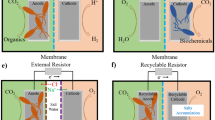
Abstract
An annual reduction in processing expenses results in the direct discharge of millions of litters of diverse wastewater into the environment, which causes eutrophication and depletes pure water sources. Traditional physicochemical treatment are widely employed for wastewater treatment (WWT). However, the optimal functioning of these systems necessitates significant operating and maintenance expenditures and the use of unique technologies for sludge treatment and disposal. One of the most crucial processes in a biorefinery is the effective pretreatment of industrial wastewater, which ensures the bioprocess overall quality and commercial feasibility. Industrial WWT is essential for improving biorefinery and valorization processes for producing biofuels, bioenergy, chemicals, and other valuable products. Consequently, industrial effluent must be managed to facilitate further bioprocessing. Bioelectrochemical systems (BESs) are an emerging field utilized for the removal of organic matter from industrial wastewater, desalination of seawater, and production of bioelectricity. In the distant future, the utilization of BESs will be focused on environmental remediation, WWT, bioanalysis, and the reduction of toxic gas emissions. In recent years, there has been a surge in research endeavors pertaining to BESs, specifically microbial fuel cells (MFCs), microbial electrolysis cells (MECs), microbial desalination cells (MDCs), and microbial electrolysis desalination cells (MEDCs), in an effort to produce energy that is both environmentally friendly and sustainable. This review focuses on the applicability of various advanced treatment approaches for industrial wastewater or sludge and the separation of recovered products from wastewater and its residues. It also highlights the basic operational characteristics of the MFCs, MECs, MDCs, and MEDCs using wastewater. The cutting-edge data presented in this review could improve further interdisciplinary and translational research.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- BES:
-
Bioelectrochemical system
- BOD:
-
Biological oxygen demand
- CH3COOH:
-
Acetic acid
- CH4 :
-
Methane
- CMs:
-
Ceramic membranes
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- MDC:
-
Microbial desalination cell
- MEC:
-
Microbial electrolysis cell
- MEDC:
-
Microbial electrolysis desalination cell
- MFC:
-
Microbial fuel cell
- OH⋅:
-
Hydroxyl radical
- TiO2 :
-
Titanium oxide
- TOC:
-
Total organic carbon
- WWB:
-
Wastewater biorefinery
- WWT:
-
Wastewater treatment
- ZnO:
-
Zinc oxide
References
Abd Elnabi MK, Elkaliny NE, Elyazied MM, Azab SH, Elkhalifa SA, Elmasry S, Mouhamed MS, Shalamesh EM, Alhorieny NA, Abd Elaty AE, Elgendy IM, Etman AE, Saad KE, Tsigkou K, Ali SS, Kornaros M, Mahmoud Y (2023) Toxicity of heavy metals and recent advances in their removal: a review. Toxics 11(7):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070580
Abdelfattah A, Ali SS, Ramadan H, El-Aswar EI, Eltawab R, Ho SH, Elsamahy T, Li S, El-Sheekh MM, Schagerl M, Kornaros M (2023) Microalgae-based wastewater treatment: mechanisms, challenges, recent advances, and future prospects. Environ Sci Ecotechnol 13:100205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2022.100205
Abuhasheesh YH, Hegab HM, Wadi VS, Al Marzooqi F, Banat F, Aljundi IH, Hasan SW (2023) Phase inverted hydrophobic polyethersulfone/iron oxide-oleylamine ultrafiltration membranes for efficient water-in-oil emulsion separation. Chemosphere 337:139431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139431
Abu-Reesh IM, Kunju A, Sevda S (2022) Performance of microbial fuel cells in treating petroleum refinery wastewater. J Water Proc Eng 49:103029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103029
Ali A, Ahmed A, Gad A (2016) Chemical and microstructural analyses for heavy metals removal from water media by ceramic membrane filtration. Water Sci Technol 75:439–450. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.537
Ali SS, Al-Tohamy R, Koutra E, El-Naggar AH, Kornaros M, Sun J (2021a) Valorizing lignin-like dyes and textile dyeing wastewater by a newly constructed lipid-producing and lignin modifying oleaginous yeast consortium valued for biodiesel and bioremediation. J Hazard Mater 403:123575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123575
Ali SS, Al-Tohamy R, Koutra E, Moawad MS, Kornaros M, Mustafa AM, Mahmoud Y, Badr A, Osman MEH, Elsamahy T, Jiao H, Sun J (2021b) Nanobiotechnological advancements in agriculture and food industry: applications, nanotoxicity, and future perspectives. Sci Total Environ 792:148359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148359
Ali SS, Elsamahy T, Al-Tohamy R, Zhu D, Mahmoud Y, Koutra E, Metwally MA, Kornaros M, Sun J (2021c) Plastic wastes biodegradation: mechanisms, challenges and future prospects. Sci Total Environ 780:146590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146590
Ali SS, Jiao H, Mustafa AM, Koutra E, El-Sapagh S, Kornaros M, Elsamahy T, Khalil M, Bulgariu L, Sun J (2021d) Construction of a novel microbial consortium valued for the effective degradation and detoxification of creosote-treated sawdust along with enhanced methane production. J Hazard Mater 418:126091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126091
Ali SS, El-Sheekh M, Manni A, Ruiz HA, Elsamahy T, Sun J, Schagerl, (2022) Microalgae-mediated wastewater treatment for biofuels production: a comprehensive review. Microbiol Res 265:127187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2022.127187
Ali SS, Abdelkarim EA, Elsamahy T, Al-Tohamy R, Li F, Kornaros M, Zuorro A, Zhu D, Sun J (2023a) Bioplastic production in terms of life cycle assessment: a state-of-the-art review. Environ Sci Technol 15:100254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2023.100254
Ali SS, Al-Tohamy R, Zuorro A, Elsamahy T, Metwally SM, Abdelfattah A, Eltawab R, Sun S, Sun J (2023a) Biodegradation of azo dyes by yeasts. In: Advances in yeast biotechnology for biofuels and sustainability. Elsevier, pp 371–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-95449-5.00012-6
Ali SS, Elsamahy T, Abdelkarim EA, Abdelfattah A, Ramadan H, Mostafa S, Metwally SM, Sun J (2023b) Engineered yeast for the production of bioplastics. In: Advances in yeast biotechnology for biofuels and sustainability. Elsevier, pp 277–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-95449-5.00017-5
Almatouq A, Babatunde AO, Khajah M, Webster G, Alfodari M (2020) Microbial community structure of anode electrodes in microbial fuel cells and microbial electrolysis cells. J Water Proc Eng 34:101140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101140
Alnajjar M, Hethnawi A, Nafie G, Hassan A, Vitale G, Nassar NN (2019) Silica-alumina composite as an effective adsorbent for the removal of metformin from water. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102994
Al-Tohamy R, Ali SS, Li F, Okasha KM, Mahmoud Y, Elsamahy T, Jiao H, Fu Y, Sun J (2022) A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113160
Anil I, Gunday ST, Bozkurt A, Alagha O (2020) Design of crosslinked hydrogels comprising poly(vinylphosphonic acid) and bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate as an efficient adsorbent for wastewater dye removal. Nanomater (basel, Switzerland) 10:131. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010131
Anwer AH, Khan N, Khan MD, Shakeel S, Khan MZ (2021) Redox mediators as cathode catalyst to boost the microbial electro-synthesis of biofuel product from carbon dioxide. Fuel 302:121124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121124
Apollo S, Onyango MS, Ochieng A (2014) Integrated UV photodegradation and anaerobic digestion of textile dye for efficient biogas production using zeolite. Chem Eng J 245:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.027
Asif MB, Zhang Z (2021) Ceramic membrane technology for water and wastewater treatment: a critical review of performance, full-scale applications, membrane fouling and prospects. Chem Eng J 418:129481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129481
Barrera-Díaz CE, Balderas-Hernández P, Bilyeu B (2018) Electrocoagulation: fundamentals and prospectives. In: Electrochemical water and wastewater treatment. Butterworth-Heinemann, pp 61–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-813160-2.00003-1
Bilal M, Ihsanullah I, Younas M, Shah MUH (2021) Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: a critical review. Sep Purif Technol 278:119510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119510
Bolognesi S, Cecconet D, Callegari A, Capodaglio AG (2021) Combined microalgal photobioreactor/microbial fuel cell system: performance analysis under different process conditions. Environ Res 192:110263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110263
Bustillo-Lecompte CF, Mehrvar M (2015) Slaughterhouse wastewater characteristics, treatment, and management in the meat processing industry: a review on trends and advances. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.07.008
Capodaglio AG (2023) Biorefinery of sewage sludge: overview of possible value-added products and applicable process technologies. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061195
Cardeña R, Moreno G, Bakonyi P, Buitrón G (2017) Enhancement of methane production from various microalgae cultures via novel ozonation pretreatment. Chem Eng J 307:948–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.016
Cecconet D, Bolognesi S, Molognoni D, Callegari A, Capodaglio AG (2018) Influence of reactor’s hydrodynamics on the performance of microbial fuel cells. J Water Proc Eng 26:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2018.10.019
Chai WS, Cheun JY, Kumar PS, Mubashir M, Majeed Z, Banat F, Ho SH, Show PL (2021) A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J Clean Prod 296:126589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126589
Chandra R, Castillo-Zacarias C, Delgado P, Parra-Saldívar R (2018) A biorefinery approach for dairy wastewater treatment and product recovery towards establishing a biorefinery complexity index. J Clean Prod 183:1184–1196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.124
Chatterjee D, Dasgupta S (2005) Visible light induced photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. J Photochem Photobiol C Photochem Rev 6(2–3):186–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2005.09.001
Chatterjee A, Shamim S, Jana AK, Basu JK (2020) Insights into the competitive adsorption of pollutants on a mesoporous alumina-silica nano-sorbent synthesized from coal fly ash and a waste aluminium foil. RSC Adv 10:15514–15522. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra01397h
Cheng S, **ng D, Call DF, Logan BE (2009) Direct biological conversion of electrical current into methane by electromethanogenesis. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3953–3958. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803531g
Conidi C, Cassano A (2022) Membrane-based biorefinery in agro-food wastewater processing. In: Membrane engineering in the circular economy. Elsevier, pp 229–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85253-1.00017-4
Conteratto C, Artuzo FD, Santos OIB, Talamini E (2021) Biorefinery: a comprehensive concept for the sociotechnical transition toward bioeconomy. Renew Sust Energ Rev 151:111527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111527
Dadari S, Rahimi M, Zinadini S (2022) Novel antibacterial and antifouling PES nanofiltration membrane incorporated with green synthesized nickel-bentonite nanoparticles for heavy metal ions removal. Chem Eng J 431:134116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134116
Danso B, Ali SS, **e R, Sun J (2022) Valorisation of wheat straw and bioethanol production by a novel xylanase-and cellulase-producing Streptomyces strain isolated from the wood-feeding termite. Microcerotermes Species Fuel 310:122333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122333
Danwittayakul S, Jaisai M, Dutta J (2015) Efficient solar photocatalytic degradation of textile wastewater using ZnO/ZTO composites. Appl Catal B Environ 163:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.07.042
Darwesh OM, Ali SS, Matter IA, Elsamahy T (2021) Nanotextiles waste management: controlling of release and remediation of wastes. In: Nanosensors and nanodevices for smart multifunctional textiles. Elsevier, pp 267–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820777-2.00016-9
Dong Y, Wu H, Yang F, Gray S (2022) Cost and efficiency perspectives of ceramic membranes for water treatment. Water Res 220:118629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118629
Donkadokula NY, Kola AK, Naz I, Saroj D (2020) A review on advanced physico-chemical and biological textile dye wastewater treatment techniques. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 19:543–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09543-z
Ebhodaghe SO, Imanah OE, Ndibe H (2022) Biofuels from microalgae biomass: a review of conversion processes and procedures. Arab J Chem 15(2):103591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103591
Elmaadawy K, Liu B, Hassan GK, Wang X, Wang Q, Hu J, Hou H, Yang J, Wu X (2022) Microalgae-assisted fixed-film activated sludge MFC for landfill leachate treatment and energy recovery. Process Saf Environ Prot 160:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2022.02.021
Ely C, Hoefling Souza D, Fernandes M, Trevisan V, Skoronski E (2020) Enhanced removal of phenol from biorefinery wastewater treatment using enzymatic and Fenton process. Environ Technol 42(17):2733–2739. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1713220
Escapa A, Mateos R, Martínez EJ, Blanes J (2016) Microbial electrolysis cells: an emerging technology for wastewater treatment and energy recovery. From laboratory to pilot plant and beyond. Renew Sust Energ Rev 55:942–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.11.029
Fu Q, Kuramochi Y, Fukushima N, Maeda H, Sato K, Kobayashi H (2015) Bioelectrochemical analyses of the development of a thermophilic biocathode catalyzing electromethanogenesis. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):1225–1232. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5052233
Gadhe A, Sonawane SS, Varma MN (2015) Enhanced biohydrogen production from dark fermentation of complex dairy wastewater by sonolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 40(32):9942–9951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.06.098
Ganigue R, Puig S, Batlle-Vilanova P, Balaguer MD, Colprim J (2015) Microbial electrosynthesis of butyrate from carbon dioxide. Chem Commun 51(15):3235–3238. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC10121A
Garrido-Cardenas JA, Esteban-García B, Agüera A, Sánchez-Pérez JA, Manzano-Agugliaro F (2020) Wastewater treatment by advanced oxidation process and their worldwide research trends. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(1):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010170
Gharbi R, Vidales AG, Omanovic S, Tartakovsky B (2022) Mathematical model of a microbial electrosynthesis cell for the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane and acetate. J CO2 Util 59:101956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2022.101956
Giannakis S, Lin KYA, Ghanbari F (2021) A review of the recent advances on the treatment of industrial wastewaters by sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes (SR-AOPs). J Chem Eng 406:127083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127083
Giwa A, Yusuf A, Balogun HA, Sambudi NS, Bilad MR, Adeyemi I, Chakraborty S, Curcio S (2021) Recent advances in advanced oxidation processes for removal of contaminants from water: a comprehensive review. Process Saf Environ Prot 146:220–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.08.015
Gomes A, Borges A, Peres JA, Lucas MS (2023) Bioenergy production from agro-industrial wastewater using advanced oxidation processes as pre-treatment. Catalysts 13(8):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13081186
Guang L, Koomson DA, **gyu H, Ewusi-Mensah D, Miwornunyuie N (2020) Performance of exoelectrogenic bacteria used in microbial desalination cell technology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(3):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031121
Halim MA, Rahman MO, Ibrahim M, Kundu R, Biswas BK (2021) Effect of anolyte pH on the performance of a dual-chambered microbial fuel cell operated with different biomass feed. J Chem 2021:5465680. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5465680
Hamad H, Bassyouni D, El-Ashtoukhy ES, Amin N, Abd El-Latif M (2018) Electrocatalytic degradation and minimization of specific energy consumption of synthetic azo dye from wastewater by anodic oxidation process with an emphasis on enhancing economic efficiency and reaction mechanism. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.061
Hii K, Baroutian S, Parthasarathy R, Gapes DJ, Eshtiaghi N (2014) A review of wet air oxidation and thermal hydrolysis technologies in sludge treatment. Bioresour Technol 155:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.066
Hua T, Li S, Li F, Zhou Q, Ondon BS (2019) Microbial electrolysis cell as an emerging versatile technology: a review on its potential application, advance and challenge. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94(6):1697–1711. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5898
Huang G, Wang H, Zhao H, Wu P, Yan Q (2018) Application of polypyrrole modified cathode in bio-electro-Fenton coupled with microbial desalination cell (MDC) for enhanced degradation of methylene blue. J Power Sources 400:350–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.08.048
Huang SJ, Dwivedi KA, Kumar S, Wang CT, Yadav AK (2023) Binder-free NiO/MnO2 coated carbon based anodes for simultaneous norfloxacin removal, wastewater treatment and power generation in dual-chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ Pollut 317:120578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120578
Hussain SM, Hussain T, Faryad M, Ali Q, Ali S, Rizwan M, Hussain AI, Ray MB, Chatha SAS (2020) Emerging aspects of Photocatalysts (TiO2 & ZnO) doped zeolites and advanced oxidation processes for degradation of azo dyes: a review. Curr Anal Chem 17:82–97. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573411016999200711143225
Hwang JH, Ryu H, Rodriguez KL, Fahad S, Santo Domingo J, Kushima A, Lee WH (2021) A strategy for power generation from bilgewater using a photosynthetic microalgal fuel cell (MAFC). J Power Sources 484:229222
Igbokwe VC, Ezugworie FN, Onwosi CO, Aliyu GO, Obi CJ (2022) Biochemical biorefinery: a low-cost and non-waste concept for promoting sustainable circular bioeconomy. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114333
Igwegbe CA, Ighalo JO, Onukwuli OD, Obiora-Okafo IA, Anastopoulos I (2021) Coagulation-flocculation of aquaculture wastewater using green coagulant from garcinia kola seeds: parametric studies, kinetic modelling and cost analysis. Sustainability 13:9177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13169177
Islam Tarekul Repon MR, Islam Tarikul Sarwar Z, Rahman MM (2022) Impact of textile dyes on health and ecosystem: a review of structure, causes, and potential solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:9207–9242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24398-3
Iwuozor KO (2019) Prospects and challenges of using coagulation-flocculation method in the treatment of effluents. Adv J Chem A 2(2):105–127. https://doi.org/10.29088/sami/ajca.2019.2.105127
Jafary T, Al-Mamun A, Alhimali H, Baawain MS, Rahman MS, Rahman S, Dhar BR, Aghbashlo M, Tabatabaei M (2020) Enhanced power generation and desalination rate in a novel quadruple microbial desalination cell with a single desalination chamber. Renew Sust Energ Rev 127:109855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.109855
Jain R, Panwar NL, Jain SK, Gupta T, Agarwal C, Meena SS (2022) Bio-hydrogen production through dark fermentation: an overview. Biomass Convers Biorefin 2022:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03282-7
Jaseela PK, Garvasis J, Joseph A (2019) Selective adsorption of methylene blue (MB) dye from aqueous mixture of MB and methyl orange (MO) using mesoporous titania (TiO2)–poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) nanocomposite. J Mol Liq 286:110908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.110908
Jeong SY, Lee JW (2016) Sequential Fenton oxidation and hydrothermal treatment to improve the effect of pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis on mixed hardwood. Bioresour Technol 200:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.015
Jiang Y, Su M, Zhang Y, Zhan G, Tao Y, Li D (2013) Bioelectrochemical systems for simultaneously production of methane and acetate from carbon dioxide at relatively high rate. Int J Hydrog Energy 38(8):3497–3502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.107
Jiang J, Mu Z, **ng H, Wu Q, Yue X, Lin Y (2019) Insights into the synergetic effect for enhanced UV/visible-light activated photodegradation activity via Cu–ZnO photocatalyst. Appl Surf Sci 478:1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.02.019
Jiao H, Sun J, Shi Y, Lu X, Ali SS, Fu Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang Q, Zhou M, Liu J (2023) Recent advances in strategies of nanocellulose surface and/or interface engineering for potential biomedical applications as well as its ongoing challenges: a review. Cellulose 30:6741–6771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05302-9
Kadier A, Simayi Y, Chandrasekhar K, Ismail M, Kalil MS (2015) Hydrogen gas production with an electroformed Ni mesh cathode catalysts in a single-chamber microbial electrolysis cell (MEC). Int J Hydrog Energy 40(41):14095–14103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.08.095
Kamali M, Suhas DP, Costa ME, Capela I, Aminabhavi TM (2019) Sustainability considerations in membrane-based technologies for industrial effluents treatment. J Chem Eng 368:474–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.075
Kamaraj M, Srinivasan NR, Assefa G, Adugna AT, Kebede M (2020) Facile development of sunlit ZnO nanoparticles-activated carbon hybrid from pernicious weed as an operative nano-adsorbent for removal of methylene blue and chromium from aqueous solution: extended application in tannery industrial wastewater. Environ Technol Innov 17:100540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.100540
Kamaroddin MF, Hanotu J, Gilmour DJ, Zimmerman WB (2016) In-situ disinfection and a new downstream processing scheme from algal harvesting to lipid extraction using ozone-rich microbubbles for biofuel production. Algal Res 17:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.05.006
Kato DM, Elía N, Flythe M, Lynn BC (2014) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass using Fenton chemistry. Bioresour Technol 162:273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.151
Keller RG, Weyand J, Vennekoetter JB, Kamp J, Wessling M (2021) An electro-Fenton process coupled with nanofiltration for enhanced conversion of cellobiose to glucose. Catal Today 364:230–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.05.059
Kitching M, Butler R, Marsili E (2017) Microbial bioelectrosynthesis of hydrogen: current challenges and scale-up. Enzyme Microb Technol 96:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.09.002
Klein EM, Knoll MT, Gescher J (2023) microbe–anode interactions: comparing the impact of genetic and material engineering approaches to improve the performance of microbial electrochemical systems (MES). Microb Biotechnol 16(6):1179–1202. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.14236
Koutra E, Mastropetros SG, Ali SS, Tsigkou K, Kornaros M (2021) Assessing the potential of Chlorella vulgaris for valorization of liquid digestates from agro-industrial and municipal organic wastes in a biorefinery approach. J Clean Prod 280:124352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124352
Kumar G, Saratale RG, Kadier A, Sivagurunathan P, Zhen G, Kim SH, Saratale GD (2017) A review on bio-electrochemical systems (BESs) for the syngas and value added biochemicals production. Chemosphere 177:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.135
Kumari A, Upadhyay V, Kumar S (2023) A critical insight into occurrence and fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their green remediation approaches. Chemosphere 329:138579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.138579
Kuwahara Y, Yamashita H (2011) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of organics diluted in water and air using TiO2 designed with zeolites and mesoporous silica materials. J Mater Chem 21(8):2407–2416. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0JM02741C
Lambert N, Van Aken P, Smets I, Appels L, Dewil R (2022) Performance assessment of ultrasonic sludge disintegration in activated sludge wastewater treatment plants under nutrient-deficient conditions. Chem Eng J 431:133979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133979
Li Q, Jia R, Shao J, He Y (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin via TiO2 nanoparticle coupling with a novel submerged porous ceramic membrane reactor. J Clean Prod 209:755–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.183
Li Z, Yang P (2018) Review on physicochemical, chemical, and biological processes for pharmaceutical wastewater. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol 113. IOP Publishing, p 012185. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/113/1/012185
Liaquat R, Mehmood T, Khoja AH, Iqbal N, Ejaz H, Mumtaz S (2021) Investigating the potential of locally sourced wastewater as a feedstock of microbial desalination cell (MDC) for bioenergy production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 44:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02433-2
Lin CF, Lin AYC, Chandana PS, Tsai CY (2009) Effects of mass retention of dissolved organic matter and membrane pore size on membrane fouling and flux decline. Water Res 43(2):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.10.042
Liu H, Grot S, Logan BE (2005) Electrochemically assisted microbial production of hydrogen from acetate. Environ Sci Technol 39(11):4317–4320. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050244p
Liu D, Zheng T, Buisman C, Ter Heijne A (2017) Heat-treated stainless steel felt as a new cathode material in a methane-producing bioelectrochemical system. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(12):11346–11353. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02367
Liu Q, Zhou Y, Lu J, Zhou Y (2020a) Novel cyclodextrin-based adsorbents for removing pollutants from wastewater: a critical review. Chemosphere 241:125043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125043
Liu SH, Lai CY, Chang PH, Lin CW, Chen YH (2020b) Enhancing copper recovery and electricity generation from wastewater using low-cost membrane-less microbial fuel cell with a carbonized clay cup as cathode. J Clean Prod 247:119118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119118
Louhichi B, Gaied F, Mansouri K, Jeday MR (2022) Treatment of textile industry effluents by electro-coagulation and electro-Fenton processes using solar energy: a comparative study. Chem Engin J 427:131735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131735
Lovley DR, Holmes DE (2022) Electromicrobiology: the ecophysiology of phylogenetically diverse electroactive microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 20(1):5–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00597-6
Lu L, Ren ZJ (2016) Microbial electrolysis cells for waste biorefinery: a state of the art review. Bioresour Technol 215:254–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.034
Maćczak P, Kaczmarek H, Ziegler-Borowska M (2020) Recent achievements in polymer bio-based flocculants for water treatment. Materials 13(18):3951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13183951
Madadi M, Shah SWA, Sun C, Wang W, Ali SS, Khan A, Arif M, Zhu D (2022) Efficient co-production of xylooligosaccharides and glucose from lignocelluloses by acid/pentanol pretreatment: synergetic role of lignin removal and inhibitors. Bioresour Technol 365:128171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.128171
Madadi M, Liu D, Qin Y, Zhang Y, Karimi K, Tabatabaei M, Gupta VK, Aghbashlo M, Ali SS (2023) Integrated pretreatment of poplar biomass employing p-toluenesulfonic acid catalyzed liquid hot water and short-time ball milling for complete conversion to xylooligosaccharides, glucose, and native-like lignin. Bioresour Technol 384:129370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129370
Manchisi J, Matinde E, Rowson NA, Simmons MJH, Simate GS, Ndlovu S, Mwewa B (2020) Ironmaking and steelmaking slags as sustainable adsorbents for industrial effluents and wastewater treatment: a critical review of properties, performance. Chall Oppor Sustain 12:2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12052118
Manthos G, Zagklis D, Ali SS, Zafiri C, Kornaros M (2023) Techno-economic evaluation of the thermochemical energy valorization of construction waste and algae biomass: a case study for a biomass treatment plant in northern Greece. Processes 11(5):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11051549
M’Arimi MM, Mecha CA, Kiprop AK, Ramkat R (2020) Recent trends in applications of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in bioenergy production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 121:109669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109669
Mastropetros SG, Pispas K, Zagklis D, Ali SS, Kornaros M (2022) Biopolymers production from microalgae and cyanobacteria cultivated in wastewater: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 60:107999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107999
Meena RAA, Kannah RY, Sindhu J, Ragavi J, Kumar G, Gunasekaran M, Banu JR (2019) Trends and resource recovery in biological wastewater treatment system. Bioresour Technol Rep 7:100235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100235
Mohanakrishna G, Vanbroekhoven K, Pant D (2018) Impact of dissolved carbon dioxide concentration on the process parameters during its conversion to acetate through microbial electrosynthesis. React Chem Eng 3(3):371–378. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RE00220C
Montañés MT, García-Gabaldón M, Roca-Pérez L, Giner-Sanz JJ, Mora-Gómez J, Pérez-Herranz V (2020) Analysis of norfloxacin ecotoxicity and the relation with its degradation by means of electrochemical oxidation using different anodes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 188:109923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109923
Naaz T, Kumar A, Vempaty A, Singhal N, Pandit S, Gautam P, Jung SP (2023) Recent advances in biological approaches towards anode biofilm engineering for improvement of extracellular electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Environ Eng Res 28(5):220666. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2022.666
Nancharaiah YV, Mohan SV, Lens PNL (2015) Metals removal and recovery in bioelectrochemical systems: a review. Bioresour Technol 195:102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.06.058
Narayan AS, Marks SJ, Meierhofer R, Strande L, Tilley E, Zurbrügg C, Lüthi C (2021) Advancements in and integration of water, sanitation, and solid waste for low-and middle-income countries. Annu Rev Environ Resour 46:193–219. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-030620-042304
Nelabhotla ABT, Dinamarca C (2019) Bioelectrochemical CO2 reduction to methane: MES integration in biogas production processes. Appl Sci 9(6):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061056
Nidheesh PV, Couras C, Karim AV, Nadais H (2022) A review of integrated advanced oxidation processes and biological processes for organic pollutant removal. Chem Eng Commun 209(3):390–432. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2020.1864626
Ninomiya K, Takamatsu H, Onishi A, Takahashi K, Shimizu N (2013) Sonocatalytic-Fenton reaction for enhanced OH radical generation and its application to lignin degradation. Ultrason Sonochem 20:1092–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2013.01.007
Nkele K, Mpenyana-Monyatsi L, Masindi V (2022) Challenges, advances and sustainabilities on the removal and recovery of manganese from wastewater: a review. J Clean Prod 377:134152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134152
Noori MT, Vu MT, Ali RB, Min B (2020) Recent advances in cathode materials and configurations for upgrading methane in bioelectrochemical systems integrated with anaerobic digestion. Chem Eng J 392:123689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123689
Okeke ES, Ejeromedoghene O, Okoye CO, Ezeorba TPC, Nyaruaba R, Ikechukwu CK, Oladipo A, Orege JI (2022) Microalgae biorefinery: an integrated route for the sustainable production of high-value-added products. Energy Convers Manag 16:100323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecmx.2022.100323
Olabi AG, Wilberforce T, Sayed ET, Elsaid K, Rezk H, Abdelkareem MA (2020) Recent progress of graphene based nanomaterials in bioelectrochemical systems. Sci Total Environ 749:141225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141225
Oller I, Malato S, Sánchez-Pérez J (2011) Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—a review. Sci Total Environ 409(20):4141–4166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.08.061
Paliya S, Mandpe A, Bhisikar D, Kumar MS, Kumar S (2022) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Indian wastewater treatment plant: occurrence, mass flow and removal. Chemosphere 303:135055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135055
Pandis PK, Kalogirou C, Kanellou E, Vaitsis C, Savvidou MG, Sourkouni G, Zorpas AA, Argirusis C (2022) Key points of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for wastewater, organic pollutants and pharmaceutical waste treatment: a mini review. Chem Eng 6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering6010008
Patel A, Arkatkar A, Singh S, Rabbani A, Medina JDS, Ong ES, Habashy MM, Jadhav DA, Rene ER, Mungray AA, Mungray AK (2021) Physico-chemical and biological treatment strategies for converting municipal wastewater and its residue to resources. Chemosphere 282:130881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130881
Pawar AA, Karthic A, Lee S, Pandit S, Jung SP (2022) Microbial electrolysis cells for electromethanogenesis: materials, configurations and operations. Environ Eng Res 27(1):200484. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.484
Phalakornkule C, Sukkasem P, Mutchimsattha C (2010) Hydrogen recovery from the electrocoagulation treatment of dye-containing wastewater. Int J Hydrog Energy 35:10934–10943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.06.100
Pratiwi WZ, Hadiyanto H, Purwanto P (2020) Bioelectricity production from tofu wastewater using microbial fuel cells with microalgae Spirulina sp as catholyte. In E3S Web Conf (Vol. 202: p. 08007) EDP Sciences.
Pu KB, Li TT, Gao JY, Chen QY, Guo K, Zhou M, Wang CT, Wang YH (2022) Floating flexible microbial fuel cells for electricity generation and municipal wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 300:121915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121915
Rahimnejad M (2023) CO2 reduction and MES. In: Biological fuel cells. Elsevier, pp 351–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85711-6.00017-5
Raj S, Singh H, Bhattacharya J (2023) Treatment of textile industry wastewater based on coagulation-flocculation aided sedimentation followed by adsorption: process studies in an industrial ecology concept. Sci Total Environ 857:159464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159464
Rani CN, Karthikeyan S, Prince Arockia Doss S (2021) Photocatalytic ultrafiltration membrane reactors in water and wastewater treatment—a review. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 165:108445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2021.108445
Rashid R, Shafiq I, Akhter P, Iqbal MJ, Hussain M (2021) A state-of-the-art review on wastewater treatment techniques: the effectiveness of adsorption method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:9050–9066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12395-x
Renslow RS, Babauta JT, Majors PD, Beyenal H (2013) Diffusion in biofilms respiring on electrodes. Energy Environ Sci 6(2):595–607. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EE23394K
Ribeiro VR, Osório HDD, Ulrich AC, Rizzetti TM, Barrios AS, de Souza Schneider RDC, Benitez LB (2022) The use of microalgae-microbial fuel cells in wastewater bioremediation and bioelectricity generation. J Water Proc Eng 48:102882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102882
Rozendal RA, Jeremiasse AW, Hamelers HV, Buisman CJ (2008) Hydrogen production with a microbial biocathode. Environ Sci Technol 42(2):629–634. https://doi.org/10.1021/es071720+
Salehmin MNI, Lim SS, Satar I, Daud WRW (2021) Pushing microbial desalination cells towards field application: Prevailing challenges, potential mitigation strategies, and future prospects. Sci Total Environ 759:143485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143485
Samadi M, Zirak M, Naseri A, Khorashadizade E, Moshfegh AZ (2016) Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Films 605:2–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.12.064
Samanta SK, Mandal B, Tripathy T (2022) Sodium alginate-cl-poly (N,N-dimethyl acryl amide-co-2-acrylamino-2-methyl-1-propane sulphonic acid)/titanium dioxide nanocomposite hydrogel: an efficient dye-removing agent. J Appl Polym Sci 139:52465. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.52465
Samsami S, Mohamadizaniani M, Sarrafzadeh MH, Rene ER, Firoozbahr M (2020) Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: overview and perspectives. Process Saf Environ Prot 143:138–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2020.05.034
Saratale GD, Banu JR, Nastro RA, Kadier A, Ashokkumar V, Lay CH, Jung JH, Shin HS, Saratale RG, Chandrasekhar K (2022) Bioelectrochemical systems in aid of sustainable biorefineries for the production of value-added products and resource recovery from wastewater: a critical review and future perspectives. Bioresour Technol 359:127435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127435
Savla N, Pandit S, Verma JP, Awasthi AK, Sana SS, Prasad R (2021) Techno-economical evaluation and life cycle assessment of microbial electrochemical systems: a review. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 4:100111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100111
Sayed ET, Nakagawa N (2018) Critical issues in the performance of yeast based microbial fuel cell. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 93(6):1588–1594. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5527
Sharma P, Nanda K, Yadav M, Shukla A, Srivastava SK, Kumar S, Singh SP (2022) Remediation of noxious wastewater using nanohybrid adsorbent for preventing water pollution. Chemosphere 292:133380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133380
Sharma A, Dahiya P (2022) Advanced oxidation processes and bioremediation techniques for treatment of recalcitrant compounds present in wastewater. In: Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. CRC Press, pp 117–129. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003165958-11
Shindhal T, Rakholiya P, Varjani S, Pandey A, Ngo HH, Guo W, Ng HY, Taherzadeh MJ (2021) A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 12(1):70–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2020.1863034
Siddique A, Yaqoob AA, Mirza MA, Kanwal A, Ibrahim MNM, Ahmad A (2023) Potential use of ultrafiltration (UF) membrane for remediation of metal contaminants. In: Emerging techniques for treatment of toxic metals from wastewater. Elsevier, pp 341–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-822880-7.00018-2
Sigonya S, Mokhothu TH, Mokhena TC, Makhanya TR (2023) Mitigation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antiretroviral drugs as environmental pollutants by adsorption using nanomaterials as viable solution—a critical review. Appl Sci 13:772. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020772
Sikiru S, Abiodun OJA, Sanusi YK, Sikiru YA, Soleimani H, Yekeen N, Haslija ABA (2022) A comprehensive review on nanotechnology application in wastewater treatment a case study of metal-based using green synthesis. J Environ Chem Eng 10:108065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108065
Singh P, Manikandan NA, Purnima M, Pakshirajan K, Pugazhenthi G (2020) Recovery of lignin from water and methanol using low-cost kaolin based tubular ceramic membrane. J Water Process Eng 38:101615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101615
Singh NK, Mathuriya AS, Mehrotra S, Pandit S, Singh A, Jadhav D (2023) Advances in bioelectrochemical systems for bio-products recovery. Environ Technol 2023:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2023.2234676
Soltani S, Khanian N, Choong TSY, Rashid U (2020) Recent progress in the design and synthesis of nanofibers with diverse synthetic methodologies: characterization and potential applications. New J Chem 44(23):9581–9606. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ01071E
Soltani F, Navidjouy N, Khorsandi H, Rahimnejad M, Alizadeh S (2021) A novel bio-electro-Fenton system with dual application for the catalytic degradation of tetracycline antibiotic in wastewater and bioelectricity generation. RSC Adv 11:27160–27173. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra04584a
Sonal S, Mishra BK (2021) Role of coagulation/flocculation technology for the treatment of dye wastewater: trend and future aspects. Water Pollut Manag Pract. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8358-2_13
Song L, Zhu B, Jegatheesan V, Gray S, Duke M, Muthukumaran S (2017) Treatment of secondary effluent by sequential combination of photocatalytic oxidation with ceramic membrane filtration. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:5191–5202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9070-x
Song HL, Zhu Y, Li J (2019) Electron transfer mechanisms, characteristics and applications of biological cathode microbial fuel cells—a mini review. Arab J Chem 12(8):2236–2243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.01.008
Srivastav M, Gupta M, Agrahari SK, Detwal P (2019) Removal of refractory organic compounds from wastewater by various advanced oxidation process—a review. Curr Environ Eng 6:8–16. https://doi.org/10.2174/2212717806666181212125216
Suhan MBK, Al-Mamun MR, Farzana N, Aishee SM, Islam MS, Marwani HM, Hasan MM, Asiri AM, Rahman MM, Islam A, Awual MR (2023) Sustainable pollutant removal and wastewater remediation using TiO2-based nanocomposites: a critical review. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects 36:101050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2023.101050
Sun M, Zhai LF, Mu Y, Yu HQ (2020) Bioelectrochemical element conversion reactions towards generation of energy and value-added chemicals. Prog Energy Combust Sci 77:100814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2019.100814
Tan SM, Ong SA, Ho LN, Wong YS, Thung WE, Teoh TP (2020) The reaction of wastewater treatment and power generation of single chamber microbial fuel cell against substrate concentration and anode distributions. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18:793–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00504-w
Tessema TD, Yemata TA (2021) Experimental dataset on the effect of electron acceptors in energy generation from brewery wastewater via a microbial fuel cell. Data Brief 37:107272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2021.107272
Tul Muntha S, Kausar A, Siddiq M (2017) Advances in polymeric nanofiltration membrane: a review. Polym Plast Technol Eng 56(8):841–856. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2016.1233562
Tungler A, Szabados E, Hosseini AM (2015) Wet air oxidation of aqueous wastes. Wastewater Treat Eng. https://doi.org/10.5772/60935
Varjani S (2022) Prospective review on bioelectrochemical systems for wastewater treatment: achievements, hindrances and role in sustainable environment. Sci Total Environ 841:156691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156691
Vievard J, Alem A, Pantet A, Ahfir ND, Arellano-Sánchez MG, Devouge-Boyer C, Mignot M (2023) Bio-based adsorption as ecofriendly method for wastewater decontamination: a review. Toxics 11(5):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11050404
Wan Y, Li R, Wang X, Liao C (2023) Recovery of reactive nitrogen from wastewater using bioelectrochemical systems. Sep Purif Technol 327:125002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125002
Wang Y, Qiu L, Qiu Q (2018) Development of ceramic membrane combination process in the treatment of industrial wastewater in China. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 392:22039. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/392/2/022039
Wang X, Li S, Chen P, Li F, Hu X, Hua T (2022) Photocatalytic and antifouling properties of TiO2-based photocatalytic membranes. Mater Today Chem 23:100650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100650
Wang S, Kong F (2022) Electricity production and the analysis of the anode microbial community in a constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell. In: Phytoremediation technology for the removal of heavy metals and other contaminants from soil and water. Elsevier, pp 571–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85763-5.00009-X
Wawrzkiewicz M, Polska-Adach E, Hubicki Z (2019) Application of titania based adsorbent for removal of acid, reactive and direct dyes from textile effluents. Adsorption 25:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-019-00062-0
Wilberforce T, Sayed ET, Abdelkareem MA, Elsaid K, Olabi AG (2021) Value added products from wastewater using bioelectrochemical systems: current trends and perspectives. J Water Proc Eng 39:101737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101737
Wong JKH, Tan HK, Lau SY, Yap PS, Danquah MK (2019) Potential and challenges of enzyme incorporated nanotechnology in dye wastewater treatment: a review. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103261
**a H, Li C, Yang G, Shi Z, ** C, He W, Xu J, Li G (2022) A review of microwave-assisted advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 287:131981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131981
Yang C, Xu W, Nan Y, Wang Y, Hu Y, Gao C, Chen X (2020a) Fabrication and characterization of a high performance polyimide ultrafiltration membrane for dye removal. J Colloid Interface Sci 562:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.11.075
Yang Y, Li X, Zhou C, **ong W, Zeng G, Huang D, Zhang C, Wang W, Song B, Tang X, Li X (2020b) Recent advances in application of graphitic carbon nitride-based catalysts for degrading organic contaminants in water through advanced oxidation processes beyond photocatalysis: a critical review. Water Res 184:116200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116200
Ye W, Ye K, Lin F, Liu H, Jiang M, Wang J, Liu R, Lin J (2020) Enhanced fractionation of dye/salt mixtures by tight ultrafiltration membranes via fast bio-inspired co-deposition for sustainable textile wastewater management. Chem Eng J 379:122321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122321
Yeoh JX, Md Jamil SNA, Syukri F, Koyama M, Nourouzi Mobarekeh M (2022) Comparison between conventional treatment processes and advanced oxidation processes in treating slaughterhouse wastewater: a review. Water. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14223778
Yogalakshmi KN, Das A, Rani G, Jaswal V, Randhawa JS (2020) Nano-bioremediation: a new age technology for the treatment of dyes in textile effluents. In: Bioremediation of industrial waste for environmental safety, vol I. Industrial Waste and Its Management, pp 313–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1891-7_15
Yun H, Liang B, Kong D, Wang A (2018) Improving biocathode community multifunctionality by polarity inversion for simultaneous bioelectroreduction processes in domestic wastewater. Chemosphere 194:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.030
Zerrouki S, Rihani R, Lekikot K, Ramdhane I (2021) Enhanced biogas production from anaerobic digestion of wastewater from the fruit juice industry by sonolysis: experiments and modelling. Water Sci Technol 84:644–655. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2021.245
Zhang S, You J, Kennes C, Cheng Z, Ye J, Chen D, Chen J, Wang L (2018) Current advances of VOCs degradation by bioelectrochemical systems: a review. Chem Eng J 334:2625–2637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.014
Zhang S, Yang YL, Lu J, Zuo XJ, Yang XL, Song HL (2020) A review of bioelectrochemical systems for antibiotic removal: efficient antibiotic removal and dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. J Water Proc Eng 37:101421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101421
Zhang X, Li F, Wang J, Zhao H, Yu XF (2021) Strategy for improving the activity and selectivity of CO2 electroreduction on flexible carbon materials for carbon neutral. Appl Energy 298:117196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117196
Zhang H, Zhang M, Zhang H, Yu T, Qu C (2023) Recent development of sludge biochar-based catalysts in advanced oxidation processes for removing wastewater contaminants: a review. Fuel 348:128444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2023.128444
Zhao Y, Lu D, Cao Y, Luo S, Zhao Q, Yang M, Xu C, Ma J (2018) Interaction analysis between gravity-driven ceramic membrane and smaller organic matter: implications for retention and fouling mechanism in ultralow pressure-driven filtration system. Environ Sci Technol 52:13718–13727. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b03618
Zhu Z, Liu D, Cai S, Tan Y, Liao J, Fang Y (2020) Dyes removal by composite membrane of sepiolite impregnated polysulfone coated by chemical deposition of tea polyphenols. Chem Eng Res Des 156:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2020.02.001
Zou D, Ni S, Yao H, Hu C, Low ZXN, Zhong Z (2022) Co-sintering of ceramic ultrafiltration membrane with gradient pore structures for separation of dye/salt wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 302:122030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122030
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFE0107100). It was also supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772529) and Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_3687) .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJ, TE and XH did writing—original draft, methodology. JS done conceptualization, funding acquisition, validation, and writing—review and editing. RA performed writing—review and editing and formal analysis. MK contributed to investigation and writing—review and editing. SA was involved in conceptualization, software, data curation, writing—review and editing. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The research does not deal with human nor animal data.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, H., He, X., Sun, J. et al. A critical review on sustainable biorefinery approaches and strategies for wastewater treatment and production of value-added products. Energ. Ecol. Environ. 9, 1–24 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-023-00312-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-023-00312-6