Abstract
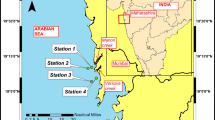
Today, there are undesired changes in the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water which impose a tremendous threat on aquatic species. Knowing the details of physical and chemical parameters and their behaviors such as temperature, salinity, density, dissolved oxygen, pH, electrical conductivity, turbidity, and chlorophyll-a for survivability of the aquatic ecosystem is essential. This paper discusses these parameters through a time series analysis of observation for the year 2007. The spatial and temporal variations of water chemical and physical parameters are investigated in nine stations in the northern part of the Persian Gulf. While many investigations have been carried out on the Persian Gulf, the innovation of this research is focusing on the northern part which is not or little discussed in the previous, historical studies, and barely data are available for this region. Analyses of the data in the study area show that the water is well mixed during the year due to the shallowness and tidal effects. Water is alkaline and tends to have a stable pH and relatively high salinity and temperature. pH is an important factor in determining the amount of toxic dissolved heavy metals in water. Turbidity and chlorophyll-a are low at the surface and increased toward the water bed as depth increases. The results of this paper are of the interest of the academic, business, and industrial communities and from a management point of view help the policymakers and environment managers to propose effective–strategic decisions that both help coastal communities and save aquatic life.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azizpour J, Chegini V, Khosravi M, (2014). Study of the physical oceanographic properties of the Persian Gulf, Strait of Hormuz and Gulf of Oman Based on PG-GOOS CTD measurements. J Persian Gulf, 5(8): 37–48. http://jpg.inio.ac.ir/browse.php?a_code=A-10-1-124&slc_lang=en&sid=1.
Barth HJ, Yar Khan N (2008) Biogeophysical setting of the Gulf. In: Abuzinada AH, Barth HJ, Krupp F, Böer B, Al-Abdessalaam TZ (eds) Protecting the Gulf’s marine ecosystems from pollution. Birkhäuser, Switzerland
Boyd, C.E., 1982. Liming fish ponds. J Soil Water Conserv, 37: 86–88. https://www.jswconline.org/content/37/2/86.
Chegini V, Hosseini S, (2012). Field investigation of physical parameters of coastal waters of Iran (case study: Bushehr bay, Persian Gulf). J Oceanograp 17(20), 125–143. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339726150_FIELD_INVESTIGATION_OF_PHYSICAL_PARAMETERS_OF_COASTAL_WATERS_OF_IRAN_CASE_STUDY_BOUSHEHR_BAY_PERSIAN_GULF.
Ebrahimi M, Moohebi Nouzar L, Ajlali Khaneghah K, Sanjani S (2008) Spatial and temporal variation of salinity, water density, and temperature of sea’s waters in Hormozgan Province, Hormuz Strait, and the Persian Gulf. Iranian Scient Fisheries J 17(3):1–14 ((In Persian))
Fatemi M, Abaie M (2003) Environmental conductivity of the Persian Gulf. (Naval Headquarters-Rapmi maritime area). Iranian Environmental Protection Organization, p 263
Fatemi M, Nabavi S, Vosoghi G, Fallahi M, Mohammadi M (2012) The relation between environmental parameters of Hormuzgan coastline in the Persian Gulf and the occurrence of the first harmful algal bloom of Cochlodinium polykrikoides (Gymnodiniaceae). Iranian J Fisheries Sci, 11. http://jifro.ir/article-1-621-fa.html.
Ghazban, F., 2009. Petroleum geology of the Persian Gulf, Tehran University Press, 707 p.
Ghotbeddin N, Mosavi Dehmordi L, (2019). Investigation of physicochemical factors, chl-a, and primary production in Mahshahr Creeks (Northwest Persian Gulf). Iranian J Fisheries Sci 18(1): 83–94. http://jifro.ir/article-1-3721-en.html
Johns WE, Yao F, Olson D, Josey S, Grist J, Smeed D (2003) Observations of seasonal exchange through the Straits of Hormuz and the inferred heat and freshwater budgets of the Persian Gulf. J Geophys Res Oceans. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JC001881
Lababpour A, (2015) Phytoplankton community and physical-chemical characteristics of Seawater in the Bandar Abbas Coastal Water, Persian Gulf: An environmental and process perspective. J Persian Gulf, 6(21), 39–50. http://jpg.inio.ac.ir/article-1-420-en.html
Miller G, Hackett D, Wolfe C, (2016). Living in the environment, Canadian edition, 4th ed., Nelson Education, ISBN: 0176756825, 9780176756826. https://www.amazon.com/LIVING-ENVIRONMENT-Wolfe-Tyler-Miller/dp/0176587187
Pous S, Carton X, Lazure P (2012) A process study of the tidal circulation in the Persian Gulf. Open Journal of Marine Sciences 2(4):131–140
ROPME Summer 2001 Cruise, 2001. Retrieved from: http://ropme.org/354_Summer2001_EN.clx.
Saleh A, Vajed Samiei J, Seyed Hashtroudi M (2017) Temporal variations of physical and chemical properties of seawater in Hengam coral patches, Persian Gulf. 5th International Conference on Oceanography and Marine Biology; 2017, October 18–20; Seoul, South Korea
Sheppard C, (1993). The physical environment of the Gulf relevant to marine pollution: An overview. J Marine Pollution Bull, 27, 3–8. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0025326X93900033
Sheppard C, Price A, Roberts C (1992) Marine ecology of the Arabian region. Academic. Press, London, p 360
Valinassab T, Daryanabard R, Dehghani R, Pierce GJ (2006) The abundance of demersal fish resources in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea. J Marine Biol Assoc United Kingdom 86(6):1455–1462
Valinassab T. et al., (2018) Stock assessment of demersal resources in the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea using the Swept Area Method. Final Report of the research project, Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute Publication. 192 p. http://fipak.areeo.ac.ir/site/catalogue/18837968
Zarepoor, V., Ezam, M., Allahyaribeik, S., 2015. Effect of thermocline formation on underwater acoustic waves propagation in the Persian Gulf. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 5(1), 1–14. ISSN 2251–6743. http://journals.srbiau.ac.ir/article_10875.html
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge their appreciation to Iran's National Elites Foundation for providing the grant, Iranian Fisheries Science Research Institute, Agricultural Research, Education and Extension Organization (AREEO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Maryam Shabani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afsharian, S., Khedri, P. & Valinassab, T. Spatial and temporal variation of physicochemical parameters in northern Persian Gulf. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1121–1130 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03187-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03187-4