Abstract
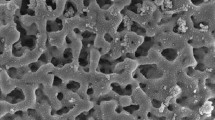
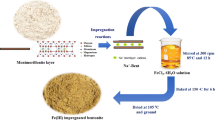
The present study examined the adsorption of As(III) and As(V) (arsenics) from aqueous solutions using FeCl3 impregnated bagasse fly ash (BFA-Fe). Batch adsorption studies were carried out to evaluate the effect of various parameters like initial pH (pH0), adsorbent dose (m), contact time (t), initial concentration (C0) and temperature (T) on the removal of As(III) and As(V) from aqueous solutions. The maximum removal of As(III) and As(V) was found ~ 95% and ~ 97% at lower concentration (< 20 μg/dm3) and ~ 86% and ~ 87% at higher concentration (500 μg/dm3), respectively, using 3 g/dm3 of BFA dosage at 303 K. The adsorption of arsenics on BFA-Fe was very rapid. Pseudo-second-order kinetic model well represented the adsorption kinetics of both As(III) and As(V). Error analyses functions for adsorption of As(III) and As(V) onto BFA-Fe. Based on these error analyses, R-P isotherm was found to be fitted. Thermodynamic parameters, i.e., ΔG°, ΔH°, and ΔS°, were also calculated. At 25.0 to 45.0 °C, the values of ΔG° lie in the range of -43.85, -45.34, -48.82, -51.31, -53.8, and -44.75, -48.3, -51.84, -55.39, -58.93, -55.57 for As (III), and As (V) respectively, indicating that adsorption is spontaneous and exothermic in nature. Regeneration study was carried out by different solvent and thermal methods. Our results revealed that BFA-Fe can be reused directly for making fire-briquettes to explore its energy value. From this study, As containment is most effective removal from aqueous solution and mimic to any contaminated water resources.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNICEF report, Safe Drinking Water http://www.unicef.org/specialsession/about/sgreport.pdf/03_SafeDrinkingWaterD7341Insert_English.pdf, cited on 10th June 10, 2019.
Mohan D, Pittman JCU. Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—A critical review. J Hazard Mater. 2007;142:1–53.
Kamsonlian S, Suresh S, Majumder CB, Chand S. Bio-sorptive behaviour of mango leaf powder and rice husk for arsenic (III) from aqueous solutions. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 2012;9:565–78.
Kamsonlian S, Suresh S, Majumder CB, Chand S. Biosorption of arsenic from contaminated water onto solid psidium guajava leaf surface: equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics, and desorption study. Bioremed J. 2012;16(2):97–112.
Kamsonlian S, Suresh S, Majumder CB, Chand S. Biosorption of As(III) from contaminated water onto low cost palm bark biomass. Int J Current Eng Technol. 2012;2(1):153–8.
Yadav SK, Ramanathan A, Kumar M, Chidambaram S, Gautam Y, Tiwari C. Assessment of arsenic and uranium co-occurrences in groundwater of central Gangetic Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci. 2020;79(6):1–14.
Sanyal T, Bhattacharjee P, Bhattacharjee S, Bhattacharjee P. Hypomethylation of mitochondrial D-loop and ND6 with increased mitochondrial DNA copy number in the arsenic-exposed population. Toxicology. 2018;408:54–61.
Shaheen SM, Niazi NK, Hassan NE, Bibi I, Wang H, Tsang DC, Ok YS, Bolan N, Rinklebe J. Wood-based biochar for the removal of potentially toxic elements in water and wastewater: a critical review. Int Mater Rev. 2019;64(4):216–47.
Amen R, Bashir H, Bibi I, Shaheen SM, Niazi NK, Shahid M, Hussain MM, Antoniadis V, Shakoor MB, Al-Solaimani SG, Wang H, Bundschuh J, Rinklebebk J. A critical review on arsenic removal from water using biochar-based sorbents: the significance of modification and redox reactions. Chem Eng J 2020;396:125195.
U.S.E.P.A. (USEPA), Arsenic, Inorganic (CASRN 7440–38–2). Integrated Risk Informa- tion System (IRIS) U.S. , Environmental Protection Agency Chemical, Assessment Summary, National Center for Environmental Assessment, 1998.
WHO. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization 2011;216:303–304.
Chen Y, Gamble PM, Islam T, Ahmed A, Argos M, Graziano JH, Ahsan H. Arsenic exposure at low-to-moderate levels and skin lesions, arsenic metabolism, neurological functions, and biomarkers for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases: review of recent findings from the Health Effects of Arsenic Longitudinal Study (HEALS) in Bangladesh. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009;239(2):184–92.
Tsuji JS, Garry MR, Perez V, Chang ET. Low-level arsenic exposure and develop- mental neurotoxicity in children: a systematic review and risk assessment. Toxicology. 2015;337:91–107.
Lynch HN, Zu K, Kennedy EM, Lam T, Liu X, Pizzurro DM, Loftus CT, Rhomberg LR. Quantitative assessment of lung and bladder cancer risk and oral expo- sure to inorganic arsenic: meta-regression analyses of epidemiological data. Environ Int. 2017;106:178–206.
Podgorski J, Berg M. Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science. 2020;368:845–50.
Kumarathilaka P, Seneweera S, Ok YS, Meharg AA, Bundschuh J. Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice: an agronomical, physico-chemical, and biological approach–A critical review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. 2020;50(1):31–71.
Kumar M, Ramanathan A. Arsenic speciation of groundwater and agricultural soils in central Gangetic basin, India, p. 225, CRC Press. 2019.
Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), IS 10500 : Drinking water Specification. 2012; 18.
Chakrabarti D, Singh S, Rashid M, Rahman MM, Arsenic: Occurrence in Ground- water, Encyclopedia of Environmental Health, 2nd Edtion Elsevier Inc, 2018.
Borho M, Wilderer P. Optimized removal of arsenate(III) by adaptation of oxidation and precipitation processes to the filtration step. Water Sci Technol. 1996;34:25–31.
Han B, Runnells T, Zimbron J, Wickramasinghe R. Arsenic removal from drinking water by flocculation and microfiltration. Desalination. 2002;145:293–8.
Singh TS, Pant KK. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of As(III) on activated alumina. Sep Purif Technol. 2004;36:139–47.
Chang YY, Song K, Yang Y. Removal of As(III) in a column reactor packed with iron-coated sand and manganese-coated sand. J Hazard Mater. 2008;150:565–72.
Soltani RDC, Safari M, Maleki A, Rezaee R, Shahmoradi B, Shahmohammadi S, Ghahramani E. Decontamination of arsenic(V)-contained liquid phase utilizing Fe3O4/bone char nanocomposite encapsulated in chitosan biopolymer. Environ Sci Poll Res. 2017;24:15157–66.
Hayati B, Maleki A, Najafi F, Gharibi F, McKay G, Gupta VK, Puttaiah SH, Marzban N. Heavy metal adsorption using PAMAM/CNT nanocomposite from aqueous solution in batch and continuous fixed bed systems. Chem Eng J. 2018;346:258–70.
DhanaRamalakshmi R, Murugan M, Jeyabal V. Arsenic removal using Prosopis spicigera L. wood (PsLw) carbon–iron oxide composite. Appl Water Sci. 2020;10:211.
Yin Y, Zhou T, Luo H, Geng J, Yu W, Jiang Z. Adsorption of arsenic by activated charcoal coated zirconium-manganese nanocomposite: performance and mechanism. Colloids Surf A. 2019;575:318–28.
Dutta PK, Pehoen So, Sharma VK, Ray AK. Photocatalytic oxidation of Arsenic(III): evidence of hydroxyl radicals. Environ Sci Technol. 2005;39:1827–34.
Basha CA, Selvi SJ, Ramasamy E, Chellammal S. Removal of arsenic and sulphate from the copper smelting industrial effluent. Chem Eng J. 2008;141:89–98.
Ballinas ML, Miguel ERDS, Rodriguez MTJ, Silva O, Munoz M, Gyves JD. Arsenic(V) removal with polymer inclusion membranes from sulfuric acid media using DBBP as carrier. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38:886–91.
Gholami MM, Mokhtari MA, Aameri A, Fard MRA. Application of reverse osmosis technology for arsenic removal from drinking water. Desalination. 2006;1–3:725–7.
Jafari A, Rezaee R, Nasseri S, Mahvi AH, Maleki A, Safari M, Shahmoradi B, Daraei H. Application of micellar enhanced ultrafiltration (MEUF) for arsenic (V) removal from aqueous solutions and process optimization. J Disper Sci Technol. 2017;38:1588–93.
Bahmania P, Maleki A, Daraei H, Khamforoush M, Rezaee R, Gharibi F, Tkachev AG, Burakov AE, Agarwal S, Gupta VK. High-flux ultrafiltration membrane based on electrospun polyacrylonitrile nano- fibrous scaffolds for arsenate removal from aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2017;506:564–71.
Bahmania P, Maleki A, Rezaee R, Mahvi AH, Khamforoush M, Athar SD, Daraei H, Gharibi F, McKay G. Arsenate removal from aqueous solutions using micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration. J Environ Health Sci Engineer. 2019;17:115–27.
Bahmania P, Malekia A, Rezaee R, Khamforoush M, Yetilmezsoy K, Athara SD, Gharibia F. Simultaneous removal of arsenate and nitrate from aqueous solutions using micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration process. J Water Process Eng. 2019;27:24–31.
Bahmania P, Malekia A, Rezaee R, Khamforoush M, Yetilmezsoy K, Athara SD, Gharibia F. Application of modified electrospun nanofiber membranes with α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles in arsenate removal from aqueous media. Environ Sci Poll Res. 2019;26:21993–2009.
Kalaruban M, Loganathan P, Kandasamy J, Vigneswaran S. Submerged membrane adsorption hybrid system using four adsorbents to remove nitrate from water. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018;25(21):20328–35.
Singh P, Sarswat A, Pittman CU, Mlsna T, Mohan, D. Singh Sustainable Low-Concentration Arsenite [As(III)] Removal in Single and Multicomponent Systems Using Hybrid Iron Oxide–Biochar Nanocomposite Adsorbents—A Mechanistic Study. ACS Omega. 2020.
Soni R, Shukla DP. Synthesis of fly ash based zeolite-reduced graphene oxide composite and its evaluation as an adsorbent for arsenic removal. Chemosphere. 2019;219:504–9.
Soni AB, Keshav A, Verma V, Suresh S. Removal of Glycolic Acid from aqueous solution using Bagasse Flyash. Int J Environ Res. 2012;6(1):297–308.
Suresh S, Srivastava VC, Mishra IM. Study of catechol and resorcinol adsorption mechanism through granular activated carbon characterization, pH and kinetic study. Sep Sci Technol. 2011;46(11):1750–66.
Cooper AM, Hristovski KD, Moller T, Westerhoff P, Sylvester P, Westerhoff P, Sylvester P. The effect of carbon type on arsenic and trichloroethylene removal capabilities of iron (hydr)oxide nanoparticle-impregnated granulated activated carbons. J Hazard Mater. 2010;183:381–8.
Kalderis D, Koutoulakis D, Paraskeva P, Diamadopoulos E, Otal E, del Valle J, Pereira CF. Adsorption of polluting substances on activated carbons prepared from rice husk and sugarcane bagasse. Chem Eng J. 2008;144:42–50.
Pintor AMA, Vieira BRC, Santos SCR, Boaventura RAR, Botelho CMS. Arsenate and arsenite adsorption onto iron-coated cork granulates. SciTotal Environ. 2018;642:1075–89.
Ocinski D, Mazur P. Highly efficient arsenic sorbent based on residual from water deironing—Sorption mechanisms and column studies. J Hazard Mater. 2020;382:1–10.
Muniz G, Fierro V, Celzard A, Furdin G, Gonzalez G, Ballinas MDL. Synthesis, characterization and performance in arsenic removal of iron-doped activated carbons prepared by impregnation with Fe(III) and Fe(II). J Hazard Mater. 2009;165:893–902.
Kleinert S, Muehe EM, Posth NR, Dippon U, Daus B, Kappler A. Biogenic Fe(III) minerals lower the efficiency of iron-mineral-based commercial filter systems for arsenic removal. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45:7533–41.
Suresh S, Srivastava VC, Mishra IM. Anubhav Pratap-Singh, Multicomponent Column Optimization of ternary adsorption based removal of phenolic compounds using Modified Activated Carbon. J Environ Chem Eng. 2021;9: 104843.
Zhu Y, Liang M, Lu R, Zhang H, Zhu Z, You S, Liu J, Liu H. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by Fe(III)-impregnated sorbent prepared from sugarcane bagasse. Fresenius Environ Bull. 2011;20:1288–96.
Suresh S, Srivastava VC, Mishra IM. Studies of adsorption kinetics and regeneration of aniline, Phenol, 4-Chlorophenol and 4-Nitrophenol by activated carbon. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q. 2013;19(2):195–212.
Sigrist ME, Brusa L, Beldomenico HR, Dosso L, Tsendra OM, González MB, Pieck CL, Vera CR. Influence of the iron content on the arsenic adsorption capacity of Fe/GAC adsorbents. J Environ Chem Eng. 2014;2(2):927–34.
Bissen M, Frimmel FH. Arsenic — a Review. Part I: occurrence, toxicity, speciation, mobility. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol. 2003;31:9–18.
Lobo C, Castellari J, Lerner JC, Bertola N, Zaritzky N. Functional iron chitosan microspheres synthesized by ionotropic gelation for the removal of arsenic (V) from water. Inter J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:1575–83.
Zeng L. Arsenic adsorption from aqueous solutions on an Fe(III)-Si binary oxide adsorbent. Water Qual Res J. 2004;39:267–75.
Almazan-Sanchez PT, Castañeda-Juárez M, Martinez-Miranda V, Solache-Ríos MJ, Lugo-Lugo V, Linares-Hernández I. Behavior of TOC and color in the presence of iron-modified activated carbon in methyl methacrylate wastewater in batch and column systems. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015;226:72.
Vitelarodriguez AV, Rangelmendez JR. Arsenic removal by modified activated carbons with iron hydro(oxide) nanoparticles. J Environ Manag. 2013;114:225–31.
Deliyanni E, Bandosz TJ, Matis KA. Impregnation of activated carbon by iron oxyhydroxide and its effect on arsenate removal. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2013;88:1058–66.
Nieto-Delgado C, Rangel-Mendez JR. Anchorage of iron hydro(oxide) nanoparticles onto activated carbon to remove As(V) from water. Water Res. 2012;46:2973–82.
Wang J, Xu W, Chen L, Huang X, Liu J. Preparation and evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles impregnated chitosan beads for arsenic removal from water. Chem Eng J. 2014;251:25–34.
Marques Neto JdO, Bellato CR, Milagres JL, Pessoa KD, Alvarenga ESd. Preparation and evaluation of chitosan beads immobilized with Iron(III) for the removal of As(III) and As(V) from water. J Braz Chem Soc. 2013;24:121–32.
Ali I, Al-Othman ZA, Alwarthan A, Asim M, Khan TA. Removal of arsenic species from water by batch and column operations on bagasse fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2014;21:3218–29.
Cho DW, Jeon BH, Chon CM, Kim Y, Schwartz FW, Lee ES, Song H. A novel chitosan/clay/magnetite composite for adsorption of Cu (II) and As (V). Chem Eng J. 2012;200:654–62.
Elwakeel K. Removal of arsenate from aqueous media by magnetic chitosan resin immobilized with molybdate oxoanions. Int J Environ Sci Technol. 2014;11(4):1051–62.
Shakoor MB, Niazi NK, Bibi I, Shahid M, Saqib ZA, Nawaz MF, Shaheen SM, Wang H, Tsang DC, Bundschuh J. Exploring the arsenic removal potential of various biosorbents from water. Environ Int. 2019;123:567–79.
Langmuir I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc. 1918;40:1361–403.
Freundlich HMF. Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem. 1906;57:385–471.
Temkin MI, Pyzhev V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys Chim USSR. 1940;12:327–56.
Redlich O, Peterson DL. A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem. 1959;63:1024–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh, S., Sillanpää, M., Banat, F. et al. Adsorption of arsenic in aqueous solution onto iron impregnated bagasse fly ash. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 20, 861–879 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-022-00827-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-022-00827-w