Abstract
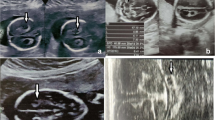
Cavum velum interpositi is the space between the layers of the tela choroidea of the third ventricle. This space occasionally appears as an anechoic lesion in routine mid-trimester targeted scans because of the presence of fluid inside. This is then called a cavum velum interpositi (CVI) cyst. CVI cyst is a rare finding with varied outcomes. Councellings management are consequently confusing. This study was aimed at assessing the outcome of CVI cysts to guide the treating clinician and address apprehensions of the expecting couple. Genetic evaluation and MRI to prove the inncocuous nature of CVI cysts is expensive and needs to be offered in an appropriate perspective. A fetal Neurosonogram was conducted in all the targeted scans and the brain was visualized in coronal, axial, sagittal and oblique saggital planes. The fetuses with a CVI cyst were followed antenatally and up to 6 months post delivery. The study concluded that CVI cysts appear to be an innocuous finding as neurological outcome of all four cases who continued pregnancy was normal. One patient terminated the pregnancy for an extra Central Nervous System anomaly.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Addario V, Pinto V, Rossi AC, Pintucci A, Di Cagno L. Cavum veli interpositi cyst: prenatal diagnosis and postnatal outcome. ISUOG. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.6419.
Tubbs RS, et al. Cavum velum interpositum, cavum septum pellucidum, and cavum vergae: a review. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011;27(11):1927–30.
Chen CY, et al. Sonographic characteristics of the cavum velum interpositum. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19:1631–5.
Tsikhanenka I, Chukanov A, Grishchenya V. Polost ppromezutochnogo parusa—klinicheskoe znachenie i differentialnaya diagnostica. Medicina. 2016;4:28–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, P., Chauhan, K., Deshpande, S. et al. Outcome of Fetuses with Cavum Velum Interpositi Cyst—Experience of a Tertiary Centre. J. Fetal Med. 7, 161–163 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40556-020-00245-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40556-020-00245-8