Abstract
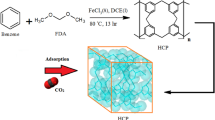
The removal of Cd(II) ions is studied using benzene-based hyper-cross-linked polymers. The FESEM, FTIR, BET, and EDX are used for recognition the morphology, functional group, surface area, and participant elements in the resin, respectively. The optimum values of initial concentration, time, pH, adsorbent dosage, and temperature are observed at 100 mg/L, 60 min, 7, 2 mL (0.08 g), and 25 °C, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity is attained at 40.19 mg/g. The R2 and uptake capacity of the pseudo-second-order obtained 0.993 and 43.672 mg/g, respectively, and implied that the adsorption was multi-layer. The R2 of the Freundlich isotherm is calculated at 0.994 and describing the non-homogenized surface of HCPs. The value of n calculated 1.313 and verified that the adsorbent is heterogeneous, and separation has occurred suitably. The E value in the D-R model has obtained 0.28 kJ/mol, which represents the behavior of the process is not chemical. Subsequently, the value of ΔHo calculated at -82.707 kJ/mol and proves the exothermic nature. ΔGo calculated 1.63, 4.46, and 7.29 kJ/mol at 25, 30, and 35℃, respectively, and the adsorption is non-spontaneous. The fabricated HCP has the highest uptake capacity of 40.1875 mg/g compare to the other adsorbents such as activated carbon, and even modified cross-linked resins. Benzene is utilized as the precursor due to its cheaper price than the other precursors such as polystyrene which makes the present process economic. Also, the Freidel-Craft reaction with the knitting strategy is selected for HCP synthesis which makes high the HCP surface area (823.892 m2/g).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelabu IO, Saleh TA, Garrison TF, Al Hamouz OCS (2020) Synthesis of polyamine-CNT composites for the removal of toxic cadmium metal ions from wastewater. J Mol Liq 297(1):18–27
Ahmad T, Danish M, Rafatullah M, Ghazali A, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ibrahim MNM (2012) The use of date palm as a potential adsorbent for wastewater treatment: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19(5):1464–1484
Aiyesanmi AF, Adebayo MA, Arowojobe Y (2020) Biosorption of lead and cadmium from aqueous solution in single and binary systems using avocado pear exocarp: effects of competing ions. Anal Lett 53(18):2868–2885
Alizadeh B, Delnavaz M, Shakeri A (2018) Removal of Cd (ӀӀ) and phenol using novel cross-linked magnetic EDTA/chitosan/TiO2 nanocomposite. Carbohyd Polym 181(1):675–683
Anito DA, Wang T-X, Liu Z-W, Ding X, Han B-H (2020) Iminodiacetic acid-functionalized porous polymer for removal of toxic metal ions from water. J Hazard Mater 400(1):123–188
Bekri-Abbes I, Bayoudh S, Baklouti M (2006) Converting waste polystyrene into adsorbent: potential use in the removal of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution. J Polym Environ 14(3):249–256
Boamah PO, Zhang Q, Hua M, Huang Y, Liu Y, Wang W, Liu Y (2014) Lead removal onto cross-linked low molecular weight chitosan pyruvic acid derivatives. Carbohyd Polym 110(1):518–527
Buema G et al (2020) Eco-friendly materials obtained by fly ash sulphuric activation for cadmium ions removal. Materials 13(16):35–84
Chen D et al (2016) Tunable porosity of nanoporous organic polymers with hierarchical pores for enhanced CO2 capture. Polym Chem 7(20):3416–3422
Chen G, Wang C, Tian J, Liu J, Ma Q, Liu B, Li X (2020) Investigation on cadmium ions removal from water by different raw materials-derived biochars. J Water Process Eng 35(1):12–23
Cochrane E, Lu S, Gibb S, Villaescusa I (2006) A comparison of low-cost biosorbents and commercial sorbents for the removal of copper from aqueous media. J Hazard Mater 137(1):198–206
Dardouri M, Ammari F, Amor AB, Meganem F (2018) Adsorption of cadmium (II), zinc (II) and iron (III) from water by new cross-linked reusable polystyrene adsorbents. Mater Chem Phys 216(1):435–445
Devatha C, Shivani S (2020) Novel application of maghemite nanoparticles coated bacteria for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution. J Environ Manage 258(1):11–21
Doshi B, Ayati A, Tanhaei B, Repo E, Sillanpää M (2018) Partially carboxymethylated and partially cross-linked surface of chitosan versus the adsorptive removal of dyes and divalent metal ions. Carbohyd Polym 197(1):586–597
El Hefnawy M, Shaaban A, ElKhawaga H (2020) Effective removal of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solution by a novel hyper cross-linked nanometer-sized chelating resin. J Environ Chem Eng 8(3):37–57
Feng K, Wen G (2017) Absorbed Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions in water by cross-linked starch xanthate. Int J Polym Sci 2017(1):1–9
Ghaemi A, Torab-Mostaedi M, Ghannadi-Maragheh M (2011) Characterizations of strontium (II) and barium (II) adsorption from aqueous solutions using dolomite powder. J Hazard Mater 190(1):916–921
Gonte R, Balasubramanian K (2016) Heavy and toxic metal uptake by mesoporous hypercrosslinked SMA beads: isotherms and kinetics. J Saudi Chem Soc 20(1):579–590
Haladu SA, Al-Hamouz OCS, Ali SA (2019) Adsorption of Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions from aqueous solutions by a cross-linked polysulfonate–carboxylate resin. Arab J Chem 12(8):2597–2607
Huang X, Gao N-Y, Zhang Q-L (2007) Thermodynamics and kinetics of cadmium adsorption onto oxidized granular activated carbon. J Environ Sci 19(11):1287–1292
Huseynli S, Bakhshpour M, Qureshi T, Andac M, Denizli A (2020) Composite polymeric cryogel cartridges for selective removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. Polymers 12(5):11–49
James AM, Harding S, Robshaw T, Bramall N, Ogden MD, Dawson R (2019) Selective environmental remediation of strontium and cesium using sulfonated hyper-cross-linked polymers (SHCPs). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(25):22464–22473
Kavand M, Eslami P, Razeh L (2020) The adsorption of cadmium and lead ions from the synthesis wastewater with the activated carbon: optimization of the single and binary systems. J Water Process Eng 34(1):1–8
Khataei MM, Yamini Y, Asiabi H, Shamsayei M (2020) Covalent organic framework and montomorillonite nanocomposite as advanced adsorbent: synthesis, characterization, and application in simultaneous adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. J Environ Health Sci Eng 18(2):1555–1567
Kim B, Lim S-T (1999) Removal of heavy metal ions from water by cross-linked carboxymethyl corn starch. Carbohyd Polym 39(3):217–223
Li B, Su F, Luo H-K, Liang L, Tan B (2011) Hypercrosslinked microporous polymer networks for effective removal of toxic metal ions from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 138(3):207–214
Li L, Han D, Wang M, Han Y, Yan H (2020) Molybdenum disulfide–hypercrosslinked polymer composite as an adsorbent for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water coupled with HPLC–FLD. Microchim Acta 187(4):1–8
Liao G et al (2020) Direct synthesis of hypercrosslinked microporous poly (para-methoxystyrene) for removal of iron (III) ion from aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 307(1):1–11
Ling X, Li H, Zha H, He C, Huang J (2016) Polar-modified post-cross-linked polystyrene and its adsorption towards salicylic acid from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 286(1):400–407
Luo Y, Li B, Wang W, Wu K, Tan B (2012) Hypercrosslinked aromatic heterocyclic microporous polymers: a new class of highly selective CO2 capturing materials. Adv Mater 24(42):5703–5707
Ma H, Chen J-J, Tan L, Bu J-H, Zhu Y, Tan B, Zhang C (2016) Nitrogen-rich triptycene-based porous polymer for gas storage and iodine enrichment. ACS Macro Lett 5(9):1039–1043
Mahmoud ME, Saleh MM, Zaki MM, Nabil GM (2020) A sustainable nanocomposite for removal of heavy metals from water based on crosslinked sodium alginate with iron oxide waste material from steel industry. J Environ Chem Eng 8(4):1–42
Masoumi H, Ghaemi A, Gilani HG (2021a) Exploiting the performance of Hyper-cross-linked polystyrene for removal of multi-component heavy metal ions from wastewaters. J Environ Chem Eng 9(4):1–17
Masoumi H, Ghaemi A, Gilani HG (2021b) Synthesis of polystyrene-based hyper-cross-linked polymers for Cd (II) ions removal from aqueous solutions: experimental and RSM modeling. J Hazard Mater 416(1):1–19
Moganavally P, Deepa M, Sudha P, Suresh R (2016) Adsorptive removal of lead and cadmium ions using cross-linked CMC schiff base: isotherm, kinetics and catalytic activity. Oriental J Chem 32(1):441454
Mone M, Lambropoulou DA, Bikiaris DN, Kyzas G (2020) Chitosan grafted with biobased 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural as adsorbent for copper and cadmium ions removal. Polymers 12(5):1173–1194
Monier M, Ayad D, Abdel-Latif D (2012) Adsorption of Cu (II), Cd (II) and Ni (II) ions by cross-linked magnetic chitosan-2-aminopyridine glyoxal Schiff’s base. Colloids Surf B 94(1):250–258
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2012) Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using meranti wood. Wood Sci Technol 46(3):221–241
Rozman U, Kalčíková G, Marolt G, Skalar T, Gotvajn AŽ (2020) Potential of waste fungal biomass for lead and cadmium removal: characterization, biosorption kinetic and isotherm studies. Environ Technol Innov 18(1):1–9
Sancey B, Trunfio G, Charles J, Minary J-F, Gavoille S, Badot P-M, Crini G (2011) Heavy metal removal from industrial effluents by sorption on cross-linked starch: Chemical study and impact on water toxicity. J Environ Manage 92(3):765–772
Shao Z-j, Huang X-l, Yang F, Zhao W-f, Zhou X-z, Zhao C-s (2018) Engineering sodium alginate-based cross-linked beads with high removal ability of toxic metal ions and cationic dyes. Carbohyd Polym 187(1):85–93
Sun C, Qu R, Ji C, Wang C, Sun Y, Yue Z, Cheng G (2006) Preparation and adsorption properties of crosslinked polystyrene-supported low-generation diethanolamine-typed dendrimer for metal ions. Talanta 70(1):14–19
Sun S, Wang A (2006) Adsorption properties of carboxymethyl-chitosan and cross-linked carboxymethyl-chitosan resin with Cu (II) as template. Sep Purif Technol 49(3):197–204
Taha A, Shreadah MA, Ahmed A, Heiba HF (2016) Multi-component adsorption of Pb (II), Cd (II), and Ni (II) onto Egyptian Na-activated bentonite; equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics, and application for seawater desalination. J Environ Chem Eng 4(1):1166–1180
Tasharrofi S et al (2020) Adsorption of cadmium using modified zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron composites as a reactive material for PRBs. Sci Total Environ 736(1):1–53
Torab-Mostaedi M, Asadollahzadeh M, Hemmati A, Khosravi A (2013) Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies for biosorption of cadmium and nickel on grapefruit peel. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 44(5):295–302
Vakili M, Rafatullah M, Ibrahim MH, Abdullah AZ, Salamatinia B, Gholami Z (2014) Oil palm biomass as an adsorbent for heavy metals. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 232(1):61–88
Waheed A, Baig N, Ullah N, Falath W (2021) Removal of hazardous dyes, toxic metal ions and organic pollutants from wastewater by using porous hyper-cross-linked polymeric materials: a review of recent advances. J Environ Manage 287(1):in press
Wang S, Song K, Zhang C, Shu Y, Li T, Tan B (2017) A novel metalporphyrin-based microporous organic polymer with high CO2 uptake and efficient chemical conversion of CO2 under ambient conditions. J Mater Chem A 5(4):1509–1515
Wang X, Liu Z, Zhou F, Huang J (2020) Imidazolium salt-incorporated postcross-linked porous polymers for efficient adsorption of rhodamine B and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 65(4):1850–1856
**ang L et al (2015) A luminescent hypercrosslinked conjugated microporous polymer for efficient removal and detection of mercury ions. Macromol Rapid Commun 36(17):1566–1571
Yang Z, Huang X, Yao X, Ji H (2018) Thiourea modified hyper-crosslinked polystyrene resin for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solutions. J Appl Polym Sci 13(1):55–68
Yang Z, Wu G, Li Q, Ai H, Yao X, Ji H (2021) Removal of various pollutants from wastewaters using an efficient and degradable hypercrosslinked polymer. Sep Sci Technol 56(5):860–869
Yılmaz SS, Kul D, Erdöl M, Özdemir M, Abbasoğlu R (2007) Synthesis of a novel crosslinked superabsorbent copolymer with diazacyclooctadecane crown ether and its sorption capability. Eur Polymer J 43(5):1923–1932
Yu C, Tang X, Liu S, Yang Y, Shen X, Gao C (2018) Laponite crosslinked starch/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels by freezing/thawing process and studying their cadmium ion absorption. Int J Biol Macromol 117(1):1–6
Yu Z et al (2017) Preparation and characterization of poly (maleic acid)-grafted cross-linked chitosan microspheres for Cd(II) adsorption. Carbohyd Polym 172(1):28–39
Yusuff AS, Popoola LT, Babatunde EO (2019) Adsorption of cadmium ion from aqueous solutions by copper-based metal organic framework: equilibrium modeling and kinetic studies. Appl Water Sci 9(4):1–11
Zeng L et al (2015) Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II) and Ni(II) ions by cross-linking chitosan/rectorite nano-hybrid composite microspheres. Carbohyd Polym 130(1):333–343
Zeng L et al (2021) Synthesis of cross-linked carboxyl modified polyvinyl alcohol and its application in selective adsorption separation of Cu(II) from Cd(II) and Ni(II). J Polym Environ 29(1):28–37
Zhang C, Liu Y, Li B, Tan B, Chen C-F, Xu H-B, Yang X-L (2012) Triptycene-based microporous polymers: synthesis and their gas storage properties. ACS Macro Lett 1(1):190–193
Zhang T, Huang J (2017) Tunable synthesis of the polar modified hyper-cross-linked resins and application to the adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 505(1):383–391
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Wang C, Wei Y (2014) Immobilization of 5-aminopyridine-2-tetrazole on cross-linked polystyrene for the preparation of a new adsorbent to remove heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 276(1):129–137
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Gobinath Ravindran.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masoumi, H., Ghaemi, A., Ghanadzadeh Gilani, H. et al. Benzene-based hypercross-linked polymers as a highly efficient adsorbent for cadmium removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 6315–6330 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03798-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03798-x