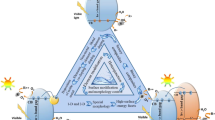
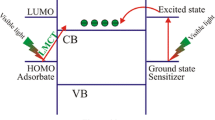
Abstract
The growth of highly ordered architectures of semiconductor metallic oxide photocatalyst has acknowledged great consideration due to natural growth along with exceptional morphology properties and potential application ways to resolve the problem of freshwater shortages in this world. Tungsten trioxide (WO3) is a well-known semiconductor photocatalyst due to its better response in solar spectrum, fine metal interactions, mechanical strength, high efficiency, harmlessness and cost-effectiveness. This review focuses on a precise and overall description of the recent literature relating pure and doped/composite WO3 catalyst, photocatalytic enhancement mechanism. Moreover, it will also elaborate the experimental conditions used photocatalyst synthesis processes, optimization of the parameters affecting the degradation efficiency of various dyes. Furthermore, strategies for improving photocatalytic activity of WO3 like metal do**, semiconductor coupling, metal sulfides and metal nitrides coupling are systematically summarized and highlighted. After this, future perspectives about advancement and applications are reviewed. It is expected that this review article could offer strategies for designing novel WO3-based photocatalysts which can have promising prospects of multifunctional applications to meet the imperative demands of highly efficient solar energy conversion.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari S, Sarkar D (2015a) Preparation of mixed semiconductors for methyl orange degradation. J Nanomater 2015:269019
Adhikari S, Sarkar D (2015b) Metal oxide semiconductors for dye degradation. Mater Res Bull 72:220–228
Adhikari R et al (2013) Microwave assisted hydrothermal synthesis of Ag/AgCl/WO3 photocatalyst and its photocatalytic activity under simulated solar light. J Solid State Chem 197:560–565
Bankura KP et al (2012) Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of dextran stabilized silver nanoparticles in aqueous medium. Carohydr Polym 89(4):1159–1165
Dinçer F et al (2016) Ozonation of reactive orange 122 using La3+ -doped WO3/TiO2/Sep photocatalyst. Ozone Sci Eng 38(4):1–11
Alfaro SO, Martínez-de La Cruz A (2010) Synthesis, characterization and visible-light photocatalytic properties of Bi2WO6 and Bi2 W2O9 obtained by co-precipitation method. Appl Catal A 383(1):128–133
Aslam I et al (2014a) Synthesis of three-dimensional WO3 octahedra: characterization, optical and efficient photocatalytic properties. RSC Adv 4(71):37914–37920
Aslam M et al (2014b) Morphology controlled bulk synthesis of disc-shaped WO3 powder and evaluation of its photocatalytic activity for the degradation of phenols. J Hazard Mater 276:120–128
Aslam I et al (2014c) The synergistic effect between WO3 and gC 3N 4 towards efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance. N J Chem 38(11):5462–5469
Aslam I et al (2015a) A novel Z-scheme WO3/CdWO4 photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for the degradation of organic pollutants. RSC Adv 5(8):6019–6026
Aslam I et al (2015b) A facile one-step fabrication of novel WO3/Fe2 (WO4) 3·10.7 H2O porous microplates with remarkable photocatalytic activities. Cryst Eng Commun 17(26):4809–4817
Bahnemann D et al (1994) Aquatic and surface photochemistry. Lewis, Boca Raton, p 261
Bo**ova AS et al (2008) Photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dyes with TiO2/WO3 composite. Eur J Anal Chem 3(1):34–43
Chatchai P, Nosaka AY, Nosaka Y (2013) Photoelectrocatalytic performance of WO3/BiVO4 toward the dye degradation. Electrochim Acta 94:314–319
Cheng X et al (2007) Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic performance of Zn-doped WO3 photocatalysts for nitrite ions degradation under visible light. Chemosphere 68(10):1976–1984
Cui Z et al (2010) Processing–structure–property relationships of Bi2WO6 nanostructures as visible-light-driven photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 183(1):211–217
de la Martínez A, Martínez DS, Cuéllar EL (2010) Synthesis and characterization of WO3 nanoparticles prepared by the precipitation method: evaluation of photocatalytic activity under vis-irradiation. Solid State Sci 12(1):88–94
de la Martínez A, Martínez DS, Cuéllar EL (2013) Synthesis of WO3 nanoparticles by citric acid-assisted precipitation and evaluation of their photocatalytic properties. Mater Res Bull 48(2):691–697
Elmorsi TM et al (2010) Decolorization of Mordant red 73 azo dye in water using H2O2/UV and photo-Fenton treatment. J Hazard Mater 174(1):352–358
Fakhri A, Behrouz S (2015) Photocatalytic properties of tungsten trioxide (WO3) nanoparticles for degradation of Lidocaine under visible and sunlight irradiation. Sol Energy 112:163–168
Feng C, Wang S, Geng B (2011) Ti(iv) doped WO3 nanocuboids: fabrication and enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance. Nanoscale 3(9):3695–3699
Gan L et al (2016) Visible light induced methylene blue dye degradation photo-catalyzed by WO3/graphene nanocomposites and the mechanism. Ceram Int 42(14):15235–15241
García-Rodríguez S (2013) Alternative metal oxide photocatalysts, in design of advanced photocatalytic materials for energy and environmental applications. Springer, New York, pp 103–122
Gondal M et al (2010) Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial application of nano-palladium-doped nano-WO3. J Mol Catal A Chem 323(1):78–83
Grätzel M (2001) Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature 414(6861):338–344
Gun Y et al (2015) Joint effects of photoactive TiO2 and fluoride-do** on SnO2 inverse opal nanoarchitecture for solar water splitting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(36):20292–20303
Hameed A, Gondal M, Yamani Z (2004) Effect of transition metal do** on photocatalytic activity of WO3 for water splitting under laser illumination: role of 3d-orbitals. Catal Commun 5(11):715–719
Hayat K et al (2011) Laser induced photocatalytic degradation of hazardous dye (Safranin-O) using self synthesized nanocrystalline WO3. J Hazard Mater 186(2):1226–1233
Ho G, Chua K, Siow D (2012) Metal loaded WO3 particles for comparative studies of photocatalysis and electrolysis solar hydrogen production. Chem Eng J 181:661–666
Huang J et al (2012) Flower-like and hollow sphere-like WO3 porous nanostructures: selective synthesis and their photocatalysis property. Mater Res Bull 47(11):3224–3232
Huang J, **ao L, Yang X (2013) WO3 nanoplates, hierarchical flower-like assemblies and their photocatalytic properties. Mater Res Bull 48(8):2782–2785
Hunge Y et al (2015) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of methyl red using sprayed WO3 thin films under visible light irradiation. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 26(11):8404–8412
Hunge Y et al (2016) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of methyl blue using sprayed WO3 thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27(2):1629–1635
Hwang DW et al (2002) Mg-doped WO3 as a novel photocatalyst for visible light-induced water splitting. Catal Lett 80(1–2):53–57
Khan MM, Khan MM, Cho MH (2016) Fabrication of WO3 nanorods on graphene nanosheets for improved visible light-induced photocapacitive and photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv 6:20824–20833
Kim J, Lee CW, Choi W (2010) Platinized WO3 as an environmental photocatalyst that generates OH radicals under visible light. Environ Sci Technol 44(17):6849–6854
Kubacka A, Fernandez-Garcia M, Colon G (2011) Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications. Chem Rev 112(3):1555–1614
Kumar SG, Rao KK (2015) Tungsten-based nanomaterials (WO3 & Bi2WO6): modifications related to charge carrier transfer mechanisms and photocatalytic applications. Appl Surf Sci 355:939–958
Lee WH, Lai CW, Hamid SBA (2015) One-step formation of WO3-loaded TiO2 nanotubes composite film for high photocatalytic performance. Materials 8(5):2139–2153
Li Q-H et al (2014) Cylindrical stacks and flower-like tungsten oxide microstructures: controllable synthesis and photocatalytic properties. Ceram Int 40(3):4969–4973
Liew S et al (2014) Yb-doped WO3 photocatalysts for water oxidation with visible light. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(9):4291–4298
Liu S, Yang J-H, Choy J-H (2006) Microporous SiO2–TiO2 nanosols pillared montmorillonite for photocatalytic decomposition of methyl orange. J Photochem Photobiol A 179(1):75–80
Liu H et al (2007) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of dysprosium doped tungsten trioxide nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 104(2):377–383
Luo J, Yartym J, Hepel M (2002) Photoelectrochemical degradation of Orange II textile dye on nanostructured WO3 film electrodes. J N Mater Electrochem Syst 5:315–321
Manikandan M et al (2014) Photocatalytic water splitting under visible light by mixed-valence Sn3O4. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(6):3790–3793
Martínez DS, Martínez- A, De La Cruz A, Cuéllar EL (2011) Photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles obtained by precipitation in presence of urea as complexing agent. Appl Catal A 398(1):179–186
Mohagheghian A et al (2015) Photocatalytic degradation of a textile dye by illuminated tungsten oxide nanopowder. J Adv Oxid Technol 18(1):61–68
Mohamed MM, Ahmed SA, Khairou KS (2014) Unprecedented high photocatalytic activity of nanocrystalline WO3/NiWO4 hetero-junction towards dye degradation: effect of template and synthesis conditions. Appl Catal B 150:63–73
Mu W et al (2014) Characterizations of Nb-doped WO3 nanomaterials and their enhanced photocatalytic performance. RSC Adv 4(68):36064–36070
Nakata K, Fujishima A (2012) TiO2 photocatalysis: design and applications. J Photochem Photobiol C Photochem Rev 13(3):169–189
Pudukudy M, Yaakob Z, Rajendran R (2013) Visible light active novel WO3 nanospheres for methylene blue degradation. Der Pharma Chemica 5:208–212
Purwanto A et al (2011) Role of particle size for platinum-loaded tungsten oxide nanoparticles during dye photodegradation under solar-simulated irradiation. Catal Commun 12(6):525–529
Qamar M, Gondal M, Yamani Z (2010) Removal of Rhodamine 6G induced by laser and catalyzed by Pt/WO3 nanocomposite. Catal Commun 11(8):768–772
Qi H, Wang C, Liu J (2003) A simple method for the synthesis of highly oriented potassium-doped tungsten oxide nanowires. Adv Mater 15(5):411–414
Ramos-Delgado N et al (2013) Synthesis by sol–gel of WO3/TiO2 for solar photocatalytic degradation of malathion pesticide. Catal Today 209:35–40
Sadakane M et al (2010) Preparation of 3-D ordered macroporous tungsten oxides and nano-crystalline particulate tungsten oxides using a colloidal crystal template method, and their structural characterization and application as photocatalysts under visible light irradiation. J Mater Chem 20(9):1811–1818
Saison T et al (2013) New insights into Bi2WO6 properties as a visible-light photocatalyst. J Phys Chem C 117(44):22656–22666
Seabold JA, Choi K-S (2011) Effect of a cobalt-based oxygen evolution catalyst on the stability and the selectivity of photo-oxidation reactions of a WO3 photoanode. Chem Mater 23(5):1105–1112
Shi J et al (2013) Controllable synthesis of WO3·n H2O microcrystals with various morphologies by a facile inorganic route and their photocatalytic activities. N J Chem 37(5):1538–1544
Sin JC et al (2012) Degrading endocrine disrupting chemicals from wastewater by TiO. Int J Photoenergy. doi:10.1155/2012/185159
Shiraishi Y et al (2012) Visible light-induced partial oxidation of cyclohexane on WO3 loaded with Pt nanoparticles. Catal Sci Technol 2(2):400–405
Singh S et al (2014) Synthesis of different crystallographic Al2O3 nano-materials from solid waste for application in dye degradation. RSC Adv 3:50801–50810
Smith W et al (2011) Quasi-core-shell TiO2/WO3 and WO3/TiO2 nanorod arrays fabricated by glancing angle deposition for solar water splitting. J Mater Chem 21(29):10792–10800
Subramani A et al (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of indigo carmine dye using TiO2 impregnated activated carbon. Bull Mater Sci 30(1):37–41
Sudrajat H, Babel S (2016) Rapid photocatalytic degradation of the recalcitrant dye amaranth by highly active N–WO3. Environ Chem Lett 14:243–249
Sun J et al (2008) Photocatalytic degradation of Orange G on nitrogen-doped TiO2 catalysts under visible light and sunlight irradiation. J Hazard Mater 155(1):312–319
Sun S et al (2010) Preparation of ordered mesoporous Ag/WO3 and its highly efficient degradation of acetaldehyde under visible-light irradiation. J Hazard Mater 178(1):427–433
Sun W et al (2015) High surface area tunnels in hexagonal WO3. Nano Lett 15(7):4834–4838
Takeuchi M et al (2011) Preparation of the visible light responsive N3-doped WO3 photocatalyst by a thermal decomposition of ammonium paratungstate. Appl Catal B 110:1–5
Tanaka D, Oaki Y, Imai H (2010) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of quantum-confined tungsten trioxide nanoparticles in mesoporous silica. Chem Commun 46(29):5286–5288
Teka T, Tadesse A (2014) Effect of selected operating parameters on the photocatalytic efficiency of nitrogen-doped TiO2/WO3 nano-composite material for photodegradation of phenol red in aqueous solution. Int J Innov Sci Res 7(1):174–185
Theerthagiri J et al (2015) Synthesis and characterization of a CuS–WO3 composite photocatalyst for enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv 5(65):52718–52725
Vamvasakis I et al (2015) Synthesis of WO3 catalytic powders: evaluation of photocatalytic activity under NUV/visible light irradiation and alkaline reaction pH. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 76(1):120–128
Wang G et al (2012a) Hydrogen-treated WO3 nanoflakes show enhanced photostability. Energy Environ Sci 5(3):6180–6187
Wang G, Ling Y, Li Y (2012b) Oxygen-deficient metal oxide nanostructures for photoelectrochemical water oxidation and other applications. Nanoscale 4(21):6682–6691
Wang C et al (2015) Nanosheets assembled hierarchical flower-like WO3 nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and their gas sensing properties. Sens Actuat B Chem 210:75–81
Wang D et al (2016) Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis of visible-light-activated I-doped TiO2 for improved dye degradation. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16(6):5676–5682
Wen Z et al (2013) Ultrahigh-efficiency photocatalysts based on mesoporous Pt–WO3 nanohybrids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(18):6773–6778
Widiyandari H et al (2012) CuO/WO3 and Pt/WO3 nanocatalysts for efficient pollutant degradation using visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J 180:323–329
Wu S et al (2013) Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization of visible-light-driven α-Bi2O3 enhanced by Pr3+ do**. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88(10):1828–1835
** G et al (2012) Synthesis of multiple-shell WO3 hollow spheres by a binary carbonaceous template route and their applications in visible-light photocatalysis. Chem A Eur J 18(44):13949–13953
**e J et al (2014) Simple preparation of WO3–ZnO composites with UV–Vis photocatalytic activity and energy storage ability. Ceram Int 40(8):12519–12524
Xu C et al (2009) Surfactant-free synthesis of Bi2WO6 multilayered disks with visible-light-induced photocatalytic activity. Mater Res Bull 44(8):1635–1641
Xue Q et al (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of geosmin by Pd nanoparticle modified WO3 catalyst under simulated solar light. Chem Eng J 283:614–621
Yang H et al (2006) Sol–gel synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles and photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. J Alloys Compd 413(1):302–306
Yin J et al (2013) Synthesis and applications of γ-tungsten oxide hierarchical nanostructures. Cryst Growth Des 13(2):759–769
Yu L et al (2012) Photoelectrocatalytic performance of TiO2 nanoparticles incorporated TiO2 nanotube arrays. Appl Catal B 113:318–325
Zhang X et al (2011) Three-dimensional WO3 nanostructures on carbon paper: photoelectrochemical property and visible light driven photocatalysis. Chem Commun 47(20):5804–5806
Zheng Y et al (2014) Template and surfactant free synthesis of hierarchical WO3 0.33 H2O via a facile solvothermal route for photocatalytic RhB degradation. Cryst Eng Commun 16(27):6107–6113
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to extend their gratitude to all who assisted in performing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Binbin Huang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tahir, M.B., Nabi, G., Rafique, M. et al. Nanostructured-based WO3 photocatalysts: recent development, activity enhancement, perspectives and applications for wastewater treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14, 2519–2542 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1394-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1394-z