Abstract
Purpose
The influence of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor gemigliptin alone or in combination with the histone deacetylase inhibitor PXD101 on survival of thyroid carcinoma cells was investigated.
Methods
SW1736, TPC-1, 8505C and BCPAP human thyroid carcinoma cells were used. To assess cell survival, cell viability, the percentage of viable cells and dead cells, cytotoxic activity, ATP levels and FACS analysis were measured. To validate the impact of gemigliptin combined with PXD101, the interactions were estimated by obtaining combination index in cells treated with two agents.
Results
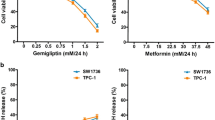
In cells treated with gemigliptin or PXD101, cell viability, the percentage of viable cells and ATP levels were reduced, and the percentage of dead cells and cytotoxic activity were elevated. In cells treated with both gemigliptin and PXD101, compared with PXD101 alone, cell death was augmented, and all of the combination index values were lower than 1.0, suggesting the synergism between gemigliptin and PXD101. The percentage of apoptotic cells, and the protein levels of Bcl2 and cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase were elevated, and the protein levels of xIAP and survivin were reduced. The protein levels of phospho-Akt and phospho-AMPK were elevated, and cell migration was reduced.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate that gemigliptin induces cytotoxicity in thyroid carcinoma cells. Moreover, gemigliptin has a synergistic activity with PXD101 in the induction of cell death through involvement of Bcl2 family proteins, xIAP and survivin as well as mediation of Akt and AMPK in thyroid carcinoma cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pacini F, Brianzoni E, Durante C, Elisei R, Ferdeghini M, Fugazzola L, Mariotti S, Pellegriti G (2016) Recommendations for post-surgical thyroid ablation in differentiated thyroid cancer: a 2015 position statement of the Italian Society of Endocrinology. J Endocrinol Invest 39:341–347
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM, Schlumberger M, Schuff KG, Sherman SI, Sosa JA, Steward DL, Tuttle RM, Wartofsky L (2016) 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 26:1–133
Chia CW, Egan JM (2008) Incretin-based therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3703–3716
Mulvihill EE, Drucker DJ (2014) Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of action of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Endocr Rev 35:992–1019
Havre PA, Abe M, Urasaki Y, Ohnuma K, Morimoto C, Dang NH (2008) The role of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV in cancer. Front Biosci 13:1634–1645
Kotani T, Aratake Y, Ogata Y, Umeki K, Araki Y, Hirai K, Kuma K, Ohtaki S (1991) Expression of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV activity in thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Lett 57:203–208
Kehlen A, Lendeckel U, Dralle H, Langner J, Hoang-Vu C (2003) Biological significance of aminopeptidase N/CD13 in thyroid carcinomas. Cancer Res 63:8500–8506
Fluge O, Bruland O, Akslen LA, Lillehaug JR, Varhaug JE (2006) Gene expression in poorly differentiated papillary thyroid carcinomas. Thyroid 16:161–175
Rathmann W, Kostev K (2017) Association of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors with risk of metastases in patients with type 2 diabetes and breast, prostate or digestive system cancer. J Diabetes Complicat 31:687–692
Wang H, Liu X, Long M, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhang R, Zheng Y, Liao X, Wang Y, Liao Q, Li W, Tang Z, Tong Q, Wang X, Fang F, de la Vega MR, Ouyang Q, Zhang DD, Yu S, Zheng H (2016) NRF2 activation by antioxidant antidiabetic agents accelerates tumor metastasis. Sci Transl Med 8:334ra51
Kim SH, Jung E, Yoon MK, Kwon OH, Hwang DM, Kim DW, Kim J, Lee SM, Yim HJ (2016) Pharmacological profiles of gemigliptin (LC15-0444), a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 788:54–64
Kim SH, Lee SH, Yim HJ (2013) Gemigliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor: first new anti-diabetic drug in the history of Korean pharmaceutical industry. Arch Pharm Res 36:1185–1188
Hwang HJ, Chung HS, Jung TW, Ryu JY, Hong HC, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH, Yoo HJ (2015) The dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor inhibits the expression of vascular adhesion molecules and inflammatory cytokines in HUVECs via Akt- and AMPK-dependent mechanisms. Mol Cell Endocrinol 405:25–34
Hwang HJ, Jung TW, Ryu JY, Hong HC, Choi HY, Seo JA, Kim SG, Kim NH, Choi KM, Choi DS, Baik SH, Yoo HJ (2014) Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor (gemigliptin) inhibits tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis and inflammation in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 392:1–7
Moon JY, Woo JS, Seo JW, Lee A, Kim DJ, Kim YG, Kim SY, Lee KH, Lim SJ, Cheng XW, Lee SH, Kim W (2016) The dose-dependent organ-specific effects of a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor on cardiovascular complications in a model of type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 11:e0150745
Marks PA, Dokmanovic M (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: discovery and development as anticancer agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 14:1497–1511
Greenberg VL, Williams JM, Cogswell JP, Mendenhall M, Zimmer SG (2001) Histone deacetylase inhibitors promote apoptosis and differential cell cycle arrest in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Thyroid 11:315–325
Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, McMullan C, Negri J, Fanourakis G, Goudopoulou A, Richon VM, Marks PA, Mitsiades N (2005) Novel histone deacetylase inhibitors in the treatment of thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:3958–3965
Catalano MG, Fortunati N, Pugliese M, Poli R, Bosco O, Mastrocola R, Aragno M, Boccuzzi G (2006) Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, enhances sensitivity to doxorubicin in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. J Endocrinol 191:465–472
Luong QT, O’Kelly J, Braunstein GD, Hershman JM, Koeffler HP (2006) Antitumor activity of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid against thyroid cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 12:5570–5577
Catalano MG, Poli R, Pugliese M, Fortunati N, Boccuzzi G (2007) Valproic acid enhances tubulin acetylation and apoptotic activity of paclitaxel on anaplastic thyroid cancer cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:839–845
Lin SF, Lin JD, Chou TC, Huang YY, Wong RJ (2013) Utility of a histone deacetylase inhibitor (PXD101) for thyroid cancer treatment. PLoS One 8:e77684
Plumb JA, Finn PW, Williams RJ, Bandara MJ, Romero MR, Watkins CJ, La Thangue NB, Brown R (2003) Pharmacodynamic response and inhibition of growth of human tumor xenografts by the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor PXD101. Mol Cancer Ther 2:721–728
Hwang JJ, Kim YS, Kim MJ, Kim DE, Jeong IG, Kim CS (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitor potentiates anticancer effect of docetaxel via modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins and tubulin in hormone refractory prostate cancer cells. J Urol 184:2557–2564
Lassen U, Molife LR, Sorensen M, Engelholm SA, Vidal L, Sinha R, Penson RT, Buhl-Jensen P, Crowley E, Tjornelund J, Knoblauch P, de Bono JS (2010) A phase I study of the safety and pharmacokinetics of the histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat administered in combination with carboplatin and/or paclitaxel in patients with solid tumours. Br J Cancer 103:12–17
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2015) The novel heat shock protein 90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 synergizes with the histone deacetylase inhibitor PXD101 in induction of death of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E253–E261
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2016) The heat shock protein 90 inhibitor SNX5422 has a synergistic activity with histone deacetylase inhibitors in induction of death of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Endocrine 51:274–282
Omar B, Ahren B (2014) Pleiotropic mechanisms for the glucose-lowering action of DPP-4 inhibitors. Diabetes 63:2196–2202
Lim KS, Kim JR, Choi YJ, Shin KH, Kim KP, Hong JH, Cho JY, Shin HS, Yu KS, Shin SG, Kwon OH, Hwang DM, Kim JA, Jang IJ (2008) Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor LC15-0444 in healthy Korean men: a dose-block-randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending single-dose, phase I study. Clin Ther 30:1817–1830
Cho SW, Yi KH, Han SK, Sun HJ, Kim YA, Oh BC, Park YJ, Park DJ (2014) Therapeutic potential of metformin in papillary thyroid cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Endocrinol 393:24–29
Frid A, Sterner GN, Löndahl M, Wiklander C, Cato A, Vinge E, Andersson A (2010) Novel assay of metformin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes and varying levels of renal function: clinical recommendations. Diabetes Care 33:1291–1293
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Tanti JF, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Bost F (2008) The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene 27:3576–3586
Borbone E, Berlingieri MT, de Bellis F, Nebbioso A, Chiappetta G, Mai A, Altucci L, Fusco A (2010) Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce thyroid cancer-specific apoptosis through proteasome-dependent inhibition of TRAIL degradation. Oncogene 29:105–116
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2:647–656
Derakhshan A, Chen Z, van Waes C (2017) Therapeutic small molecules target inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in cancers with deregulation of extrinsic and intrinsic cell death pathways. Clin Cancer Res 23:1379–1387
Tran J, Master Z, Yu JL, Rak J, Dumont DJ, Kerbel RS (2002) A role for survivin in chemoresistance of endothelial cells mediated by VEGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4349–4354
Zhang M, Latham DE, Delaney MA, Chakravarti A (2005) Survivin mediates resistance to antiandrogen therapy in prostate cancer. Oncogene 24:2474–2482
Altieri DC (2010) Survivin and IAP proteins in cell-death mechanisms. Biochem J 430:199–205
Chen X, Duan N, Zhang C, Zhang W (2016) Survivin and tumorigenesis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. J Cancer 7:314–323
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2017) Doxorubicin has a synergistic cytotoxicity with cucurbitacin B in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Tumor Biol 39:1–9
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2015) The effect of 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin alone or in combination with paclitaxel on anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Endocrine 48:886–893
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2013) Akt inhibition enhances the cytotoxic effect of apigenin in combination with PLX4032 in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells harboring BRAFV600E. J Endocrinol Invest 36:1099–1104
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2013) Inhibition of p21 and Akt potentiates SU6656-induced caspase-independent cell death in FRO anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Horm Metab Res 45:408–414
Kim SH, Kang JG, Kim CS, Ihm S-H, Choi MG, Yoo HJ, Lee SJ (2015) Suppression of AKT potentiates synergistic cytotoxicity of apigenin with TRAIL in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 35:6529–6537
Choi H-J, Kim TY, Chung N, Yim JH, Kim WG, Kim J, Kim WB, Shong YK (2011) The influence of the BRAFV600E mutation in thyroid cancer cell lines on the anticancer effects of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-ribonucleoside. J Endocrinol 211:79–85
Chen G, Xu S, Renko K, Derwahl M (2012) Metformin inhibits growth of thyroid carcinoma cells, suppresses self-renewal of derived cancer stem cells, and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E510–E520
Wang B, Wang XB, Chen LY, Huang L, Dong RZ (2013) Belinostat-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition in pancreatic cancer cells involve activation of TAK1-AMPK signaling axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 437:1–6
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (no. 2015R1A2A2A01003589) to S.J. Lee, Republic of Korea, and also by Hallym University Research Fund to S.J. Lee, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee.
Informed consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H., Kang, J.G., Kim, C.S. et al. Gemigliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor, exerts a synergistic cytotoxicity with the histone deacetylase inhibitor PXD101 in thyroid carcinoma cells. J Endocrinol Invest 41, 677–689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0792-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0792-x