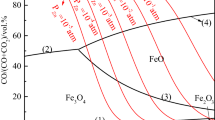
Abstract
It is urgent to dispose of zinc-bearing dust from steel plants, and direct reduction process is an effective method to remove hazardous metals and recycle iron from the dust. The reduction behavior of carbon-containing pellets which were made from three kinds of zinc-bearing dust was investigated. When the pellets were reduced at 1200 °C for 50 min, the reduced pellets with cold compressive strength of 1164 N pellet−1 and Zn content < 0.1 wt.% could be directly used as burden for improving the blast furnace operation without further agglomeration. The results of isothermal kinetic study showed that the iron oxide reduction rate was controlled by the chemical reactions. The strengthening mechanism of reduced pellets and iron oxide reduction mechanism was investigated by thermodynamic calculation besides X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy combined with energy dispersive spectrometry, and optical microscopy analyses. It was found that higher temperatures are required for the reduction of spinel phase (zinc ferrite) and olivine phase (hedenbergite). The generation and growth of metallic iron bridges could significantly increase the compressive strength of reduced pellets. The iron oxide reduction in the carbon-containing pellets followed the uniform internal reduction model and possessed a high apparent reaction rate, which can improve energy utilization rate and production efficiency.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Sikalidis, M. Mitrakas, R. Tsitouridou, Global Nest J. 12 (2010) 368–373.
R. Chairaksa-Fujimoto, Y. Inoue, N. Umeda, S. Itoh, T. Nagasaka, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 22 (2015) 788–797.
X.W. An, J.S. Wang, X.F. She, Q.G. Xue, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 20 (2013) 627–635.
X.L. Lin, Z.W. Peng, J.X. Yan, Z.Z. Li, J.Y. Hwang, Y.B. Zhang, G.H. Li, T. Jiang, J. Clean. Prod. 149 (2017) 1079–1100.
A. Andersson, A. Gullberg, A. Kullerstedt, H. Ahmed, L. Sundqvist-Ökvist, C. Samuelsson, J. Sustain. Metall. 5 (2019) 350–361.
Z. Youcai, R. Stanforth, J. Hazard. Mater. 80 (2000) 223–240.
P. Halli, J. Hamuyuni, H. Revitzer, M. Lundström, J. Clean. Prod. 164 (2017) 265–276.
H.G. Wang, Y. Li, J.M. Gao, M. Zhang, M. Guo, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 23 (2016) 146–155.
M. Al-harahsheh, S. Kingman, L. Al-Makhadmah, I.E. Hamilton, J. Hazard. Mater. 274 (2014) 87–97.
L.G. **a, R. Mao, J.L. Zhang, X.N. Xu, M.F. Wei, F.H. Yang, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 22 (2015) 122–131.
J.T. Ju, Y.J. Dang, Mater. Rep. 28 (2014) No. 9, 109–113.
X.F. She, J.S. Wang, G. Wang, Q.G. Xue, X.X. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 (2014) 488–495.
C.C. Wu, F.C. Chang, W.S. Chen, M.S. Tsai, Y.N. Wang, J. Environ. Manage. 143 (2014) 208–213.
E. Junca, T.A.G. Restivo, J.R. de Oliveira, D.C.R. Espinosa, J.A.S. Tenório, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 126 (2016) 1889–1897.
E. Junca, J.R. de Oliveira, T.A.G. Restivo, D.C.R. Espinosa, J.A.S. Tenório, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 123 (2016) 631–641.
D.Q. Zhu, D.Z. Wang, J. Pan, H.Y. Tian, Y.X. Xue, Powder Technol. 380 (2021) 273–281.
J. Peng, B. Peng, D. Yu, M.T. Tang, J. Lobel, J.A. Kozinski, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 14 (2004) 392–396.
D.Y. Wang, J.L. Zhang, S.L. Wu, Baosteel Technol. Res. 7 (2013) No. 3, 46–49.
D.Y. Wang, W.Q. Che, R.Z. Zhou, W.Z. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 6 (1999) No. 1, 12–18.
J. Peng, B. Peng, D. Yu, M.T. Tang, H.C. Song, J. Lobel, J.A. Kozinski, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 14 (2004) 593–598.
Y.L. Wu, Z.Y. Jiang, X.X. Zhang, P. Wang, X.F. She, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 20 (2013) 636–644.
Z.D. Tang, Q. Zhang, Y.S. Sun, P. Gao, Y.X. Han, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 172 (2021) 105680.
O.A. Mohamed, M.E.H. Shalabi, N.A. El-Hussiny, M.H. Khedr, F. Mostafa, Powder Technol. 130 (2003) 277–282.
S.C. Panigrahy, P. Verstraeten, J. Dilewijns, Metall. Trans. B 15 (1984) 23–32.
Y. Man, J.X. Feng, F.J. Li, Q. Ge, Y.M. Chen, J.Z. Zhou, Powder Technol. 256 (2014) 361–366.
M. Omran, T. Fabritius, Sep. Purif. Technol. 210 (2019) 867–884.
D. Mombelli, S. Barella, A. Gruttadauria, C. Mapelli, Appl. Sci. 9 (2019) 4902.
D. Mombelli, C. Mapelli, S. Barella, A. Gruttadauria, E. Spada, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7 (2019) 102966.
D.J.C. Stewart, D. Thomson, A.R. Barron, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 170 (2021) 105592.
Y.G. Ding, J.S. Wang, X.F. She, G. Wang, Q.G. Xue, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 5, 28–33.
M. Kumar, S. Nath, S.K. Patel, Miner. Process. Ext. Met. Rev. 31 (2010) 256–268.
Z.Q. Guo, J. Pan, D.Q. Zhu, C.C. Yang, Powder Technol. 329 (2018) 55–64.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904347), which supplied us with the facilities and funds needed to complete the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Dz., Zhu, Dq., Pan, J. et al. A high-efficiency separation process of Fe and Zn from zinc-bearing dust by direct reduction. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29, 1559–1572 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00722-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00722-y