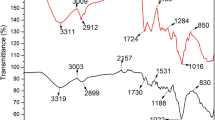
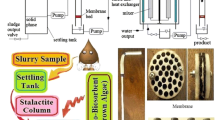
Abstract
Contamination of water sources with heavy metals is a very important pollution problem in the current scenario. Biosorption is an effective method for the removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters. In this study, the removal of Nickel(II) ions from electroplating industrial wastewater using biosorbent prepared from fresh water algal biomass Zygnema was investigated under batch mode. The sorption efficiency of nickel on Zygnema sp. was evaluated as a function of time, pH and sorbent dosage. The Nickel(II) uptake was dependent on initial pH with pH 3 being the optimum value. For 100 mg/L initial Nickel(II) concentration, sorption equilibrium was attained at a contact time of 100 min. The sorbent dosage affected the biosorption efficiency and maximum removal of 76.4 % was obtained at a dosage of 7.5 g/L. From the performance studies, algal biosorbent Zygnema is found to be a valuable material for the removal of Nickel from industrial wastewater and a better substitute for the conventional adsorbents.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- X:
-
Weight of substance adsorbed
- M:
-
Weight of adsorbent
- Ce :
-
Concentration remaining in solution
- R :
-
Gas constant (8.314 J/mol K)
- T :
-
Absolute temperature, K
- b & qmax :
-
Langmuir isotherm constants
- Co :
-
Initial concentration of the adsorbate in solution
- K:
-
Freundlich adsorption capacity
- n:
-
Freundlich adsorption intensity
- qt (mg/g):
-
Amount of adsorbate adsorbed at time (t), min
- qe :
-
Biosorption capacity at equilibrium (mg/g)
- k1 :
-
Pseudo-first-order rate constant, min−1
- t:
-
Contact time, min
- k2 :
-
Pseudo-second-order rate constant
References
Z. Aksu, G. Dönmez, Binary biosorption of cadmium(II) and nickel(II) onto dried Chlorella vulgaris: Co-ion effect on mono-component isotherm parameters. Process Biochem. 41, 860–868 (2006)
J.P.K. Wong, Y.S. Wong, N.F.Y. Tam, Nickel biosorption by two Chlorella species, C. Vulgaries (a commercial species) and C. Miniata (a local isolate). Bioresour. Technol. 73, 133–137 (2000)
S. Congeevarama, S. Dhanarani, J. Park, M. Dexilin, K. Thamaraiselvi, Biosorption of chromium and nickel by heavy metal resistant fungal and bacterial isolates. J. Hazard. Mater. 146, 270–277 (2007)
S. Schiewer, B. Volesky, Modelling of the proton–metal ion exchange in biosorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 3049–3058 (1995)
B. Volesky, Removal and recovery of heavy metals by biosorption, in Biosorption of Heavy Metals, ed. by B. Volesky (CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, 1990), pp. 7–43
B. Volesky, Sorption and Biosorption (BV Sorbex, St. Lambert, 2003), pp. 311–316
P. Loderio et al., Biosorption of cadmium by the protonated microalga Sargassum muticum: binding analysis with a non ideal, competitive and thermodynamically consistent adsorption model. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 289(2), 352–358 (2005)
G.J. Ramelow, D. Fralick, Y. Zhao, Factors affecting the uptake of aqueous metal ions by dried seeweed biomass. Microbios 72, 81–93 (1992)
N. Ahalya, T.V. Ramachandra, R.D. Kanamadi, Biosorption of heavy metals. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 7(4), 71–79 (2003)
K. Chojnacka, A. Chojnacki, H. Gorecka, Biosorption of Cr3+, Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions by blue–green algae Spirulina sp.: kinetics, equilibrium and the mechanism of the process. Chemosphere 59, 75–84 (2005)
G.C. Donmez, Z. Aksu, A. Ozturk, T. Kutsal, A comparative study on heavy metal biosorption characteristics of some algae. Process Biochem. 34, 885–892 (1995)
I. Reya Isaac, M. Lakshmi Prabha, Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of Cr (VI) by non-living mycelial suspensions of Aspergillus niger. Int. J. Pharm. Bio. Sci. 2(3), B212–B222 (2011)
A. Rezaee, B. Ramavandi, F. Ganati, M. Ansari, A. Solimanian, Biosorption of mercury by biomass of filamentous algae Spirogyra species. J. Biol. Sci. 6, 695–700 (2006)
E. Thirunavukkarasu, K. Palanivelu, Biosorption of Cr(VI) from plating effluent using marine algal mass. Indian J. Biotechnol. 6, 359–364 (2007)
H. Yin, B. He, H. Peng, J. Ye, F. Yang, N. Zhang, Removal of Cr(VI) and Ni(II) from aqueous solution by fused yeast: study of cations release and biosorption mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 158, 568–576 (2008)
N.R. Bishnoi, R. Kumar, S. Kumar, S. Rani, Biosorption of Cr(III) from aqueous solution using algal biomass Spirogyra spp. J. Hazard. Mater. 145(1–2), 142–147 (2007)
S.M. Hamza, H.F. Ahmed, A.M. Ehab, F.M. Mohammad, Optimization of cadmium, zinc and copper biosorption in an aqueous solution by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Am. Sci. 6(12), 597–604 (2010)
M. Ghasemi, M. Rahimnejad, G.D. Najafpour, M. Sedighi, M. Asadi, B. Hashemiyeh, Investigation on batch biosorption of lead using Lactobacillus bulgaricus in an aqueous phase system. Biokemistri 20(2), 41–46 (2008)
R. Soni, A. Gupta, Batch biosorption studies of Cr(VI) by using Zygnema (green algae). J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 3(6), 950–960 (2011)
M.Y. Arica, I. Tuzun, Process Biochem. 40, 2351–2358 (2005)
S. Karthikeyan, R. Balasubramanian, C.S.P. Iyer, Evaluation of the marine algae Ulva fasciata and Sargassum sp. for the biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 452–455 (2007)
S. Ahmady-Asbchin, Y. Andres, C. Gerente, P.L. Cloirec, Biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by Fucus serratus: surface characterization and sorption mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 6150–6155 (2008)
M.D. Mullen, D.C. Wolf, F.G. Ferris, T. Beveridge, C.A. Flemming, G.W. Bailey, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55, 3143–3149 (1989)
F.N. Acar, E. Malkoc, The removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions by Fagus orientalis. Bioresour. Technol. 94(12), 13–15 (2004)
L.G. Gazso, The key microbial processes in the removal of toxic metals and radionuclides from the environment. Cent. Eur. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 7(3–4), 178–185 (2001)
I. Langmuir, Adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 40(9), 1361–1403 (1918)
H. Freundlich, Colloid and Capillary Chemistry (E.P. Dutton and Co., New York, 1928)
M.I. Tempkin, V. Pyzhev, Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys. Chim. USSR 12, 327–356 (1940)
D. Sarkar, D.K. Chattoraj, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 157, 219–226 (1993)
Y.S. Ho, G. McKay, J. Environ. Sci. Health 34, 1179–1204 (1999)
Y.S. Ho, G. McKay, Proc. Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Tamilnadu State Council for Science and Technology for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivaprakash, K., Blessi T.L., A. & Madhavan, J. Biosorption of Nickel from Industrial Wastewater using Zygnema sp.. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 96, 319–326 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-015-0131-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-015-0131-1