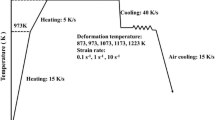
Abstract
The constitutive relationship is the basis for studying the material processing technology and controlling the quality of products. Data and models of the plastic flow behavior of materials are often required during the manufacturing process. Therefore, establishing constitutive models with high precision and generalization and enriching material database is of great significance for optimizing processing technology and product quality of the material. Based on the Gleeble thermal compression test results, the essential relationship of 25 steel between the flow stress and thermal–mechanical state variables, such as temperature, strain rate, and strain, is quantitatively discussed for the first time. Combined with the Zener–Hollomon parameter and considering the influence of strain compensation, the constitutive model of 25 steel is built by the hyperbolic-sine equation over the full strain range. In the modeling process, the influence of strain on material constants is characterized by polynomial fitting. The selection basis of polynomial order is discussed in-depth, and the inconsistency between calculation accuracy and fitting effect is clarified. Finally, the accuracy of the model is analyzed, and the generalization and applicability are discussed. It is proved that the developed model can accurately predict the flow behavior of materials in the full strain range.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.W. Lei, G.Q. Chen, K.H. Liu, X. Wang, X.M. Jiang, J.L. Pan, Q.Y. Shi, Metals 9 (2019) 42.
C.B. Huang, The research on extrusion process of large diameter steel pipe of ferrous metals, Tsinghua University, Bei**g, China, 2015.
N. Thakur, P. Kumar, R.S. Bharj, Materialtoday Proceed. 5 (2018) 27884–27892.
N.E. Karkalos, A.P. Markopoulos, Proced. Manuf. 22 (2018) 107–113.
Y.M. Li, H.C. Ji, Z.M. Cai, X.F. Tang, Y.G. Li, J.P. Liu, Materials 12 (2019) 1893.
D.N. Zhang, Q.Q. Shangguan, C.J. **e, F. Liu, J. Alloy. Compd. 619 (2015) 186–194.
Y.C. Lin, X.M. Chen, Mater. Des. 32 (2011) 1733–1759.
E.X. Pu, H. Feng, M. Liu, W.J. Zheng, H. Dong, Z.G. Song, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23 (2016) 178–184.
P.T. Liu, Q.X. Huang, L.F. Ma, T. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25 (2018) 1054–1061.
Y. Han, S. Yan, Y. Sun, H. Chen, Metals 7 (2017) 114.
A. Rudra, M. Ashiq, S. Das, R. Dasgupta, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50 (2019) 1060–1076.
M.S. Arun, U. Chakkingal, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 754 (2019) 659–673.
J. Li, J. Liu, Metals 9 (2019) 212.
Z.J. Tao, H. Yang, H. Li, J. Ma, P.F. Gao, Rare Metals 35 (2016) 162–171.
J.H. Hollomon, C. Zener, J. Appl. Phys. 17 (1946) 82–90.
K. Li, Q.L. Pan, R.S. Li, S.H. Liu, Z.Q. Huang, X. He, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28 (2019) 981–994.
S. Long, Y.F. **a, P. Wang, Y.T. Zhou, F.J. Gongye, J. Zhou, J.S. Zhang, M.L. Cui, J. Alloy. Compd. 796 (2019) 65–76.
Z.M. Cai, H.C. Ji, W.C. Pei, X.F. Tang, X.M. Huang, J.P. Liu, Vacuum 165 (2019) 324–336.
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, J. Zhong, Comput. Mater. Sci. 42 (2008) 470–477.
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, A.K. Bhaduri, Mater. Des. 31 (2010) 981–984.
G.W. Ge, L.Q. Zhang, J.J. **n, J.P. Lin, M. Aindow, L.C. Zhang, Sci. Rep. 8 (2018) 5453.
S. Mandal, V. Rakesh, P.V. Sivaprasad, S. Venugopal, K.V. Kasiviswannathan, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 500 (2009) 114–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Yuan, Cl., Wu, Rd. et al. Constitutive modeling and analysis on high-temperature flow behavior of 25 steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 76–85 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00445-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00445-6