Abstract
This study investigates the combined effects of UV/TiO2 and UV/H2O2 processes on the degradation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene in aqueous media, employing a recycled current photo-reactor equipped with a water jacket. Evaluation of various factors—initial pH, TiO2 dosage, initial H2O2 concentration, pollutant concentration, and temperature—contributed to the optimization of degradation rates and operational costs for both processes. For the degradation of 50 mg/L of DCB, the optimal operating conditions were found to be for UV/TiO2: pH = 3, [TiO2] = 30 mg/L and T = 25 °C, and for UV/H2O2: pH = 3, [H2O2]0 = 350 mg/L and T = 25 °C. After 60 min of irradiation time, the degradation efficiency, pseudo first order rate constant and operational cost value for the UV/TiO2 and UV/H2O2 processes were as 98.9%, 0.0771 min−1, 11.6 $/m3 and 96.3%, 0.0573 min−1, 11.8 $/m3 respectively. Also, thermodynamic parameters of activation energy, enthalpy change, entropy change and standard Gibbs free energy were calculated as 21.78 (kJ/mol), 19.37 (kJ/mol), − 0.20 (kJ/mol K) and 73.34 (kJ/mol at 25 °C) for UV/TiO2 process and 7.62 (kJ/mol), 5.18 (kJ/mol), − 0.25 (kJ/mol K) and 80.14 (kJ/mol at 25 °C) for UV/H2O2 process. The investigation also encompassed the exploration of 13 hybridization scenarios, including UV/TiO2/H2O2 and UV/H2O2/TiO2, revealing notable findings. Notably, a specific hybridization scenario, namely UV/TiO2 (30 mg/L)/H2O2(250 mg/L), demonstrated a significant synergistic effect (29.5%). Evaluating pollutant mineralization unveiled compelling results, with approximately 85% mineralization achieved after 90 min for the UV/TiO2(30 mg/L)/H2O2(250 mg/L) scenario, showcasing a remarkable synergism (44%) in the mineralization process.
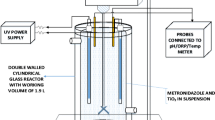
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCB:
-
1,2-Dichlorobenzen
- AOPs:
-
Advanced oxidation processes
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- [DCB]0 :
-
Initial concentration of DCB
- [DCB]:
-
DCB concentration at any time
- DE%:
-
Degradation efficiency percentage
- SG%:
-
Synergism percentage
- UV:
-
Ultra violet
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- ZPC:
-
Zero point charge
- IUPAC:
-
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
- POC:
-
Process operating cost
- CC:
-
Chemical cost
- EEC:
-
Electricity energy cost
- CEE:
-
Consumed electrical energy
- ThEC:
-
Thermal energy cost
- US$:
-
United States Dollar
- EQ :
-
Thermal energy
- m:
-
Mass of one cubic meter of polluted water
- C p :
-
Specific heat capacity of water
- T :
-
Temperature
- R :
-
Ideal gas universal constant
- k app :
-
Apparent rate constant
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- P :
-
Electrical power
- t :
-
Reaction time
- V :
-
Reaction solution volume
- E a :
-
Activation energy
- ΔH°:
-
Enthalpy change
- ΔS°:
-
Entropy change
- ΔG°:
-
Gibbs free energy change
- N A :
-
Avogadro's constant
- h :
-
Planck's constant
- \({e}_{CB}^{-}\) :
-
Conduction band electron
- \({h}_{VB}^{+}\) :
-
Valance band electron
- \({\uplambda }_{max}\) :
-
Maximum absorbance wavelength
References
J. Wang, S. Wang, Effect of inorganic anions on the performance of advanced oxidation processes for degradation of organic contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 411, 128392 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128392
M. Karimi-Nazarabad, E.K. Goharshadi, R. Mehrkhah, M. Davardoostmanesh, Highly efficient clean water production: reduced graphene oxide/graphitic carbon nitride/wood. Sep. Purif. Technol. 279, 119788 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119788
S.G. Poulopoulos, A. Yerkinova, G. Ulykbanova, V.J. Inglezakis, Photocatalytic treatment of organic pollutants in a synthetic wastewater using UV light and combinations of TiO2, H2O2 and Fe (III). PLoS ONE 14(5), e0216745 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216745
M. Pera-Titus, V. Garcia-Molina, M.A. Banos, J. Gimenez, S. Esplugas, Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: a general review. Appl. Catal. B 47(4), 219 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.09.010
O. Sacco, V. Vaiano, L. Rizzo, D. Sannino, Photocatalytic activity of a visible light active structured photocatalyst developed for municipal wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 175, 38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.088
D. Li, H. Zheng, F. Zhang, Y. Zhao, Y. Miao, J. Yang, Effect of copper do** in the TiO2 film electrodes on the performance of photoelectrochemical biofuel cells. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 21(4), 1021 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-024-02972-5
A. Salabat, F. Mirhoseini, F.H. Nouri, Microemulsion strategy for preparation of TiO2–Ag/poly(methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite and its photodegradation application. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 20(3), 599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02693-7
H. Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, Z. Talleb, M. Khalili, Photocatalytic degradation of Indigo Carmine using aluminum-doped titanium dioxide/zinc ferrite nanocomposite under visible light. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 20(2), 389 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-022-02671-z
S.G. Poulopoulos, C.J. Philippopoulos, Photo-assisted oxidation of chlorophenols in aqueous solutions using hydrogen peroxide and titanium dioxide. J. Environ. Sci. Health A. 39(6), 1385–1397 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-120037840
M. Al-Mamun, S. Kader, M. Islam, M. Khan, Photocatalytic activity improvement and application of UV-TiO2 photocatalysis in textile wastewater treatment: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(5), 103248 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103248
C. Galindo, P. Jacques, A. Kalt, Photodegradation of the aminoazobenzene acid orange 52 by three advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2, UV/TiO2 and VIS/TiO2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. Chem. 130(1), 35–47 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(99)00199-9
J.L. Wang, L.J. Xu, Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: formation of hydroxyl radical and application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42(3), 251 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2010.507698
J. Garcia, J. Oliveira, A. Silva, C. Oliveira, J. Nozaki, N. De Souza, Comparative study of the degradation of real textile effluents by photocatalytic reactions involving UV/TiO2/H2O2 and UV/Fe2+/H2O2 systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 147(1–2), 105 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.053
Q. Zhang, C. Li, T. Li, Rapid photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue using high photon flux UV/TiO2/H2O2 process. Chem. Eng. J. 217, 407 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.106
M. Saquib, M.A. Tariq, M. Haque, M. Muneer, Photocatalytic degradation of disperse blue 1 using UV/TiO2/H2O2 process. J. Environ. Manag. 88(2), 300 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.03.012
E.T. Wahyuni, R. Roto, M. Sabrina, V. Anggraini, N. Leswana, A. Vionita, Photodegradation of detergent anionic surfactant in wastewater using UV/TiO2/H2O2 and UV/Fe2+/H2O2 processes. Am. J. Appl. Chem. 4(5), 174 (2016). https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajac.20160405.13
P. Verma, J. Kumar, Degradation and microbiological validation of Meropenem antibiotic in aqueous solution using UV, UV/H2O2, UV/TiO2 and UV/TiO2/H2O2 processes. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 4(7), 58 (2014)
W.Y. Li, Y. Liu, X.L. Sun, F. Wang, L. Qian, X. Chen, J.P. Zhang, Photocatalytic degradation of MC-LR in water by the UV/TiO2/H2O2 process. Water Supply 16(1), 34–43 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2015.110
P. Ncube, C. Zvinowanda, M. Belaid, F. Ntuli, Heterogeneous Photocatalytic degradation of nevirapine in wastewater using the UV/TiO2/H2O2 process. Environ. Process. 10(1), 1 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-022-00615-6
R. Arshad, T.H. Bokhari, T. Javed, I.A. Bhatti, S. Rasheed, M. Iqbal, A. Nazir, S. Naz, M.I. Khan, M.K.K. Khosa, M. Iqbal, M. Zia-ur-Rehman, Degradation product distribution of Reactive Red-147 dye treated by UV/H2O2/TiO2 advanced oxidation process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9(3), 3168 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.062
N.A. Mohammed, A.I. Alwared, M.S. Salman, Photocatalytic degradation of reactive yellow dye in wastewater using H2O2/TiO2/UV technique. Iraqi J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 21(1), 15–21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.31699/IJCPE.2020.1.3
M. Kulkarni, P. Thakur, The effect of UV/TiO2/H2O2 process and influence of operational parameters on photocatalytic degradation of azo dye in aqueous TiO2 suspension. Chem. Chem. Technol 4, 265–270 (2010)
T.H. Bokhari, W. Abbas, M. Munir, M. Zuber, M. Usman, M. Iqbal, I.A. Bhatti, I.H. Bukhari, M.K. Khan, Impact of UV/TiO2/H2O2 on Degradation of Disperse Red F3BS. Asian J. Chem. 27(1), 282–286 (2015). https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2015.17553
T.F. Chen, R.A. Doong, W.A. Lei, Photocatalytic degradation of parathion in aqueous TiO2 dispersion: the effect of hydrogen peroxide and light intensity. Water Sci. Technol. 37(8), 187 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00249-2
X. Peng, W. Li, J. Chen, X. Jia, Photocatalytic degradation of tetrabromobisphenol a with a combined UV/TiO2/H2O2 process. Desalin. Water Treat. 65, 451 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2017.20232
Y. Zang, R. Farnood, Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on the Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl tert-butyl Ether. Top. Catal. 37, 91 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-006-0009-6
K. Seyyedi, S. Khoshbin, R. Piri, Removing of acid red 1 dye pollutant from contaminated waters by UV/TiO2/H2O2 process using a recirculating tubular reactor. J. Appl. Chem. Res. 17(3), 21 (2023)
J. Saien, Z. Ojaghloo, A.R. Soleymani, M. Rasoulifard, Homogeneous and heterogeneous AOPs for rapid degradation of Triton X-100 in aqueous media via UV light, nano titania hydrogen peroxide and potassium persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 167(1), 172 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.017
A. Dixit, A.J. Tirpude, A.K. Mungray, M. Chakraborty, Degradation of 2, 4 DCP by sequential biological–advanced oxidation process using UASB and UV/TiO2/H2O2. Desalin. 272(1–3), 265 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.035
B. Karimi, M. Rajaei, M. Eesvand, M. Habibi, Application of UV/TiO2/H2O2 advanced oxidation to remove naphthalene from water. J. Water Wastewater Ab va Fazilab 27(5), 53 (2016)
E.M. Cuerdacorrea, J.R. Dominguezvargas, M.J. Munozpena, T. Gonzalez, Ultraviolet-photoassisted advanced oxidation of parabens catalyzed by hydrogen peroxide and titanium dioxide Improving the system. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55(18), 5152 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b04560
D. Ovhal Sheetal, T. Pragati, Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in a TiO2 slurry reactor. Res. J. Chem. Environ 14(4), 9 (2010)
A. Riga, K. Soutsas, K. Ntampegliotis, V. Karayannis, G. Papapolymerou, Effect of system parameters and of inorganic salts on the decolorization and degradation of procion H-exl dyes comparison of H2O2/UV, fenton, UV/fenton, TiO2/UV and TiO2/UV/H2O2 processes. Desalin. 211(1–3), 72 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.04.082
A.T. Nguyen, R.S. Juang, Photocatalytic degradation of p-chlorophenol by hybrid H2O2 and TiO2 in aqueous suspensions under UV irradiation. J. Environ. Manage. 147, 271 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.08.023
A.R. Soleymani, A.M. Tavassoli, H. Rezaei-Vahidian, Assessment of back-side activation of titania thin film using a fixed-bed photocatalytic-reactor: kinetic study, operating cost and ANN modeling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 190, 759 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2022.12.047
J. Saien, A.R. Soleymani, Feasibility of using a slurry falling film photo-reactor for individual and hybridized AOPs. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 18(5), 1683 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.03.014
R. Ma, J. Sun, D.H. Li, J.J. Wei, Review of synergistic photo-thermo-catalysis: Mechanisms, materials and applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 45(55), 30288 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.127
E. Unosson, E.K. Tsekoura, H. Engqvist, K. Welch, Synergetic inactivation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Streptococcus mutansin a TiO2/H2O2/UV system. Biomatter. 3(4), e26727 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4161/biom.26727
S. Apollo, M.S. Onyongo, A. Ochieng, UV/H2O2/TiO2/Zeolite hybrid system for treatment of molasses wastewater. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 33(2), 107 (2014)
J.M. Monteagudo, A. Durán, I. San Martín, B. Vellón, Photocatalytic degradation of aniline by solar/TiO2 system in the presence of the electron acceptors Na2S2O8 and H2O2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 238, 116456 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116456
T.A. Egerton, H. Purnama, Does hydrogen peroxide really accelerate TiO2 UV-C photocatalyzed decolouration of azo-dyes such as Reactive Orange 16? Dyes Pigm. 101, 280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2013.10.019
M.E. Simonsen, C.V. Jensen, E.G. Søgaard, Comparison of different UV-activated AOP methods. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 16(1), 179 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1515/jaots-2013-0120
M.K. Aulakh, B. Pal, Solar irradiated selective nitroaromatics reduction over plasmonic Ag-TiO2: deposition time dependent size growth and oxidation state of co-catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 429, 132385 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.132385
U.S. Government Energy Information Administration, Independent Statisticsand Analysis in, http://www.eia.gov (2023).
Chemicals Cost, 2023, http://www.alibaba.com and http://www.made-in-china.com.
A.R. Soleymani, M. Mahdiei, M. Haerifar, Nano-titania/light expanded clay aggregate fixed bed as an effective adsorbent for removal of organic pollutant from water: equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Clean. Prod. 211, 1328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.258
A.R. Soleymani, R. Chahardoli, M. Kaykhaii, Development of UV/H2O2/TiO2–LECA hybrid process based on operating cost: application of an effective fixed bed photo-catalytic recycled reactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 44, 90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2016.08.009
J. Saien, A.R. Soleymani, Degradation and mineralization of Direct Blue 71 in a circulating upflow reactor by UV/TiO2 process and employing a new method in kinetic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 144(1), 506 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.10.065
K.-I. Ishibashi, A. Fujishima, T. Watanabe, K. Hashimoto, Detection of active oxidative species in TiO2 photocatalysis using the fluorescence technique. Electrochem. commun. 2(3), 207 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2481(00)00006-0
S. Khezrianjoo, J. Lee, K.-H. Kim, V. Kumar, Eco-toxicological and kinetic evaluation of TiO2 and ZnO nanophotocatalysts in degradation of organic dye. Catal. 9(10), 871 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100871
M.R.D. Khaki, M.S. Shafeeyan, A.A.A. Raman, W.M.A.W. Daud, Application of doped photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation—a review. J. Environ. Manag. 198, 78 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.099
Z. Shams-Ghahfarokhi, A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, As-synthesized ZSM-5 zeolite as a suitable support for increasing the photoactivity of semiconductors in a typical photodegradation process. Mater. Sci. Semicond. 39, 265 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.05.022
S. Findik, Decolorization of Direct Black 22 by Photo Fenton like Method Using UV Light and Zeolite Modified Zinc Ferrite: Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Acta Chim. Slov. 69(3), 552–563 (2022). https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2022.7431
U.J. Ahile, R.A. Wuana, A.U. Itodo, R. Sha’Ato, R.F. Dantas, Stability of iron chelates during photo-fenton process: The role of pH, hydroxyl radical attack and temperature. J. Water Process Eng. 36, 101320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101320
P.P. Gan, S.F.Y. Li, Efficient removal of Rhodamine B using a rice hull-based silica supported iron catalyst by Fenton-like process. Chem. Eng. J. 229, 351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.020
Z. Ghasemi, H. Younesi, A.A. Zinatizadeh, Kinetics and thermodynamics of photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in petroleum refinery wastewater over nano-TiO2 supported on Fe-ZSM-5. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 65, 357 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.05.039
J. Saien, A. Soleymani, J. Sun, Parametric optimization of individual and hybridized AOPs of Fe2+/H2O2 and UV/S2O82− for rapid dye destruction in aqueous media. Desalin. 279(1–3), 298 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.06.024
H. Gerischer, A. Heller, The role of oxygen in photooxidation of organic molecules on semiconductor particles. J. Phys. Chem. 95(13), 5261 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1021/j100166a063
R. Thiruvenkatachari, T.O. Kwon, J.C. Jun, S. Balaji, M. Matheswaran, I.S. Moon, Application of several advanced oxidation processes for the destruction of terephthalic acid (TPA). J. Hazard. Mater. 142(1–2), 308 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.08.023
Y. Chen, Z. Sun, Y. Yang, Q. Ke, Heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol in water. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A. 142(1), 85 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(01)00477-4
R.C. Testolin, L. Mater, E. Sanches-Simões, A. Dal Conti-Lampert, A.X.R. Corrêa, M.L. Groth, M. Oliveira-Carneiro, C.M. Radetski, Comparison of the mineralization and biodegradation efficiency of the Fenton reaction and Ozone in the treatment of crude petroleum-contaminated water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8(5), 104265 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104265
O. Ganzenko, C. Trellu, N. Oturan, D. Huguenot, Y. Péchaud, E.D. van Hullebusch, M.A. Oturan, Electro-Fenton treatment of a complex pharmaceutical mixture: Mineralization efficiency and biodegradability enhancement. Chemosphere 253, 126659 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126659
S. Sahinkaya, COD and color removal from synthetic textile wastewater by ultrasound assisted electro-fenton oxidation process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19(2), 601 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2012.09.023
T. Xu, X.M. **ao, H.Y. Liu, Advanced oxidation degradation of dichlorobenzene in Water by the UV/H2O2 Process. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. A. 40(4), 751 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1081/ESE-200048256
E. Selli, C.L. Bianchi, C. Pirola, G. Cappelletti, V. Ragaini, Efficiency of 1,4-dichlorobenzene degradation in water under photolysis, photocatalysis on TiO2 and sonolysis. J. of Hazard. Mater. 153(3), 1136 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.071
R. Nadarajan, W.A. Wan Abu Bakar, R. Ali, R. Ismail, Photocatalytic degradation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene using immobilized TiO2/SnO2/WO3 photocatalyst under visible light: application of response surface methodology. Arab. J. Chem. 11(1), 34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.03.006
R. Andreozzi, M. Canterino, R. Marotta, Fe(III) homogeneous photocatalysis for the removal of 1,2-dichlorobenzene in aqueous solution by means UV lamp and solar light. Water Res. 40(20), 3785 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.05.029
S.A. Mahmoud, E. Yassitepe, S.I. Shah, Photolysis and photocatalysis of 1,4 dichlorobenzene using sputtered TiO2 thin films. Mater. Sci. Forum 734, 215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.734.215
R. Nadarajan, W.A. Wan Abu Bakar, R. Ali, R. Ismail, Effect of structural defects towards the performance of TiO2/SnO2/WO3 photocatalyst in the degradation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 64, 106 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.044
S.C. Jung, H. Lee, S.J. Ki, S.J. Kim, Y.K. Park, Effect of constituent processes and conditions of the hybrid TiO2 photocatalytic system on 1,4-dichlorobenzene degradation. Catal. Today 348, 270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.08.021
R.R. Ozer, J.L. Ferry, Investigation of the photocatalytic activity of TiO2−polyoxometalate systems. Environ. sci. technol. 35(15), 3242 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/es0106568
E.Y. Kim, Y.H. Kim, C.M. Whang, Nd3+-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol-hydrothermal process. Mater. sci. forum 510–511, 122 (2006). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.510-511.122
Acknowledgements
We express our sincere thanks and appreciation to the Malayer and Payame Noor Universities authorities for providing the financial support to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Soleymani, A.R., Azimi, S. & Rahnama, A. Hybrid photocatalytic/photochemical degradation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene: kinetic, thermodynamic, operating cost, synergism and mineralization study. J IRAN CHEM SOC 21, 1977–1996 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-024-03044-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-024-03044-4