Abstract
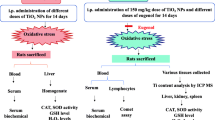
Nanoparticles (NPs) are being used in several industries worldwide and can introduce into the human body through different exposure routes, including inhalation, oral administration, intravenous injection, and intramuscular or transdermal delivery. The present in vivo study aimed to evaluate the acute oral toxicological effects of silica (SiO2) and magnesium oxide (MgO) NPs in rats by using histological, biochemical, and biodistribution parameters. The results revealed that acute exposure to higher doses of these NPs produced a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase serum levels lactate dehydrogenase, and aspartate aminotransferase. Mild congestion, non-zonal hepatocellular swelling and degeneration, and apoptotic cells with significant pyknotic or shrunken nuclei were found in the liver of the treated rats at 2000 mg/kg of the MgO NPs. Moreover, under the microscopic examination, focal hepatocellular degeneration and necrosis, accumulation of mononuclear inflammatory cells within the necrotic area and in the portal tract, and severe central vein and sinusoidal congestion and focal edematous fluids in the hepatic parenchyma were observed in the livers of the treated rats with 2000 mg/kg of SiO2 NPs. Moreover, MgO NPs exhibited higher liver and kidney accumulation than SiO2 NPs. In conclusion, these NPs at a high concentration could have toxicological effects on rats' liver and kidney tissues. However, further studies require examining the safety and the other possible toxic effects of these NPs before entering the consumer market.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan WT, Liu CC, Chiau JS, Tsai ST, Liang CK, Cheng ML, Lee HC, Yeung CY, Hou SY (2017) In vivo toxicologic study of larger silica nanoparticles in mice. Int J Nanomed 12:3421. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S126823
Cho M, Cho WS, Choi M, Kim SJ, Han BS, Kim SH, Kim HO, Sheen YY, Jeong J (2009) The impact of size on tissue distribution and elimination by single intravenous injection of silica nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 189(3):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.04.017
Dhal JP, Sethi M, Mishra BG, Hota G (2015) MgO nanomaterials with different morphologies and their sorption capacity for removal of toxic dyes. Mater Lett 15(141):267–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.10.055
Ding T, Yao L, Liu C (2016) Kinetically-controlled synthesis of ultra-small silica nanoparticles and ultra-thin coatings. Nanoscale 8(8):4623–4627. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NR08224B
Dummer NF, Joyce L, Ellicott H, Jiang Y (2016) Surfactant controlled magnesium oxide synthesis for base catalysis. Catal Sci Technol 6(6):1903–1912. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CY01107H
Fu C, Liu T, Tang F, Chen D, Li L, Liu H, Li X (2012) Acute toxicity and oxidative damage induced by silica nanorattle in vivo. Chin Sci Bull 57(20):2525–2532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5187-y
Fu C, Liu T, Li L, Liu H, Chen D, Tang F (2013) The absorption, distribution, excretion and toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in mice following different exposure routes. Biomaterials 34(10):2565–2575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.12.043
Gelli K, Porika M, Anreddy RN (2015) Assessment of pulmonary toxicity of MgO nanoparticles in rats. Environ Toxicol 30(3):308–314. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.21908
Ghobadian M, Nabiuni M, Parivar K, Fathi M, Pazooki J (2017) Histopathological evaluation of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae following embryonic exposure to MgO nanoparticles. IJFS 16(3):959–969
Go MR, Bae SH, Kim HJ, Yu J, Choi SJ (2017) Interactions between food additive silica nanoparticles and food matrices. Front Microbiol 8:1013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01013
Hassankhani R, Esmaeillou M, Tehrani AA, Nasirzadeh K, Khadir F, Maadi H (2015) In vivo toxicity of orally administrated silicon dioxide nanoparticles in healthy adult mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(2):1127–1132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3413-7
Hochella MF Jr, Lower SK, Maurice PA, Penn RL, Sahai N, Sparks DL, Twining BS (2008) Nanominerals, mineral nanoparticles, and earth systems. Science 319(5870):1631–1635
Ivask A, Voelcker NH, Seabrook SA, Hor M, Kirby JK, Fenech M, Davis TP, Ke PC (2015) DNA melting and genotoxicity induced by silver nanoparticles and graphene. Chem Res Toxicol 28(5):1023–1035. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00052
Kim YR, Lee SY, Lee EJ, Park SH, Seong NW, Seo HS, Shin SS, Kim SJ, Meang EH, Park MK, Kim MS (2014) Toxicity of colloidal silica nanoparticles administered orally for 90 days in rats. Int J Nanomedicine 9(Suppl 2):67–78. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S57925
Krishnamoorthy K, Moon JY, Hyun HB, Cho SK, Kim SJ (2012) Mechanistic investigation on the toxicity of MgO nanoparticles toward cancer cells. J Mater Chem 22(47):24610–24617. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM35087D
Latimer KS (2011) Duncan and Prasse’s veterinary laboratory medicine, clinical pathology book, 5th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, New York
Mangalampalli B, Dumala N, Grover P (2017) Acute oral toxicity study of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and microparticles in female albino Wistar rats. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 1(90):170–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.09.005
Martinez-Boubeta C, Balcells L, Cristòfol R, Sanfeliu C, Rodríguez E, Weissleder R, Lope-Piedrafita S, Simeonidis K, Angelakeris M, Sandiumenge F, Calleja A (2010) Self-assembled multifunctional Fe/MgO nanospheres for magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 6(2):362–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.09.003
Mazaheri N, Naghsh N, Karimi A, Salavati H (2019) In vivo toxicity investigation of magnesium oxide nanoparticles in rat for environmental and biomedical applications. Iran J Biotechnol 17(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.21859/IJB.1543
Morishita Y, Yoshioka Y, Satoh H, Nojiri N, Nagano K, Abe Y, Kamada H, Tsunoda SI, Nabeshi H, Yoshikawa T, Tsutsumi Y (2012) Distribution and histologic effects of intravenously administered amorphous nanosilica particles in the testes of mice. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 420(2):297–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.153
Nishimori H, Kondoh M, Isoda K, Tsunoda SI, Tsutsumi Y, Yagi K (2009) Histological analysis of 70-nm silica particles-induced chronic toxicity in mice. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 72(3):626–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2009.03.007
Park SB, Jung WH, Kim KY, Koh B (2020) Toxicity assessment of SiO2 and TiO2 in normal colon cells, in vivo and in human colon organoids. Molecules 25(16):3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25163594
Purwajanti S, Zhou L, Ahmad Nor Y, Zhang J, Zhang H, Huang X, Yu C (2015) Synthesis of magnesium oxide hierarchical microspheres: a dual-functional material for water remediation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(38):21278–21286. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b05553
Sahoo SK, Parveen S, Panda JJ (2007) The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomed: Nanotechnol Biol Med 3(1):20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2006.11.008
SCENIHR (Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly-Identified Health Risks) (2007) Opinion on the scientific aspects of the existing and proposed definitions relating to products of nanoscience and nanotechnologies. 29 November 2007, the existing and proposed definitions relating to products of nanotechnologies
Sharma V, Singh P, Pandey AK, Dhawan A (2012) Induction of oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis in mouse liver after sub-acute oral exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mutat Res/genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 745(1–2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.12.009
Sulaiman FA, Adeyemi OS, Akanji MA, Oloyede HOB, Sulaiman AA, Olatunde A, Hoseni AA, Olowolafe YV, Nlebedim RN, Muritala H, Nafiu MO, Salawu MO (2015) Biochemical and morphological alterations caused by silver nanoparticles in Wistar rats. J Acute Med 5(4):96–102
Van Der Zande M, Vandebriel RJ, Groot MJ, Kramer E, Herrera Rivera ZE, Rasmussen K, Ossenkoppele JS, Tromp P, Gremmer ER, Peters RJ, Hendriksen PJ (2014) Sub-chronic toxicity study in rats orally exposed to nanostructured silica. Part Fibre Toxicol 11(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-11-8
Wang B, Feng WY, Wang TC, Jia G, Wang M, Shi JW, Zhang F, Zhao YL, Chai ZF (2006) Acute toxicity of nano-and micro-scale zinc powder in healthy adult mice. Toxicol Lett 161(2):115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.08.007
Yu T, Greish K, McGill LD, Ray A, Ghandehari H (2012) Influence of geometry, porosity, and surface characteristics of silica nanoparticles on acute toxicity: their vasculature effect and tolerance threshold. ACS Nano 6(3):2289–2301. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2043803
Yu Y, Li Y, Wang W, ** M, Du Z, Li Y, Duan J, Yu Y, Sun Z (2013) Acute toxicity of amorphous silica nanoparticles in intravenously exposed ICR mice. PLoS ONE 8(4):e61346. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061346
Zhang H, Ji Z, **a T, Meng H, Low-Kam C, Liu R, Pokhrel S, Lin S, Wang X, Liao YP, Wang M (2012) Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 6(5):4349–4368. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3010087
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ms. M. Aghazi, Mr. Y Khosravi, Dr. S Zeinali, Dr. F. Zarei, and Mr. H. A. Shamsaei for their technical assistance.
Funding
Shahrekord University and Shiraz University financially supported this research, Ministry of Science, Research, and Technology, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Hamid Reza Gheisari: Deceased
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani, S., Moshtaghi, H., Shekarforoush, S.S. et al. Histopathologic, Biochemical, and Biodistribution Studies of Orally Administrated Silica and Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles in Rats. Iran J Sci 47, 695–705 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-023-01451-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-023-01451-5