Abstract
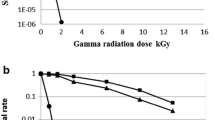
Different groups of bacteria live in radioactive environments and microbial diversity of these regions depend on their geographical conditions. Overall, little is known about the bacterial diversity of naturally radioactive regions in Iran and the aim of this study was to investigate the biodiversity of radiation-resistant bacteria in a radioactive site in Ramsar, Iran. The soil samples were collected from the radioactive site and the samples were exposed to various doses of gamma radiation using a 60Co source. After exposure, the samples were spread on TGY agar, and the surviving bacteria were purified and preserved for further studies. The 16S rRNA gene sequencing and the UV–Gamma radiation-resistant level of each strain were determined. After radiation and the cultivation of the soil samples, two Gamma and UV radiation-resistant, Gram-positive, yellow-pigmented, cocci, strictly aerobic, and catalase-positive bacterial strains were isolated. Phylogenetic analysis, based of 16S rRNA gene sequences, showed that the strains belonged to the Kocuria sp. and the Dermacoccus sp. In addition, both strains were resistant to > 15 kGy of gamma radiation and > 300 J m2 UV radiation. An analysis of these strains constitutes the first report on radioresistant bacteria belonging to the K. rhizophila and D. nishinomiyaensis isolates recovered from the radioactive region in Iran. In addition, due to the radiation-resistant characteristic of our strains and their antioxidant activity properties, we supposed that these isolates could be ideal candidates for industrial and bioremediation applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appukuttan D, Rao AS, Apte SK (2006) Engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans R1 for bioprecipitation of uranium from dilute nuclear waste. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7873–7878
Asker D, Beppu T, Ueda K (2007) Unique diversity of carotenoid-producing bacteria isolated from Misasa, a radioactive site in Japan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77(2):383–392
Besaratinia A, Synold TW, Chen HH, Chang C, ** B, Riggs AD, Pfeifer GP (2005) DNA lesions induced by UV A1 and B radiation in human cells: comparative analyses in the overall genome and in the p53 tumor suppressor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(29):10058–10063
Christensen EA, Kristensen H (1981) Radiation resistance of microorganisms from air in clean premises. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Sect B 89(5):293–301
Confalonieri F, Sommer S (2011) Bacterial and archaeal resistance to ionizing radiation. J Phys 261:012005
De Groot A, Chapon V, Servant P, Christen R, Saux MFL, Sommer S (2005) Deinococcus deserti sp. nov., a gamma-radiation–tolerant bacterium isolated from the Sahara Desert. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2441–2446
Grant IR, Patterson MF (1989) A novel radiation-resistant Deinobacter sp. isolated from irradiated pork. Lett Appl Microbiol 8:21–24
Ito H, Watanabe H, Takehisa M, Iizuka H (1983) Isolation and identification of radiation-resistant cocci belonging to the genus Deinococcus from sewage sludge’s and animal feeds. Agric Biol Chem 47:1239–1247
Kocur M, Schleifer KH, Kloos WE (1975) Taxonomic status of Micrococcus nishinomiyaensis Oda 1935. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 25:290–293
Kolari M, Nuutinen J, Rainey FA, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2003) Colored moderately thermophilic bacteria in paper-machine biofilms. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:225–238
La Duc MT, Dekas A, Osman S, Moissl C (2007) Isolation and characterization of bacteria capable of tolerating the extreme conditions of clean room environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2600–2611
Lewis NF (1973) Radio resistant Micrococcus radiophilus sp. nov. isolated from irradiated Bombay duck (Harpadon nehereus). J Gen Microbiol 66:29–35
Nicholson WL, Munakata N, Horneck G, Melosh HJ, Setlow P (2000) Resistance of Bacillus endospores to extreme terrestrial and extraterrestrial environments. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:548–572
Pathom-aree W, Nogi Y, Sutcliffe IC, Ward AC, Horikoshi K, Bull AT, Goodfellow M (2006) Dermacoccus abyssi sp. nov., a novel piezotolerant actinomycete isolated from the Mariana Trench. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1233–1237
Rainey FA, Ray K, Ferreira M, Gatz BZ (2005) Extensive diversity of ionizing radiation resistant bacteria recovered from Sonoran desert soil and description of nine new species of the genus Deinococcus obtained from a single soil sample. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5225–5235
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shahmohammadi HR, Asgarani E, Terato H, Saito T (1998) Protective roles of bacterioruberin and intracellular KCl in the resistance of Halobacterium salinarium against DNA damaging agents. J Radiat Res 39:251–262
Shukla M, Chaturvedi R, Tamhane D, Vyas P (2007) Multiple stress tolerance of ionizing radiation-resistant bacteria isolated obtained from various habitats: correlation between stresses. Curr Microbiol 54:142–148
Slade D, Radman M (2011) Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75:133–191
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood RA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 607–654
Stackebrandt E, Koch C, Gvozdiak O, Schumann P (1995) Taxonomic dissection of the genus Micrococcus: Kocuria gen. nov., Nesterenkonia gen. nov., Kytococcus gen. nov., Dermacoccus gen. nov., and Micrococcus Cohn 1872 gen emend. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:682–692
Tian B, Xu Z, Sun Z, Lin J (2007) Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of carotenoids from Deinococcus radiodurans through targeted mutagenesis, chemiluminescence, and DNA damage analyses. Biochim Biophys Acta 40:902–911
Tian B, Shen S, Wang J, Jiao J, Wan L, Hu Y, Hua Y (2009) Effects of carotenoids from Deinococcus radiodurans on protein oxidation. Lett Appl Microbiol 49:689–694
Vaisanen OM, Weber A, Bennasar A, Rainey FA, Busse HJ (1998) Microbial communities of printing paper machines. J App Microbiol 84:1069–1084
Acknowledgements
The authors are gratefully to Mr. Naseri for assistance in providing the soil samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arjomandi, Z., Salehzadeh, A. & Mirzaie, A. Isolation and Characterization of Two Novel Radiation-Resistant Bacteria from a Radioactive Site in Iran. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 42, 1007–1013 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0389-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0389-4