Abstract
Purpose
The cavernous sinus (CS) region is a common region of dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF). Over time, treatment strategies are gradually changing. In this study, we present our center's experience in managing CS-DAVF over the past 20 years.
Methods
Medical records of patients diagnosed with CS-DAVF between 2002 and 2021 were collected for analysis. Patients meeting the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria were included. This study summarized and analyzed their clinical characteristics, CS-DAVF angioarchitecture, treatment strategies, and outcomes.
Results
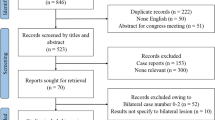
A total of 141 patients (mean age 55 years, 46 males) were included in this study. Ocular/orbital symptoms were the most frequently reported initial symptoms, with 84 (59.6%) patients experiencing these symptoms first. Presentation with ocular/orbital symptoms as the first symptom was associated with thrombosis of the inferior petrosal sinus (p = 0.032). Presentation with headache/dizziness and tinnitus/intracranial murmur as the first symptom was associated with sphenoparietal sinus/superficial middle cerebral vein drainage (p = 0.011). Among the patients, 131 (92.9%) patients received endovascular treatment, with 114 (87.0%) undergoing transvenous embolization. Onyx (92.4%) and coil (74.8%) were the most used embolic materials. 17 (13.0%) of the patients who received endovascular treatment suffered intraoperative or postoperative complications, and 11 (64.7%) patients fully recovered within 6 months after discharge.
Conclusion
Ocular/orbital symptoms were the most common first symptom of CS-DAVF. The mode of venous drainage played a significant role in determining the first symptoms. Transvenous embolization using Onyx or a combination of Onyx and coils was the primary treatment modality.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study were available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, Landman JA, Tindall SC, Tindall GT (1985) Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg 62(2):248–256. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1985.62.2.0248
Guo H, Yin Q, Liu P, Guan N, Huo X, Li Y (2018) Focus on the target: angiographic features of the fistulous point and prognosis of transvenous embolization of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Interv Neuroradiol 24(2):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019917751894
Zhang S, Wang J, Liu D, Lv M (2021) Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula (CSDAVF) via transvenous approaches: practice, experience summary and literature review. J Clin Neurosci 89:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2021.05.005
Hou K, Li G, Luan T, Xu K, Yu J (2020) Endovascular treatment of the cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: current status and considerations. Int J Med Sci 17(8):1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.45210
Xu B, Wang Z, Bai W, Li T (2019) Treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula using different surgical approaches: analysis of 32 consecutive cases. J Interv Med 2(3):118–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimed.2019.09.011
Thomas AJ, Chua M, Fusco M, Ogilvy CS, Tubbs RS, Harrigan MR, Griessenauer CJ (2015) Proposal of venous drainage-based classification system for carotid cavernous fistulae with validity assessment in a multicenter cohort. Neurosurgery 77(3):380–385. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000829. (discussion 5)
Rhim JK, Cho YD, Park JJ, Jeon JP, Kang HS, Kim JE et al (2015) Endovascular treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula with ipsilateral inferior petrosal sinus occlusion: a single-center experience. Neurosurgery 77(2):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000751. (discussion 9)
Oka Y, Komatsu K, Abe S, Yoshimoto N, Taki J, Matsumoto S (2020) Acute brainstem dysfunction caused by cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Case Rep Neurol Med 2020:2630959. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2630959
Suh DC, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Chung SJ, Choi CG, Kim HJ et al (2005) New concept in cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: correlation with presenting symptom and venous drainage patterns. Stroke 36(6):1134–1139. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000166194.82027.63
Alexander MD, Halbach VV, Hallam DK, Cooke DL, Ghodke BV, Dowd CF et al (2019) Long-term outcomes of endovascular treatment of indirect carotid cavernous fistulae: superior efficacy, safety, and durability of transvenous coiling over other techniques. Neurosurgery 85(1):E94–E100. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy486
Liu P, Liu Y, Shi Y, An Q, Zhu W, Liu Y et al (2022) The vascular architecture of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula and its impact on endovascular treatment approach selection and outcome. World Neurosurg 166:e770–e780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2022.07.094
Leone G, Renieri L, Enriquez-Marulanda A, Dmytriw AA, Nappini S, Laiso A et al (2019) Carotid cavernous fistulas and dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus: validation of a new classification according to venous drainage. World Neurosurg 128:e621–e631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.220
Miller NR (2012) Dural carotid-cavernous fistulas: epidemiology, clinical presentation, and management. Neurosurg Clin N Am 23(1):179–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2011.09.008
Santillan A, Nanaszko M, Burkhardt JK, Patsalides A, Gobin YP, Riina HA (2013) Endovascular management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(3):241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.11.021
Miller TR, Gandhi D (2015) Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: clinical presentation and management strategies. Stroke 46(7):2017–2025. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.008228
Tan WN, Rajadurai A, Balakrishnan D (2021) Endovascular treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula via radial artery and median cubital vein. Neurointervention 16(2):194–198. https://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2021.00157
Shibata T, Nishikawa Y, Kitamura T, Mase M (2021) Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula accessed through a straightened superficial temporal vein. Surg Neurol Int 12:634. https://doi.org/10.25259/SNI_1035_2021
Kim SC, Kim JH, Kim CH, Lee CY (2022) Middle temporal vein access for transvenous embolization of Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: a case report and review of literature. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 24(1):44–50. https://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.06.008
Wenderoth J (2017) Novel approaches to access and treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula (CS-DAVF): case series and review of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg 9(3):290–296. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012742
Alexandre AM, Visconti E, Lozupone E, D’Argento F, Pedicelli A (2017) Embolization of dural arteriovenous fistula of the cavernous sinus through percutaneous ultrasound-guided puncture of the facial vein. World Neurosurg 99(812):e13–e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.12.048
Venturi C, Bracco S, Cerase A, Gennari P, Lore F, Polito E, Casasco AE (2003) Endovascular treatment of a cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula by transvenous embolisation through the superior ophthalmic vein via cannulation of a frontal vein. Neuroradiology 45(8):574–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1020-2
Wenderoth J (2017) Proposal for an improved classification system for cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula (CS-DAVF). J Neurointerv Surg 9(3):220–224. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012743
Lv M, Jiang C, Liu D, Ning Z, Yang J, Wu Z (2015) Direct percutaneous transorbital puncture under fluoroscopic guidance with a 3D skull reconstruction overlay for embolisation of intraorbital and cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas. Interv Neuroradiol 21(3):357–361. https://doi.org/10.1177/1591019915582925
Hong Duc P, Thai Hoa NT, Quang Huy H, Nguyen AQ (2020) Percutaneous ultrasound-guided access to the superior ophthalmic vein for embolization of a cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula. Cureus 12(5):e8053. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.8053
Yoshida K, Melake M, Oishi H, Yamamoto M, Arai H (2010) Transvenous embolization of dural carotid cavernous fistulas: a series of 44 consecutive patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(4):651–655. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1882
Luo CB, Chang FC, Wang AG, Lin CJ, Guo WY, Ting TW (2016) Transvenous coil embolization of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula on a revised classification. World Neurosurg 95:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.08.028
Nishino K, Ito Y, Hasegawa H, Kikuchi B, Shimbo J, Kitazawa K, Fujii Y (2008) Cranial nerve palsy following transvenous embolization for a cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: association with the volume and location of detachable coils. J Neurosurg 109(2):208–214. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/8/0208
de Castro-Afonso LH, Trivelato FP, Rezende MT, Ulhoa AC, Nakiri GS, Monsignore LM et al (2018) Transvenous embolization of dural carotid cavernous fistulas: the role of liquid embolic agents in association with coils on patient outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg 10(5):461–462. https://doi.org/10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013318
Wen J, Duan CZ, Huang LJ, Zhang X, He XY, Li XF (2015) Transarterial onyx embolization for patients with cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas who have failed transvenous embolization. Cell Biochem Biophys 73(1):163–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0615-7
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China. Award Number: 82101460.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZS and YM and contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors. ZS, wrote the manuscript and arranged ideas. YM revised the manuscript and designed writing ideas. XS collected clinical and radiological data. YF followed up patients and did the statistics. HZ analyzed imaging data and ideas supervision. MY analyzed imaging data and ideas supervision. PZ analyzed imaging data and analyzed ideas supervision. All the authors made critical revisions of the manuscript and reviewed the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by Ethics Committee of Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Ma, Y., Su, X. et al. Clinical features, treatment, and outcomes of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: a cohort study of 141 patients. Acta Neurol Belg 124, 803–811 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02405-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02405-9