Abstract
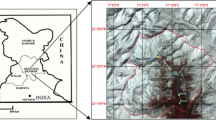
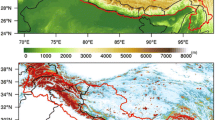
Accurate snow spectral albedo measurements from satellite data can essentially help to determine the changes over the snow surface area. In the current study, spectral snow albedo is measured over the northern region of Pakistan using spatio-temporal imagery datasets taken by Landsat satellite series equipped with TM and ETM+ sensors. An Automatic Cloud Cover Assessment (ACCA) algorithm is used to mask cloudy pixels from further processing. Furthermore, an image independent model, Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum (6S) is used in the current research work to atmospherically correct the satellite data. The snow cover albedo of northern Pakistan is estimated using pixel values prior to correction, ACCA output values, and 6S model output values. The results of the study show that highest albedo values are estimated using Landsat band 4 data with albedo model. The results of the study also show that the albedo values measured (band 4) in the year 1992 (0.989) are reduced in the year 2000 (0.931). It is expected that the results of the study could be utilized to predict climatic variations for spring runoff estimation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhutiyani M, Kale V, Pawar N (2010) Climate change and the precipitation variations in the northwestern Himalaya: 1866–2006. Int J Climatol 30:535–548
Butt MJ (2012) Characteristics of snow cover in the Hindukush, Karakoram and Himalaya (HKH) region using Landsat satellite data. Hydrological Processes 26:3689–3698. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8375
Butt MJ (2013) Exploitation of Landsat data for Snow Zonation Map** in Hindukush, Karakoram and Himalaya (HKH) Region of Pakistan. Hydrol Sci J 58(5):1088–1096. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.799774
Chander G, Markham BL (2003) Revised Landsat-5 TM radiometric calibration procedures and postcalibration dynamic ranges. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 41(11):2674–2677
Chander G, Markham BL, Helder DL (2009) Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens Environ 113:893–903
Cheng Q, Shen H, Zhang L, Yuan Q, Zeng C (2014) Cloud removal for remotely sensed images by similar pixel replacement guided with a spatio-temporal MRF model. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 92:54–68
Csiszar I, Gutman G (1999) Map** global land surface albedo from NOAA AVHRR. J Geophys Res 104:6215–6228
Déry SJ, Brown RD (2007) Recent Northern Hemisphere snow cover extent trends and implications for the snow-albedo feedback. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl031474
Dimri AP, Chevuturi A (2016) Western disturbances—an Indian meteorological perspective. Springer, Switzerland
Dimri AP, Dash SK (2012) Wintertime climatic trends in the western Himalayas. Clim Change 111(3–4):775–800
Dobhal DP, Mehta M, Srivastava D (2013) Influence of debris cover on terminus retreat and mass changes of Chorabari Glacier, Garhwal region, central Himalaya, India. J Glaciol 59(217):961–971
Dozier J (1989) Spectral signature of alpine snow cover from the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens Environ 28:9–22
Dozier J, Marks D (1987) Snow map** and classification from Landsat Thematic Mapper. Ann Glaciol 9:97–103
Fletcher CG, Kushner PJ, Hall A, Qu X (2009) Circulation responses to snow albedo feedback in climate change. Geophys Res Lett 36:L09702
Gao Y, **e H, Lu N, Yao T, Liang T (2010) Toward advanced daily cloud-free snow cover and snow water equivalent products from Terra-Aqua MODIS and Aqua AMSR-E measurements. J Hydrol 385(1–4):23–35
Graversen RG, Wang M (2009) Polar amplification in a coupled climate model with locked albedo. Clim Dyn 33:629–643
Greuell W, de Wildt MD (1999) Anisotropic reflection by melting glacier ice: measurements and parameterizations in Landsat TM bands 2 and 4. Remote Sens Environ 70(3):265–277
Grünewald T, Bühler Y, Lehning M (2014) Elevation dependency of mountain snow depth. Cryosphere 8(6):2381–2394
Gupta RP, Ghosh A, Haritashya UK (2007) Empirical relationship between near-IR reflectance of melting seasonal snow and environmental temperature in a Himalayan basin. Remote Sens Environ 107:402–413
Gurung DR, Maharjan SB, Shrestha AB, Shrestha MS, Bajracharya SR, Murthy MSR (2017) Climate and topographic controls on snow cover dynamics in the Hindu Kush Himalaya. Int J Climatol 37(10):3873–3882
Haeberli W (2004) Glaciers and ice caps: historical background and strategies of world-wide monitoring. In: Bamber JL, Payne AJ (eds) Mass balance of the cryosphere: observations and modelling of contemporary and future change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 559–578
Haeberli W, Whiteman C, Shroder JF (eds) (2014) Snow and ice-related hazards, risks and disasters. Academic Press, Waltham
Hall DK, Martinec J (1985) Remote sensing of ice and snow. Chapman and Hall, London, p 189
Hall DK, Riggs GA, Foster JL, Kumar SV (2010) Development and evaluation of a cloud-gap-filled MODIS daily snow-cover product. Remote Sens Environ 114(3):496–503
Hu B, Lucht W, Strahler AH (1999) The interrelationship of atmospheric correction of reflectances and surface BRDF retrieval: a sensitivity study. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 36:724–738
Immerzeel WW, Van Beek LP, Bierkens MF (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328(5984):1382–1385
IPCC (2013) Summary for policymakers. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, **a Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9781107415324
Joshi R, Kumar K, Pandit J, Palni LMS (2015) Variations in the seasonal snow cover area (SCA) for Upper Bhagirathi Basin, India. In: Kumar K, Palni L (eds) JoshiR. Dynamics of climate change and water resources of Northwestern Himalaya. Springer, Cham, pp 9–21
Kääb A, Paul F, Maisch M, Hoelzle M, Haeberli W (2002) The new remote-sensing-derived Swiss glacier inventory: II. First results. Ann Glaciol 34:362–366
Kaser G, Großhauser M, Marzeion B (2010) Contribution potential of glaciers to water availability in different climate regimes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:20223–20227
Kasturirangan K, Navalgund RR, Ajai (2013) Observed changes in the Himalayan–Tibetan glaciers. Fate of Mountain Glaciers in the Anthropocene Pontifical Academy of Sciences, Vatican City
Khromova TE, Dyurgerov M, Barry RG (2003) Late-twentieth century changes in glacier extent in the Ak-shirak Range, Central Asia, determined from historical data and ASTER imagery. Geophys Res Lett 30(16):1863
Knap WH, Brock BW, Oerlemans J, Willis IC (1999) Comparison of Landsat TM derived and ground-based albedos of Haut Glacier d’Arolla, Switzerland. Int J Remote Sens 20(17):3293–3310
Kukla GJ, Kukla HJ (1974) Incresead surface albedo in the northern hemisphere. Science 189:709–714
Kulkarni AV, Rathore BP, Singh SK, Bahuguna IM (2011) Understanding changes in the Himalayan cryosphere using remote sensing techniques. Int J Remote Sens 32(3):601–615
Li Z, Garand L (1994) Estimation of surface albedo from space: a parameterization for global application. J Geophys Res 99:8335–8350
Li X, Shen H, Zhang L, Zhang H, Yuan Q, Yang G (2014) Recovering quantitative remote sensing products contaminated by thick clouds and shadows using multitemporal dictionary learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 52(11):7086–7098
Liang S, Fang H, Chen M (2001) Atmospheric correction of Landsat ETM+ land surface imagery-part I: methods. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39(11):2490–2498
López-Burgos V, Gupta HV, Clark M (2013) Reducing cloud obscuration of MODIS snow cover area products by combining spatio-temporal techniques with a probability of snow approach. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17(5):1809–1823
Maisch M (2000) The long-term signal of climate change in the Swiss Alps: glacier retreat since the end of the Little Ice Age and future ice decay scenarios. Geografia Fisica e Dinamica Quaternaria 23(2):139–152
Negi HS, Shekhar MS, Gusain HS, Ganju A (2018) Winter climate and snow cover variability over north-west Himalaya. In: Goel P, Ravindra R, Chattopadhyay S (eds) Science and geopolitics of the white world. Springer, Cham, pp 127–142
Oleson KW, Bonan GB, Schaaf CB, Gao F, ** Y, Strahler AH (2003) Assessment of global climate model land surface albedo using MODIS data. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002gl016749
Ollinger SV, Richardson AD, Martin ME, Hollinger DY, Frolking SE, Reich PB et al (2008) Canopy nitrogen, carbon assimilation and albedo in temperate and boreal forests: functional relations and potential climate feedbacks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:19335–19340
Parajka J, Pepe M, Rampini A, Rossi S, Blöschl G (2010) A regional snow-line method for estimating snow cover from MODIS during cloud cover. J Hydrol 381(3–4):203–212
Paudel KP, Andersen P (2011) Monitoring snow cover variability in an agropastoral area in the Trans Himalayan region of Nepal using MODIS data with improved cloud removal methodology. Remote Sens Environ 115(5):1234–1246
Paul F, Huggel C, Kääb A (2004a) Combining satellite multispectral image data and a digital elevation model for map** of debris-covered glaciers. Remote Sens Environ 89(4):510–518
Paul F, Kääb A, Maisch M, Kellenberger T, Haeberli W (2004b) Rapid disintegration of Alpine glaciers observed with satellite data. Geophys Res Lett 31(21):L21402
Qu X, Hall A (2007) What controls the strength of snow-albedo feedback? J Clim 20:3971–3981
Rathore BP, Singh SK, Jani P, Bahuguna IM, Brahmbhatt R, Rajawat AS, Randhawa SS, Vyas A (2018) Monitoring of snow cover variability in Chenab Basin using IRS AWiFS sensor. J Indian Soc Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-018-0797-8
Robinson N, Regetz J, Guralnick RP (2014) EarthEnv-DEM90: a nearly-global, voidfree, multi-scale smoothed, 90 m digital elevation model from fused ASTER and SRTM data. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 87:57–67
Roesch A, Schaaf CB, Gao F (2004) Use of Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer bidirectional reflectance distribution function products to enhance simulated surface albedos. J Geophys Res 109(D12):D12105
SAC (2016) Monitoring snow and glaciers of Himalayan region. Space Applications Centre, ISRO, Ahmedabad (ISBN: 978-93-82760-24-5)
Schaaf CL, Martonchik J, Pinty B, Govaerts Y, Gao F, Lattanzio A et al (2008) Retrieval of surface albedo from satellite sensors. In: Liang S (ed) Advances in land remote sensing: system, modeling, inversion and application. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 219–243
Shukla S, Kansal ML, Jain SK (2017) Snow cover area variability assessment in the upper part of the Satluj river basin in India. Geocarto Int 32(11):1285–1306 (Springer 978-1-4020-6449-4)
Smith T, Bookhagen B (2018) Changes in seasonal snow water equivalent distribution in High Mountain Asia (1987 to 2009). Sci Adv 4(1):e1701550
Snehmani, Singh MK, Gupta RD, Bhardwaj A, Joshi PK (2015) Remote sensing of mountain snow using active microwave sensors: a review. Geocarto Int 30(1):1–27
Snehmani, Dharpure JK, Kochhar I, Hari Ram RP, Ganju A (2016) Analysis of snow cover and climatic variability in Bhaga basin located in western Himalaya. Geocarto Int 31(10):1094–1107
Snyder JP (1987). Map projections. A working manual. US Geological Survey professional paper 1395. United States Geological Survey, Reston
Souma K, Wang YQ (2010) A comparison between the effects of snow albedo and infiltration of melting water of Eurasian snow on East Asian summer monsoon rainfall. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:D02115
Srinivasulu J, Kulkarni AV (2004) Estimation of spectral reflectance of snow from IRS-1D LISS-III sensor over the Himalayan terrain. Proc Indian Acad Sci Earth Planet Sci 113(1):117–128
Stigter EE, Wanders N, Saloranta TM, Shea JM, Bierkens MF, Immerzeel WW (2017) Assimilation of snow cover and snow depth into a snow model to estimate snow water equivalent and snowmelt runoff in a Himalayan catchment. Cryosphere 11(4):1647–1664
Tekeli AE, Sönmez I, Erdi E (2016) Snow-covered area determination based on satellitederived probabilistic snow cover maps. Arab J Geosci 9(3):198
Thayyen RJ, Dimri AP (2018) Slope environmental lapse rate (SELR) of temperature in the monsoon regime of the western Himalaya. Front Environ Sci 6:42
Thayyen RJ, Gergan JT (2010) Role of glaciers in watershed hydrology: a preliminary study of a” Himalayan catchment”. Cryosphere 4(1):115–128
Tian Y, Dickinson RE, Zhou L, Myneni RB, Friedl M, Schaaf CB et al (2004) Land boundary conditions from MODIS data and consequences for the albedo of a climate model. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003gl019104
Viterbo P, Betts AK (1999) Impact on ECMWF forecasts of changes to the albedo of the boreal forests in the presence of snow. J Geophys Res 104:27803–27810
Wang W, Huang X, Deng J, **e H, Liang T (2014) Spatio-temporal change of snow cover and its response to climate over the Tibetan Plateau based on an improved daily cloudfree snow cover product. Remote Sens 7(1):169–194
** snow and ice cover: a Normalised Difference Snow and Ice Index. Int J Remote Sens 22:2479–2487
Yang FL, Kumar A, Wang WQ, Juang HMH, Kanamitsu M (2001) Snow- lbedo feedback and seasonal climate variability over North America. J Clim 14:4245–4248
Zhang Y, Wang X, Chen Y (2012) An improved 6S code for atmospheric correction based on water vapor content. Adv Remote Sens 1(1):14–18. https://doi.org/10.4236/ars.2012.11002
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD) for providing the data for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butt, M.J., Assiri, M.E. & Waqas, A. Spectral Albedo Estimation of Snow Covers in Pakistan Using Landsat Data. Earth Syst Environ 3, 267–276 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00104-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-019-00104-1