Abstract
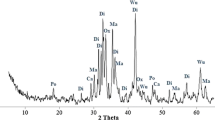
Carbon dioxide mineral sequestration with steelmaking slag is a promising method for reducing carbon dioxide in a large-scale setting. Existing calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide in steelmaking slag can be easily leached by water, and the formed calcium carbonate can be easily wrapped on the surface of unreacted steelmaking slag particles. Thus, further increase in the carbonation reaction rate can be prevented. Enhanced carbon dioxide mineral sequestration with steelmaking slag in dilute alkali solution was analysed in this study through experiments and process evaluation. Operating conditions, namely alkali concentration, reaction temperature and time, and liquid-to-solid ratio, were initially investigated. Then, the material and energy balance of the entire process was calculated, and the net carbon dioxide sequestration efficiency at different reaction times was evaluated. Results showed that dilute alkali solution participated in slowing down the leaching of active calcium in the steelmaking slag and in significantly improving carbonation conversion rate. The highest carbonation conversion rate of approximately 50% can be obtained at the optimal conditions of 20 g/L alkali concentration, 2 mL/L liquid-to-solid ratio, and 70 °C reaction temperature. Carbonation reaction time significantly influences the net carbon dioxide sequestration efficiency. According to calculation, carbon dioxide emission of 52.6 kg/t-slag was avoided at a relatively long time of 120 min.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.S. Lackner, Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 27, 193 (2002)
K.S. Lackner, Science 300, 1677 (2003)
A. Sanna, M. Uibu, G. Caramanna, R. Kuusikand, M.M. Maroto-Valera, Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 8049 (2014)
J. Sipilä, S. Teir, R. Zevenhoven, Åbo Akademi Rep. VT. 1, 12 (2008)
E.R. Bobicki, Q.X. Liu, Z.H. Xu, H.B. Zeng, Prog. Energy Combust. 38, 302 (2012)
W.J.J. Huijgen, G. Witkamp, R. Comans, Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 9676 (2005)
S. Eloneva, S. Teir, J. Salminen, C.J. Fogelholm, R. Zevenhoven, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 47, 7104 (2008)
Y. Sun, M.S. Yao, J.P. Zhang, G. Yang, Chem. Eng. J. 173, 437 (2011)
W.J. Bao, H.Q. Li, Y. Zhang, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49, 2055 (2010)
W.J. Bao, H.Q. Li, Y. Zhang, Greenh. Gases. 4, 785 (2014)
J. Yu, K. Wang, Energy Fuels 25, 5483 (2011)
S.C. Tian, J.G. Jiang, X.J. Chen, F. Yan, K.M. Li, Chem. Sustain. Chem. 6, 2348 (2013)
W.J.J. Huijgen, R.N.J. Comans, Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 2790 (2006)
W.J.J. Huijgen, G.J. Ruijg, R.N.J. Comans, G.J. Witkamp, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 9184 (2006)
W.J.J. Huijgen, R.N.J. Comans, G.J. Witkamp, Energy Convers. Manag. 48, 1923 (2007)
J.K. Stolaroff, G.V. Lowry, D.W. Keith, Energy Convers. Manag. 46, 687 (2005)
E.E. Chang, C.H. Chen, Y.H. Chen, S.Y. Pan, P.C. Chiang, J. Hazard. Mater. 186, 558 (2011)
S.Y. Pan, E.G. Eleazar, E.E. Chang, Y.P. Lin, H. Kim, P.C. Chiang, Appl. Energy 148, 23 (2015)
S.Y. Pan, Y.H. Chen, C.D. Chen, A.L. Shen, M. Lin, P.C. Chiang, Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 12380 (2015)
S.Y. Pan, A.M.L. Lafuente, P.C. Chiang, Appl. Energy 170, 269 (2016)
R.M. Santos, D. François, G. Mertens, J. Elsen, T.V. Gerven, Appl. Thermal. Eng. 5, 154 (2013)
S. Eloneva, A. Said, C.J. Fogelholm, R. Zevenhoven, Appl. Energy 90, 329 (2012)
N.J. Du, L.J. Wang, Inorg. Chem. Ind. 41, 38 (2009)
H.P. Mattila, R. Zevenhoven, Chem. Sustain. Chem. 7, 903 (2014)
Y.Z. Chen, X.Q. Wang, Petro-Chem. Equip. Technol. 18, 13 (1997)
S.Q. Yuan, W.L. Cao, Fluid Eng. 20, 35 (1999)
Q. Zheng, P. Liu, Y. Fang, Mod. Mach. 6, 87 (2010)
Q.S. Ding, J. Filtr. Sep. 19, 41 (2009)
S. Datta, M.P. Henry, Y.J. Lin, A.T. Fracaro, C.S. Millard, S.W. Snyder, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 15177 (2013)
C.M. Ma, Q.S. Ge, Adv. Clim. Change Res. 5, 92 (2014)
M.A. Gadalla, Z. Olujic, P.J. Jansens, Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 6860 (2005)
R. Smith, O. Delaby, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 69A, 492 (1991)
O. Delaby, R. Smith, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 73B, 21 (1995)
J. Xu, Y. Fan, Prog. Res. Clim. Change 9, 341 (2013)
W. Wang, D. Jiang, D.J. Chen, Z.B. Chen, W.J. Zhou, B. Zhu, J. Clean. Prod. 112, 787 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21300212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Available online at http://springer.longhoe.net/journal/40195
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CY., Bao, WJ., Guo, ZC. et al. Carbon Dioxide Sequestration via Steelmaking Slag Carbonation in Alkali Solutions: Experimental Investigation and Process Evaluation. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 31, 771–784 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-017-0694-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-017-0694-0