Abstract
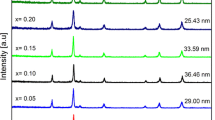
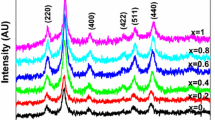
Nanoparticles of Ni0.6–xZn0.4CoxFe2O4 were prepared via an aqueous sol–gel auto-combustion route. The Ni–Zn–ferrite system was doped with Co to improve the magnetic properties. Structural determination of the phase and crystallite size was achieved using the X-ray diffraction technique. Spinel cubic (single-phase) nanoparticles were formed at some specific compositions, x = 0.264 and x = 0.528, whereas at other compositions, a partial hematite secondary phase was formed. The values of saturation magnetization depend upon the concentration of the hematite phase; in this situation, the value of magnetic saturation decreases, causing a high spin canting effect that results in a decrease in the net magnetic moment. Further do** of Co2+ ions enhances the magnetic properties because of its high magnetic moment and distributions. Theoretical analysis using the most suitable proposed cation distribution verified the experimental findings. The observed structural and magnetic findings may contribute to improve electromagnetic-interference-shielding and magnetic-recording-device applications.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data is the part of ongoing research, can be made available on genuine request.
References
Suzuki, T., Tanaka, T., Ikemizu, K.: High density recording capability for advanced particulate media. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 235(1), 159 (2001)
Giannakopoulou, T., Kompotiatis, L., Kontogeorgakos, A., Kordas, G.: Microwave behavior of ferrites prepared via sol–gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 46, 360 (2002)
Olsen, E., Thonstad, J.: Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminium electrolysis: part I Material fabrication and preliminary testing. J. Appl. Electrochem. 29(3), 293 (1999)
Augustion, C.O., Prabhakaran, D., Srinivasan, L.K.: Fabrication and characterization of NiCr2O4 spinel. J. Mater Sci. 12, 383 (1993)
Huq, M.F., Saha, D.K., Ahmed, R., Mahmood, Z.H.: Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite research: a brief review. J. Sci. Res. 5(2), 215 (2013)
Amiri, G.R., Yousefi, M.H., Abolhassani, M.R., Manouchehri, S., Keshavarz, M.H., Fatahian, S.: Magnetic properties and microwave absorption in Ni–Zn and Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by low-temperature solid-state reaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(6), 730 (2011)
Mohapatra, M., Anand, S.: Synthesis and applications of nano-structured iron oxides/hydroxides–a review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2(8), 127 (2010)
Verma, A., Chatterjee, R.: Effect of zinc concentration on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of mixed Mn–Zn and Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized by the citrate precursor technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 306(2), 313 (2006)
Kwon, Y.M., Lee, M.Y., Mustaqima, M., Liu, C., Lee, B.W.: Journal of Magnetics. 19, 34 (2014)
Bercoff, P.G., Bertorello, H.R.: Localized canting effect in Zn-substituted Ni ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 213, 56 (2000)
Leng, P.L., Naseri, M.G., Saion, E., Shaari, A.H., Kamaruddin, M.A.: Synthesis and characterization of Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles (Ni0.25Zn0.75Fe2O4) by thermal treatment method. Advances in Nanoparticles 2(4), 378 (2013)
Sláma, J., Grusková, A., Ušáková, M., Ušák, E., Šubrt, J., Lukáč, J.: Substituted Ni–Zn ferrites for passive sensor applications. J. Electr. Eng. 57(8), 159 (2006)
Costa, A.C.F.M., Tortella, E., Morelli, M.R., Kiminami, R.H.G.A.: Synthesis, microstructure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 256(1), 174 (2003)
Da Silva, J.B., Mohallem, N.D.S.: Preparation of composites of nickel ferrites dispersed in silica matrix. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 226, 1393 (2001)
Jalaly, M., Enayati, M.H., Karimzadeh, F.: Investigation of structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni0.3Zn0.7Fe2O4 prepared by high energy ball milling. J. Alloys. Compd 480(2), 737 (2009)
Sertkol, M., Köseoğlu, Y., Baykal, A., Kavas, H., Başaran, A.C.: Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Zn0.6Ni0.4Fe2O4 nanoparticles via a polyethylene glycol-assisted hydrothermal route. J Magn Magn Mater 321, 3157 (2009)
Damnjanovic, M., Stojanovic, G., Desnica, V., Zivanov, L., Raghavendra, R., Bellew, P., Mcloughlin, N.: Analysis, design, and characterization of ferrite EMI suppressors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 42(2), 270 (2006)
Abdeen, A.M.: Dielectric behaviour in Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192(1), 121 (1999)
Shannigrahi, S.R., Pramoda, K.P., Nugroho, F.A.A.: Synthesis and characterizations of microwave sintered ferrite powders and their composite films for practical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(2), 140 (2012)
Rao, B.P., Kumar, A.M., Rao, K.H., Murthy, Y.L.N., Caltun, O.F., Dumitru, I., Spinu, L.: Synthesis and magnetic studies of Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Opto. electron. Adv. M. 8(5), 1703 (2006)
Pereira, S.L., Pfannes, H.D., Mendes Filho, A.A., Pinto, L.C.B., Chíncaro, M.A.: A comparative study of NiZn ferrites modified by the addition of cobalt. Mater. Res. 2(3), 231 (1999)
Li, L.Z., Peng, L., Zhu, X.H., Yang, D.Y.: Effects of Cu and Co substitution on the properties of NiZn ferrite thin films. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology. 10(1), 88 (2012)
Rezlescu, E., Sachelarie, L., Popa, P.D., Rezlescu, N.: Effect of substitution of divalent ions on the electrical and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn–Me ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 36(6), 3962 (2000)
**a, Y., Song, Y.Q., Lin, C.G., Cui, S., Fang, Z.Z.: Effect of carbide formers on microstructure and thermal conductivity of diamond-Cu composites for heat sink materials. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. 19(5), 1161 (2009)
Mao, W.W., Yao, Q.F., Fan, Y.F., Wang, Y.L., Wang, X.F., Pu, Y., Li, X.A.: Combined experimental and theoretical investigation on modulation of multiferroic properties in BiFeO3 ceramics induced by Dy and transition metals co-do**. J. Alloys. Compds. 784, 117 (2019)
Zhang, W.Z., Zhu, X.Y., Wang, L.J., Xu, X., Yao, Q.F., Mao, W.W., Li, X.A.: Study on the magnetic and ferroelectric properties of Bi0.95Dy0.05Fe0.95M0.05O3 (M= Mn, Co) ceramics. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn 30, 11–3001 (2017)
Zhu, Y.Y., Quan, C.Y., Ma, Y.H., Wang, Q., Mao, W.W., Wang, X.F., Zhang, J., Min, Y.G., Yang, J.P., Li, X.A., Huang, W.: Effect of Eu, Mn co-do** on structural, optical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3nanoparticles. Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 57, 178 (2017)
Kumar, R., Kumar, H., Singh, R.R., Barman, P.B.: Variation in magnetic and structural properties of Co-doped Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles: a different aspects. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 78(3), 566 (2016)
Veverka, M., Jirák, Z., Kaman, O., Knížek, K., Maryško, M., Pollert, E., Závěta, K., Lančok, A., Dlouhá, M., Vratislav, S.: Distribution of cations in nanosize and bulk Co–Zn ferrites. Nanotechnology 22, 34–345701 (2011)
Choi, E.J., Ahn, Y.K., Song, K.C., An, D.H., Lee, B.G., Kang, K.U.: Cation distribution and spin-canted structure in cobalt ferrite particles from a cobalt-iron hydroxide carbonate complex. J. Korean. Phys. Soc. 44(6), 1518 (2004)
Fayek, M.K., Bahgat, A.A., Abbas, Y.M., Moberg, L.: Neutron diffraction and Mossbauer effect study on a cobalt substituted zinc ferrite. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 15(11), 2509 (1982)
Sawatzky, G.A., van der Woude, F., Morrish, A.H.: Mössbauer study of several ferrimagnetic spinels. Phys. Rev. 187(2), 747 (1969)
Kumar, A.M., Rao, P.A., Verma, M.C., Chaudhary, G.S.V.R.K., Rao, K.H.: Cation distribution in Co0.7Me0.3Fe2O4 (Me= Zn, Ni and Mn). J Mod Phys 2(9), 1083 (2011)
Prabahar, S., Dhanam, M.: CdS thin films from two different chemical baths—structural and optical analysis. J. Cryst. Growth. 285(1), 41 (2005)
**a, A.L., Liu, S.K., **, C.G., Chen, L., Lv, Y.H.: Hydrothermal Mg1-xZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites: phase formation and mechanism of saturation magnetization. Mater. Lett. 105, 199 (2013)
Zaki, H.M., Al-Heniti, S.H., Elmosalami, T.A.: Structural magnetic and dielectric studies of copper substituted nano-crystalline spinel magnesium zinc ferrite. J Alloys Compd 633, 104 (2015)
Hakim, M.A., Kumar Nath, S., Sikder, S.S., Hanium Maria, K.: Cation distribution and electromagnetic properties of spinel type Ni–Cd ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 74(9), 1316 (2013)
Mohammed, K.A., Al-Rawas, A.D., Gismelseed, A.M., Sellai, A., Widatallah, H.M., Yousif, A., Elzain, M.E., Shongwe, M.: Infrared and structural studies of Mg1–xZnxFe2O4 ferrites. Physica B. 407(4), 795 (2012)
Sharma, R., Thakur, P., Kumar, M., Thakur, N., Negi, N.S., Sharma, P., Sharma, V.: Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via co-precipitation route. J. Alloys Compd 684, 569 (2016)
Houshiar, M., Zebhi, F., Razi, Z.J., Alidoust, A., Askari, Z.: Synthesis of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles using combustion, coprecipitation, and precipitation methods: A comparison study of size, structural, and magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 371, 43 (2014)
Goldman, A.: 2006 Modern Ferrite Technology. Spring. Sci. & Bus. Med. Germ
Shen, X., Wang, Y.X., Yang, X., Lu, L.Q., Huang, L.: 0.3–3 GHz magneto-dielectric properties of nanostructured NiZnCo ferrite from hydrothermal process. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 21(6), 630 (2010)
Thakur, S., Katyal, S.C., Singh, M.: Structural and magnetic properties of nano nickel–zinc ferrite synthesized by reverse micelle technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1 (2009)
Shenoy, S.D., Joy, P.A., Anantharaman, M.R.: Effect of mechanical milling on the structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of coprecipitated ultrafine zinc ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 269(2), 217 (2004)
Lodhi, M.Y., Mahmood, K., Mahmood, A., Malik, H., Warsi, M.F., Shakir, I., Asghar, M., Khan, M.A.: New Mg0.5CoxZn0.5− xFe2O4 nano-ferrites: structural elucidation and electromagnetic behavior evaluation. Curr. Appl. Phys 14, 5–716 (2014)
Arana, M., Galván, V., Jacobo, S.E., Bercoff, P.G.: Cation distribution and magnetic properties of LiMnZn ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 568, 5 (2013)
Kumar, G., Shah, J., Kotnala, R.K., Singh, V.P., Garg, G., Shirsath, S.E., Batoo, K.M., Singh, M.: Superparamagnetic behaviour and evidence of weakening in super-exchange interactions with the substitution of Gd3+ ions in the Mg–Mn nanoferrite matrix. Mater. Res. Bull. 63, 216 (2015)
Vasoya, N.H., Lakhani, V.K., Sharma, P.U., Modi, K.B., Kumar, R., Joshi, H.H.: Study on the electrical and dielectric behaviour of Zn-substituted cobalt ferrialuminates. J. Phys-Condens. Mat 18(34), 8063 (2006)
Lakhani, V.K., Pathak, T.K., Vasoya, N.H., Modi, K.B.: Structural parameters and X-ray Debye temperature determination study on copper-ferrite-aluminates. Solid State Sci. 13(3), 539 (2011)
Acknowledgements
We are very thankful for the financial aid to this work provided by Jaypee University of Information Technology, Waknaghat, Solan, H.P., India. We also thank SAIF, Panjab University, Chandigarh for characterization of our samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Ra**der Kumar (first author) All the work has been done: sample preparation, characterization, interpretation, and manuscript writing. Dipti Rawat (joint first author) Interpretation and manuscript writing. Prof. P.B. Barman (third author) Manuscript corrections and guidance. Dr. Ragini Raj Singh (corresponding and senior author) All work has been planned and guided, interpretation of the results, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Un-doped and cobalt-doped Ni–Zn nanoparticles synthesized by aqueous route.
2. Single phase spinel cubic nanoparticles have been prepared at x = 0.264 and 0.528.
3. Hematite phase and do** of Co2+ can tune the saturation magnetization.
4. Mr, Mc increased on Co2+ do** due to + ve magneto-crystalline anisotropy energy.
5. Theoretical evaluation supports the experimental results.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Rawat, D., Barman, P.B. et al. Experimental and theoretical verification of cation distribution and spin canting effect via structural and magnetic studies of NiZnCo ferrite nanoparticles. J Aust Ceram Soc 58, 101–111 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-021-00671-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-021-00671-5