Abstract
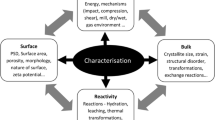
While iron is a pivotal metal that is exploited commercially, its extraction from ores, subsequent processing and purification follows a series of steps, and material characterization in terms of physical, chemical and mineralogical features and behavior is imperative at each stage. Some characterization tests rely solely on physical measurements, while others are based on optical and chemical data. Thus, employing these techniques is critical for gaining a complete understanding of ore characteristics such as physical, chemical, textural, mineralogical, granulometric, etc., in order to forecast its behavior during processing operations, and as a result, to optimize the process. Consequently, this review highlights some of the primary characterization tests such as SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy), XRD (X-ray Diffraction), and FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy) used in iron ore processing and their significance in analyzing various properties such as elemental composition, porosity, mineral association, and liberation, among others, while also introducing additional and emerging techniques used in iron ore mineralogical assays and processing operations. Characterization tests are presented used not just for high-grade iron ores, but also for low-grade discard materials such as fines and tailings. While optical microscopy and SEM aid in micro-morphological examinations, and XRD, FTIR, and other techniques aid in detailed chemical investigations, TGA and BET assist in physical characterization. A combination of these techniques may be deemed ideal for gaining a thorough understanding of ore characteristics as well as ore processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K. Dwari, D.S. Rao, P.S.R. Reddy, Mineralogical and beneficiation studies of a low grade iron ore sample. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. D 95(2), 115–123 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-014-0045-5
M. Manjunatha et al., XRD, internal field-NMR and Mössbauer spectroscopy study of composition, structure and magnetic properties of iron oxide phases in iron ores. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8(2), 2192–2200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.01.022
O.J. Kolawole, A.A. Akanni, B.S. Ameenullahi, A.A. Adediran, Preliminary characterisation of iron ores for steel making processes. Proc. Manuf. 35, 1123–1128 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.07.020
S. Patra, A. Pattanaik, V. Rayasam, Characterisation of low-grade Barsua iron ore fines and identification of possible beneficiation strategies. Can. Metall. Q. 58(1), 28–45 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/00084433.2018.1516598
A.B. Kotta, S.K. Karak, M. Kumar, Chemical, physical, thermal, textural and mineralogical studies of natural iron ores from Odisha and Chhattisgarh regions, India. J. Cent. South Univ. 25(12), 2857–2870 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3958-6
I.D. Delbem, R. Galéry, P.R.G. Brandão, A.E.C. Peres, Semi-automated iron ore characterisation based on optical microscope analysis: Quartz/resin classification. Miner. Eng. 82, 2–13 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2015.07.021
O.D.F.M. Gomes, J.C.A. Iglesias, S. Paciornik, M.B. Vieira, Classification of hematite types in iron ores through circularly polarized light microscopy and image analysis. Miner. Eng. 52, 191–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2013.07.019
T. Chaudhuri, R. Mazumder, M. Arima, Petrography and geochemistry of Mesoarchaean komatiites from the eastern Iron Ore belt, Singhbhum craton, India, and its similarity with ‘Barberton type komatiite.’ J. Afr. Earth Sci. 101, 135–147 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAFREARSCI.2014.09.014
E.N. Ndime, S. Ganno, L.S. Tamehe, J.P. Nzenti, Petrography, lithostratigraphy and major element geochemistry of Mesoarchean metamorphosed banded iron formation-hosted Nkout iron ore deposit, north western Congo craton, Central West Africa. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 148, 80–98 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAFREARSCI.2018.06.007
T. Teutsong, J.P. Temga, A.A. Enyegue, N.N. Feuwo, D. Bitom, Petrographic and geochemical characterization of weathered materials developed on BIF from the Mamelles iron ore deposit in the Nyong unit, South-West Cameroon. Acta Geochim. 40(2), 163–175 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-020-00421-7
G.M. da Costa, V. Barrón, C.M. Ferreira, J. Torrent, The use of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for the characterization of iron ores. Miner. Eng. 22(14), 1245–1250 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2009.07.003
F. Nellros, M.J. Thurley, Automated image analysis of iron-ore pellet structure using optical microscopy. Miner. Eng. 24(14), 1525–1531 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2011.08.001
E. Donskoi et al., Automated optical image analysis of goethitic iron ores. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. 131(1), 14–24 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/25726641.2019.1706375
S. Roy, Recovery improvement of fine magnetic particles by floc magnetic separation. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 33(3), 170–179 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2011.562948
D. Wang, J. Pan, D. Zhu, Z. Guo, C. Yang, Z. Yuan, An efficient process to upgrade siderite ore by pre oxidation-magnetization roasting-magnetic separation-acid leaching. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 19, 4296–4307 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.008
R.K. Dishwar, A.K. Mandal, O.P. Sinha, Studies on reduction behaviour of highly fluxed iron ore pellets for application in steelmaking. Mater. Today Proc. 46, 1471–1475 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2020.10.886
J.C.Ø. Andersen, G.K. Rollinson, B. Snook, R. Herrington, R.J. Fairhurst, Use of QEMSCAN® for the characterization of Ni-rich and Ni-poor goethite in laterite ores. Miner. Eng. 22(13), 1119–1129 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MINENG.2009.03.012
K. Guanira et al., Methodological approach for mineralogical characterization of tailings from a Cu(Au, Ag) skarn type deposit using QEMSCAN (quantitative evaluation of minerals by scanning electron microscopy). J. Geochemical Explor. 209, 106439 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GEXPLO.2019.106439
L. Zhang, K. Qiu, Z. Hou, F. Pirajno, E. Shivute, Y. Cai, Fluid-rock reactions of the Triassic Taiyangshan porphyry Cu-Mo deposit (West Qinling, China) constrained by QEMSCAN and iron isotope. Ore Geol. Rev. 132, 104068 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.OREGEOREV.2021.104068
S.K. Jena, H. Sahoo, S.S. Rath, D.S. Rao, S.K. Das, B. Das, Characterization and processing of iron ore slimes for recovery of iron values. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 36(3), 174–182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2014.898300
J. Zhao, K. Ni, Y. Su, Y. Shi, An evaluation of iron ore tailings characteristics and iron ore tailings concrete properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 286, 122968 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CONBUILDMAT.2021.122968
P. Prusti, S.S. Rath, N. Dash, B.C. Meikap, S.K. Biswal, Pelletization of hematite and synthesized magnetite concentrate from a banded hematite quartzite ore: A comparison study. Adv. Powder Technol. 32(10), 3735–3745 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.08.025
J.S. Guiral-Vega, L. Pérez-Barnuevo, J. Bouchard, A. Ure, E. Poulin, C. Du Breuil, Particle-based characterization and classification to evaluate the behavior of iron ores in drum-type wet low-intensity magnetic separation. Miner. Eng. 186, 107755 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MINENG.2022.107755
N. Khajehzadeh, O. Haavisto, L. Koresaar, On-stream mineral identification of tailing slurries of an iron ore concentrator using data fusion of LIBS, reflectance spectroscopy and XRF measurement techniques. Miner. Eng. 113, 83–94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MINENG.2017.08.007
M. Omran, T. Fabritius, A.M. Elmahdy, N.A. Abdel-Khalek, M. El-Aref, A.E.H. Elmanawi, XPS and FTIR spectroscopic study on microwave treated high phosphorus iron ore. Appl. Surf. Sci. 345, 127–140 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.209
S. Yuan, H. **ao, R. Wang, Y. Li, P. Gao, Improved iron recovery from low-grade iron ore by efficient suspension magnetization roasting and magnetic separation. Miner. Eng. 186, 107761 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MINENG.2022.107761
C. Scharm et al., Direct reduction of iron ore pellets by H2 and CO: In-situ investigation of the structural transformation and reduction progression caused by atmosphere and temperature. Miner. Eng. 180, 107459 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MINENG.2022.107459
J.P.R. de Villiers, L. Lu, Quantitative XRD analysis and evaluation of iron ore, sinter, and pellets. Iron Ore Mineral. Process. Environ. Sustain. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820226-5.00004-5
A.A. Shaltout, M.M. Gomma, M.W. Ali-Bik, Utilization of standardless analysis algorithms using WDXRF and XRD for Egyptian iron ore identification. X-Ray Spectrom. 41(6), 355–362 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/xrs.2410
J.P.R. De Villiers, L. Lu, XRD analysis and evaluation of iron ores and sinters. Iron Ore Mineral. Process. Environ. Sustain. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-78242-156-6.00003-4
M.I. Pownceby, S. Hapugoda, J. Manuel, N.A.S. Webster, C.M. MacRae, Characterisation of phosphorus and other impurities in goethite-rich iron ores – Possible P incorporation mechanisms. Miner. Eng. 143, 106022 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2019.106022
G. Tiu, Y. Ghorbani, N. Jansson, C. Wanhainen, N.J. Bolin, Ore mineral characteristics as rate-limiting factors in sphalerite flotation: Comparison of the mineral chemistry (iron and manganese content), grain size, and liberation. Miner. Eng. 185, 107705 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MINENG.2022.107705
S. Dwivedy, P.R. Sahoo, Geology and trace element geochemistry of the albitite hosted iron ore mineralization around Khetri copper deposit, India: Implications for an IOA type deposit. Ore Geol. Rev. 138, 104343 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104343
I.C. Ferreira et al., Reuse of iron ore tailings for production of metakaolin-based geopolymers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 18, 4194–4200 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.03.192
Y. Mochizuki, N. Tsubouchi, Removal of gangue components from low-grade iron ore by hydrothermal treatment. Hydrometallurgy 190, 105159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105159
J.C.Á. Iglesias et al., Automatic characterization of iron ore by digital microscopy and image analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 7(3), 376–380 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.06.014
J. Yu, Z. Guo, H. Tang, Dephosphorization treatment of high phosphorus oolitic iron ore by hydrometallurgical process and leaching kinetics. ISIJ Int. 53(12), 2056–2064 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.53.2056
L.D. Santos, P.R.G. Brandao, Morphological varieties of goethite in iron ores from Minas Gerais, Brazil. Miner. Eng. 16(11 SUPPL.), 1285–1289 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2003.07.007
D.S. Rao, T.V.V. Kumar, S.S. Rao, S. Prabhakar, G.B. Raju, Mineralogy and Geochemistry of a low grade iron ore sample from bellary-hospet sector, India and their implications on beneficiation. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 08(02), 115–132 (2009). https://doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2009.82011
G. Liu, V. Strezov, J.A. Lucas, L.J. Wibberley, Thermal investigations of direct iron ore reduction with coal. Thermochim. Acta 410, 133–140 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(03)00398-8
E. Donskoi et al., Iron ore textural information is the key for prediction of downstream process performance. Miner. Eng. 86, 10–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2015.11.009
A. Poliakov, E. Donskoi, Separation of touching particles in optical image analysis of iron ores and its effect on textural and liberation characterization. Eur. J. Mineral. 31(3), 485–505 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/2019/0031-2844
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, literature review, and writing-original draft preparation contributed by MP; writing—original draft preparation contributed by HMJ; writing—review and editing contributed by HV.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Poojari, M., Vardhan, H. & Jathanna, H.M. Iron Ore Characterization Techniques in Mineral Processing. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 105, 543–551 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-023-00483-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-023-00483-w