Abstract
Context
The previous studies suggested a possible increased risk of hypercalcaemia and reduced bone mineral density (BMD) in Williams’ syndrome (WS). However, an extensive study regarding bone metabolism has never been performed.
Objective
To investigate bone health in young adults with WS.
Design
Cross-sectional study.
Settings
Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases and Medical Genetic Units.
Patients
29 WS young adults and 29 age- and sex-matched controls.
Main outcome measures
In all subjects, calcium, phosphorus, bone alkaline phosphatase (bALP), parathyroid hormone (PTH), 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHVitD), osteocalcin (OC), carboxyterminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX), 24-h urinary calcium and phosphorus, femoral-neck (FN) and lumbar-spine (LS) BMD and vertebral fractures (VFx) were assessed. In 19 patients, serum fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) levels were measured.
Results
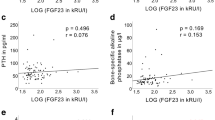
WS patients showed lower phosphorus (3.1 ± 0.7 vs 3.8 ± 0.5 mg/dL, p = 0.0001) and TmP/GFR (0.81 ± 0.32 vs 1.06 ± 0.25 mmol/L, p = 0.001), and an increased prevalence (p = 0.005) of hypophosphoremia (34.5 vs 3.4%) and reduced TmP/GFR (37.9 vs 3.4%). Moreover, bALP (26.3 ± 8.5 vs 35.0 ± 8.0 U/L), PTH (24.5 ± 12.6 vs 33.7 ± 10.8 pg/mL), OC (19.4 ± 5.3 vs 24.5 ± 8.7 ng/mL), and FN-BMD (− 0.51 ± 0.32 vs 0.36 ± 0.32) were significantly lower (p < 0.05), while CTX significantly higher (401.2 ± 169.3 vs 322.3 ± 122.4 pg/mL, p < 0.05). Serum and urinary calcium and 25OHVitD levels, LS-BMD and VFx prevalence were comparable. No cases of hypercalcemia and suppressed FGF23 were documented. Patients with low vs normal phosphorus and low vs normal TmP/GFR showed comparable FGF23 levels. FGF23 did not correlate with phosphorus and TmP/GFR values.
Conclusions
Adult WS patients have reduced TmP/GFR, inappropriately normal FGF23 levels and an uncoupled bone turnover with low femoral BMD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris CA (2010) Introduction: Williams syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 154C(2):203–208
Strømme P, Bjornstad P, Ramstad K (2002) Prevalence estimation of Williams syndrome. J Child Neurol 17:269–271
Schubert C (2009) The genomic basis of the Williams–Beuren syndrome. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(7):1178–1197
Pober BR (2010) Williams–Beuren syndrome. N Engl J Med 362(3):239–252 (Review)
Masserini B, Bedeschi MF, Bianchi V, Scuvera G, Beck-Peccoz P, Lalatta F, Selicorni A, Orsi E (2013) Prevalence of diabetes and pre-diabetes in a cohort of Italian young adults with Williams syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 161A(4):817–821
Sforzini C, Milani D, Fossali E, Barbato A, Grumieri G, Bianchetti MG, Selicorni A (2002) Renal tract ultrasonography and calcium homeostasis in Williams–Beuren syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 17(11):899–902
Amenta S, Sofocleous C, Kolialexi A, Thomaidis L, Giouroukos S, Karavitakis E, Mavrou A, Kitsiou S, Kanavakis E, Fryssira H (2005) Clinical manifestations and molecular investigation of 50 patients with Williams syndrome in the Greek population. Pediatr Res 57(6):789–795
Jurado LP, Peoples R, Kaplan P, Hamel BC, Francke U (1996) Molecular definition of the chromosome 7 deletion in Williams syndrome and parent-of-origin effects on growth. Am J Hum Genet 59(4):781–792
Sindhar S, Lugo M, Levin MD, Danback JR, Brink BD, Yu E, Dietzen DJ, Clark AL, Purgert CA, Waxler JL, Elder RW, Pober BR, Kozel BA (2016) Hypercalcemia in patients with Williams–Beuren syndrome. J Pediatr 178:254–260
Cagle AP, Waguespack SG, Buckingham BA, Shankar RR, Dimeglio LA (2004) Severe infantile hypercalcemia associated with Williams syndrome successfully treated with intravenously administered pamidronate. Pediatrics 114(4):1091–1095
Garabédian M, Jacqz E, Guillozo H, Grimberg R, Guillot M, Gagnadoux MF, Broyer M, Lenoir G, Balsan S (1985) Elevated plasma 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D concentrations in infants with hypercalcemia and an elfin facies. N Engl J Med 312(15):948–952
Culler FL, Jones KL, Deftos LJ (1985) Imparied calcitonin secretion in patients with Williams syndrome. J Pediatr 107(5):720–723
Cherniske EM, Carpenter TO, Klaiman C, Young E, Bregman J, Insogna K, Schultz RT, Pober BR (2004) Multisystem study of 20 older adults with Williams syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 131:255–264
Garrow JS, Webster J (1985) Quetelet’s index (W/H2) as a measure of fatness. Int J Obes 9(2):147–153
Figge J, Jabor A, Kazda A, Fencl V (1998) Anion gap and hypoalbuminemia. Crit Care Med 26(11):1807–1810
Hodgkinson A, Pyrah LN (1958) The urinary excretion of calcium and inorganic phosphate in 344 patients with calcium stone of renal origin. Br J Surg 46(195):10–18
Yamazaki Y, Okazaki R, Shibata M, Hasegawa Y, Satoh K, Tajima T, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Nakahara K, Yamashita T, Fukumoto S (2002) Increased circulatory level of biologically active full-length FGF-23 in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(11):4957–4960
Walton RJ, Bijvoet OL (1975) Nomogram for derivation of renal threshold phosphate concentration. Lancet 2(7929):309–310
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8(9):1137–1148
Stagi S, Manoni C, Scalini P, Chiarelli F, Verrotti A, Cecchi C, Lapi E, Giglio S, Romano S, de Martino M (2016) Bone mineral status and metabolism in patients with Williams–Beuren syndrome. Hormones (Athens) 15(3):404–412
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2006) Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 444(7120):770–774
Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Miyoshi M, Yamamoto M, Nandi A, Rosenblatt KP, Baum MG, Schiavi S, Hu MC, Moe OW, Kuro-o M (2006) Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-23 signaling by klotho. J Biol Chem 281(10):6120–6123
Razzaque MS, Lanske B (2007) The emerging role of the fibroblast growth factor-23-klotho axis in renal regulation of phosphate homeostasis. J Endocrinol 194(1):1–10 (Review)
Frishberg Y, Ito N, Rinat C, Yamazaki Y, Feinstein S, Urakawa I, Navon-Elkan P, Becker-Cohen R, Yamashita T, Araya K, Igarashi T, Fujita T, Fukumoto S (2007) Hyperostosis-hyperphosphatemia syndrome: a congenital disorder of O-glycosylation associated with augmented processing of fibroblast growth factor 23. J Bone Miner Res 22(2):235–242
El-Maouche D, Dumitrescu CE, Andreopoulou P, Gafni RI, Brillante BA, Bhattacharyya N, Fedarko NS, Collins MT (2016) Stability and degradation of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23): the effect of time and temperature and assay type. Osteoporos Int 27(7):2345–2353
Smith ER, McMahon LP, Holt SG (2013) Method-specific differences in plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 measurement using four commercial ELISAs. Clin Chem Lab Med 51(10):1971–1981
Smith ER, Cai MM, McMahon LP, Holt SG (2012) Biological variability of plasma intact and C-terminal FGF23 measurements. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(9):3357–3365
Pool LR, Wolf M (2017) FGF23 and nutritional metabolism. Ann Rev Nutr 21(37):247–268
Rodriguez-Ortiz ME, Lopez I, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Martinez-Moreno JM, Ramírez AP, Pineda C, Canalejo A, Jaeger P, Aguilera-Tejero E, Rodriguez M, Felsenfeld A, Almaden Y (2012) Calcium deficiency reduces circulating levels of FGF23. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(7):1190–1197
Eller-Vainicher C, Cairoli E, Zhukouskaya VV, Morelli V, Palmieri S, Scillitani A, Beck-Peccoz P, Chiodini I (2013) Prevalence of subclinical contributors to low bone mineral density and/or fragility fracture. Eur J Endocrinol 169(2):225–237
Albers J, Schulze J, Beil FT, Gebauer M, Baranowsky A, Keller J, Marshall RP, Wintges K, Friedrich FW, Priemel M, Schilling AF, Rueger JM, Cornils K, Fehse B, Streichert T, Sauter G, Jakob F, Insogna KL, Pober B, Knobeloch KP, Francke U, Amling M, Schinke T (2011) Control of bone formation by the serpentine receptor Frizzled-9. J Cell Biol 192(6):1057–1072
Tenenhouse HS (1999) X-linked hypophosphataemia: a homologous disorder in humans and mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14(2):333–341 (Review)
**ao ZS, Crenshaw M, Guo R, Nesbitt T, Drezner MK, Quarles LD (1998) Intrinsic mineralization defect in Hyp mouse osteoblasts. Am J Physiol 275(4 Pt 1):E700–E708
Bruin WJ, Baylink DJ, Wergedal JE (1975) Acute inhibition of mineralization and stimulation of bone resorption mediated by hypophosphatemia. Endocrinology 96(2):394–399
Baylink D, Wergedal J, Stauffer M (1971) Formation, mineralization, and resorption of bone in hypophosphatemic rats. J Clin Invest 50(12):2519–2530
Krajisnik T, Björklund P, Marsell R, Ljunggren O, Akerström G, Jonsson KB, Westin G, Larsson TE (2007) Fibroblast growth factor-23 regulates parathyroid hormone and 1alpha-hydroxylase expression in cultured bovine parathyroid cells. J Endocrinol 195(1):125–131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palmieri, S., Bedeschi, M.F., Cairoli, E. et al. Bone involvement and mineral metabolism in Williams’ syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest 42, 337–344 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-018-0924-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-018-0924-y