scripta Metall. 18 (1984) 739–742.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U21A20113 and 52074198) and also supported by the Project for Technology Talents Serving Enterprises of Hubei Province (Grant No. KJRQ2023000073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Cheng-song Liu is a youth editorial board member for Journal of Iron and Steel Research International and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Cs., Li, Fk., Zhang, H. et al. Mechanisms of interfacial reactions between 316L stainless steel and MnO–SiO2 oxide during isothermal heating. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 1511–1523 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01013-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01013-4