Abstract
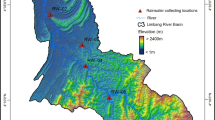
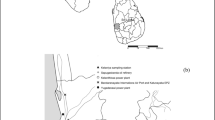
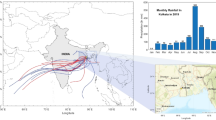
The composition of rainwater is highly dependent upon the air quality of the area. Thirty-four samples of monsoon rainwater were obtained during the monsoon season of June to September, 2015, in Bangladesh’s heavily polluted megacity, Dhaka, and a regional background island area, Bhola. The physical properties of rainwater, such as electrical conductivity and pH, were evaluated. The concentrations of various cations and trace metals such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and Zn, Fe, Mn, respectively, in rainwater were determined using atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). In addition, ion chromatography was used to calculate concentrations of anions such as Cl−, SO42−, NO3−, and HCO3. The source proportion of chemical species in rainwater was determined using percent source contribution, correlation analysis, enrichment factor analysis, and air mass trajectory analysis. Among Dhaka and Bhola, there were differences in physicochemical properties and anthropogenic contribution. The average concentration of SO42− in rainwater from Dhaka and Bhola was 12.53 and 8.48 μeq L−1, respectively, while the NO3− concentrations were 40.64 and 33.93 μeq L−1. Dhaka’s rainwater contained 8.85 mg L−1 of total dissolved solids, and Bhola’s rainwater contained 6.78 mg L−1. Zn was found in higher concentration in Dhaka’s rain water, while Fe was found in higher concentration in Bhola. Neutralization factor analysis revealed that Ca2+ and Mg2+ were the predominant neutralization components of rainwater at both the locations. The obtained high enrichment factors for SO42− and NO3− were a strong indicator of anthropogenic origins. It is the first time that the aqueous atmospheric chemistry of monsoon rainwater in Bangladesh has been reported over urban and background locations.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed M, Hossain A, Akther T, Shohel M, Salam A (2018) Chemical composition and source identification of fog water at an indo-gangetic plain (IGP) outflow location (Coastal Bhola Island). Bangladesh J Environ Pollut Manag 1(1):104
Akther A, Ahmed M, Shohel M, Ferdousi FK, Salam A (2019) Particulate matters and gaseous pollutants in indoor environment and and association of ultra-fine particulate matters (PM1) with lung function. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(6):5475–5484
Atkins W (1947) Electrical conductivity of river, rain and snow water. Nature 159:674
Avila A, Alarcon M (1991) Relationship between precipitation chemistry and meteorological situations at a ruralsite in NE Spain. Atmos Environ 33(11):1663–1677
Beysens D, Ohayon C, Muselli M, Clus O (2006) Chemical and biological characteristics of dew and rainwater in an urban coastal area (Bordeaux, France). Atmos Environ 40(20):3710–3723
Cao YZ, Wang S, Zhang G, Luo J, Lu S (2009) Chemical characteristics of wet precipitation at an urban site of Guangzhou, South China. Atmos Res 94:462–469
Dikaiaka JG, Tsitouris CG, Siskos PA, Melissos DA, Nastos P (1990) Rainwater composition in Athens. Greece Atmos Environ 24(B1):171–176
Feng Z, Huang Y, Feng Y, Ogura N, Zhang F (2001) Chemical composition of precipitation in Bei**g area, northern China. Water Air Soil Pollut 125:345–356
Fishman MJ, Downs SC (1996) Methods for analysis of selected metals in water by atomic absorption. US Government Printing Office, Washington D.C. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 1540-C
Furiness C, Smith L, Ran L, Cowling E (1998) Comparison of emissions of N and sulfur oxides to deposition of nitrate and sulfate in the USA by state in 1990. Environ Pollut 102:313–320
Galloway JN, Likens GE, Edgerton ES (1976) Acid precipitation in the northeastern United States; pH and acidity. Science 194:722–724
Han G, Tang Y, Wu Q, Tan Q (2011) Acid rain and alkalization in southwestern China: chemical and strontium isotope evidence in rainwater from Guiyang. J Atmos Chem 68:139–155
Hileman B (1981) Particulate matter: the inevitable variety. Environ Sci Technol 15:983–986
Ito M, Mitchel MJ, Driscoll CT (2002) Spatial patterns of precipitation quantity and chemistry and air temperature in the Adirondack region of New York. Atmos Environ 36(6):1051–1062
Jalali M, Kolahchi Z (2008) Groundwater quality in an irrigated, agricultural area of Northern Malayer, Western Iran. Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems 80:95–105
Jawad AO, Joshi H (2006) Chemical composition of rainwater in a tropical urban area northern India. Atmos Environ 40:6886–6891
Keene WC, Galloway JN, Holden JD Jr (1983) Measurement of weak organic acidity in precipitation from remote areas of the world. J Geophys Res 88:5122–5130
Kidron GJ, Starinsky A (2012) Chemical composition of dew and rain in an extreme desert (Negev): cobbles serve as sink for nutrients. J Hydrol 420–421:284–291
Kulshrestha UC, Sarkar AK, Srivastava SS, Parashar DC (1996) Investigation into atmospheric deposition through precipitation studies at New Delhi (India). Atmos Environ 30(24):4149–4154
Kulshrestha UC, Kulshrestha MJ, Sekar R, Sastry GSR, Vairamani M (2003) Chemical characteristics of rainwater at an urban site of south-central India. Atmos Environ 37(21):3019–3026
Kuylenstierna JCI, Hicks WK, Cinderby S, Cambridge H (1998) Critical loads for N deposition and their exceedance at European scale. Environ Pollut 102:591–598
Larssen T, Carmichael GR (2000) Acid rain and acidification in China: the importance of base cation deposition. Environ Pollut 110:89–102
Larssen T, Seip HM, Semb A, Mulder J (1999) Acid deposition and its effects in China: an overview. Environ Sci Policy 2:9–24
Lee BK, Hong SH, Lee DS (2000) Chemical composition of precipitation and wet deposition of major ions on the Korean peninsula. Atmos Environ 34(4):563–575
Lekouch I, Mileta M, Muselli M (2010a) Comparative chemical analysis of dew and rainwater. Atmos Res 95(23):224–234
Lekouch I, Muselli M, Mileta M, Milimouck-Melnytchouk I, Sojat V (2010b) Physical and chemical properties of dew and rainwater in the Dalmatian coast, Croatia. In: 5th International conference on fog, fog collection and dew, Munster, Germany.
Lu X, Li LY, Li N, Yang G, Luo D, Chen J (2011) Chemical characteristics of spring rainwater of **’an city. NW China Atmos Environ 45(28):5058–5063
Migliavacca D, Teixeira EC, Wiegand F, Machado ACM, Sanchez Z (2005) Atmospheric precipitation and chemical composition of an urban site, Guaiba hydrographic basin, Brazil. Atmos Environ 39:1829–1844
Mouli PC, Mohan SV, Reddy SJ (2005) Rainwater chemistry at a regional representative urban site: influence of terrestrial sources on ionic composition. Atmos Environ 39(6):999–1008
Munger JW, Eisenreich SJ (1983) Continental-scale variations in precipitation chemistry. Environ Sci Technol 17:32–42
Nriagu JO, Pacyna JM (1998) Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water, and soils by trace metals. Nature 333(6169):134–139
Okuda T, Iwase T, Ueda H (2005) Longterm trend of chemical constituents in precipitation in Tokyo metropolitan area, Japan, from 1990 to 2002. Sci Total Environ 339(1):127–141
Petrovich MB, Filho VRA, Neto JAG (2007) Direct determination of calcium in milk by atomic absorption spectrometry using flow injection analysis. Eclet Quim 32(3):25–30
Pfaff JD (1993) Determination Of Inorganic Anions By Ion Chromatography. Environmental Monitoring Systems Laboratory, Office Of Research And Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Cicinnati, Ohio.
Polkowska Ż, Błaś M, Klimaszewska K, Sobik M, Małek S, Namieśnik J (2008) Chemical characterization of dew water collected in different geographic regions of poland. Sensors 8(6):4006–4032
Puxbaum H, Simeonov V, Kalina MF (1998) Ten years trends (1984–1993) in the precipitation chemistry in central Austria. Atmos Environ 32:193–202
Rubio MA, Lissi E, Herrera N, P´erez V, Fuentes N (2012) Phenol and Nitrophenols in the air and dew waters of Santiago de Chile. Chemosphere 86(10):1035–1039
Safai PD, Rao PSP, Momin GA, Ali K, Chate DM, Praveen PS (2004) Chemical composition of precipitation during 1984–2002 at Pune. India Atmos Environ 38(12):1705–1714
Salam A, Bauer H, Kassin K, Ullah SM, Puxbaum H (2003a) Aerosol chemical characteristics of a mega-city in Southeast Asia (Dhaka–Bangladesh). Atmos Environ 37(18):2517–2528
Salam A, Bauer H, Kassin K, Ullah SM, Puxbaum H (2003b) Aerosol chemical characteristics of an island site in the Bay of Bengal (Bhola-Bangladesh). J Environ Monitor 5(3):483–490
Salam A, Ullah MB, Islam MS, Salam MA, Ullah SM (2013) Carbonaceous species in total suspended particulate matters at different urban and suburban locations in the greater Dhaka region, Bangladesh. Air Qual Atmos Health 6:239–245
Samiha R, Ahmed M, Shohel M, Salam A (2018) Chemical composition and source characterization of hailstones in Dhaka, Bangladesh. J Geosci and Environ Protec 6:71–82
Sasakawa M, Uematsu M (2005) Relative contribution of chemical composition to acidification of sea fog (stratus) over the northern North Pacific and its marginal seas. Atmos Environ 39(7):1357–1362
Sequeira R, Lai CC (1998) Small-scale spatial variability in the presentative ionic composition of rainwater within urban Hong Kong. Atmos Environ 32:133–144
Shen Z, Zhang L, Cao J, Tian J (2012) Chemical composition, sources, and deposition fluxes of water-soluble inorganic ions obtained from precipitation chemistry measurements collected at an urban site in northwest China. J Environ Monitor 14:3000–3008
Shohel M, Simol HA, Reid E, Reid JS, Salam A (2017) Dew water chemical composition and source characterization in the IGP outflow location (coastal Bhola, Bangladesh). Air Qual Atmos Health 10:981–990
Shohel M, Kistler M, Rahman MA, Kasper-Giebl A, Reid JS, Salam A (2018) Chemical characterization of PM2.5 collected from a rural coastal island of the Bay of Bengal (Bhola, Bangladesh). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:558–4569
Takeuchi M, Okochi H, Igawa M (2000) A study on chemical components and acidification mechanism of dew-water. J Japan Soc Atmos Environ 35(3):158–169
Takeuchi M, Okochi H, Igawa M (2003) Deposition of coarse soil particles and ambient gaseous components dominating dew water chemistry. J Geophys Res 108(10):4319
Tang A, Zhuang G, Wang Y, Yuan H, Sun Y (2005) The chemistry of precipitation and its relation to aerosol in Bei**g. Atmos Environ 39:3397–3406
Taylor SR (1964) Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: a new table. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 28:1273–1285
Torseth K, Semb A (1998) Deposition of N and other major inorganic compounds in Norway, 1992–1996. Environ Pollut 102:299–304
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW (1997) Human alteration of the global N cycle: sources and consequences. Ecol Appl 7:737–750
Wahid A (2006) Influence of atmospheric pollutants on agriculture in develo** countries: a case study with three new varieties in Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 371(13):304–313
Wilson EJ, Skeffington RA (1994) The effects of excess N deposition on young Norway spruce trees. Part II the Vegetation Environ Pollut 86:153–160
**ao HW, **ao HY, Long AM, Wang YL, Liu CQ (2013) Chemical composition and source apportionment of rainwater at Guiyang, SW China. J Atmos Chem 70:269–281
Yadav S, Kumar P (2014) Pollutant scavenging in dew water collected from an urban environmentand related implications. Air Qual Atmos Health 7(4):559–566
Yang F, Tan J, Shi ZB, Cai Y (2012) Five-year record of atmospheric precipitation chemistry in urban Bei**g, China. Atmos Chem Phys 12:2025–2035
Yu S, Gao C, Cheng Z, Cheng X (1998) An analysis of chemical composition of different rain types in ‘Minnan Golden Triangle’ region in the southeastern coast of China. Atmos Res 47–48:245–269
Zhang J (1994) Atmospheric wet deposition of nutrient elements: correlation with harmful biological blooms in Northwest Pacific Coastal zones. Ambio 23:464–468
Zhang M, Wang S, Wu F, Yuan X, Zhang Y (2007) Chemical composition of wet precipitation and anthropogenic influence at a develo** urban site in Southeastern China. Atmos Res 84:311–322
Zhao Y, Gao Y (2008) Mass size distributions of water soluble inorganic organic ions in size segregated aerosols over metropolitan Newark in the US East Coast. Atmos Environ 42:4063–4078
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Office of the Naval Research Global (ONRG Global), USA, for financial support to establish the Bhola Island Observatory and also to the Centre of Advanced Research in Science (CARs), Dhaka University, for hel** with chemical analysis. Authors acknowledge the support of the sampling crews at both Dhaka and Bhola Observatory.
Funding
This study was funded by Department of Chemistry, University of Dhaka.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Ta Yeong Wu.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, M., Islam, M.S., Akter, F. et al. Chemical composition and source apportionment of rainwater over Bangladesh during the monsoon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 8445–8456 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04507-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04507-y