Abstract
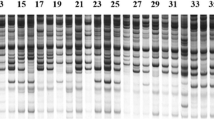
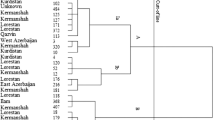
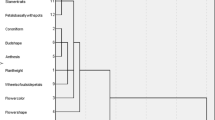
Knowledge of genetic diversity and relatedness of cultivars; is essential for a successful breeding scheme. The present study was conducted to assess the genetic diversity of 30 Iranian Chrysanthemum morifolium cultivars using sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) molecular markers and morphological traits. For this purpose, 30 cultivars were planted in a completely randomized block design with three replications at the Research Farm of Isfahan University of Technology in 2015. The evaluation of morphological traits during the two consecutive years showed a wide range of variations among different cultivars. The results obtained by the analysis of variance also revealed the significant effects of cultivar, environment and cultivar × environment interaction on all studied traits. Correlation analysis of variables further showed that flowering durability was affected by plant morphology. Results of cluster analysis based on the phenotypic data divided the cultivars into six groups. Molecular analysis using SRAP markers produced a total of 213 identifiable fragments with an average of 21.3 polymorphic bands per combination. The polymorphic information content (PIC) value was 0.46. Along with the Bayesian structure analysis which showed that the highest value of the maximum delta log likelihood (ΔK) was K = 3, cluster analysis also grouped the cultivars into three main clusters. The high value of admixture revealed ancestral relationships between the studied cultivars. Overall, our findings revealed the potential of SRAP markers and morphological traits for the analysis of genetic diversity in Chrysanthemum. This can be, in turn, used in selecting the desired parents in the hybrid breeding programs as well as develo** superior cultivars for ornamental applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad HM, Ahsan M, Ali Q, Javed I (2012) Genetic variability, heritability and correlation studies of various quantitative traits of mungbean (Vigna radiate L.) at different radiation levels. Int Res J Microbiol 3:352–362
Aneja B, Yadav NR, Yadav RC, Kumar R (2013) Sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) analysis for genetic diversity and micronutrient content among gene pools in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19:399–407
Arzani A, Ashraf M (2016) Smart engineering of genetic resources for enhanced salinity tolerance in crop plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 35:146–189
Banerji BK, Batra A, Dwivedi AK (2012) Morphological and biochemical characterization of Chrysanthemum. J Hortic Sci 7:51–55
Chen H, Morrell PL, Ashworth VE, De La Cruz M, Clegg MT (2008) Tracing the geographic origins of major avocado cultivars. J Hered 100:56–65
Choudhary SB, Sharma HK, Kumar AA, Maruthi RT, Mitra J, Chowdhury I, Singh BK, Karmakar PG (2017) SSR and morphological trait based population structure analysis of 130 diverse flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) accessions. C R Biol 340:65–75
Da Silva JAT (2004) Ornamental Chrysanthemums: improvement by biotechnology. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 79:1–18
Falconer DS, Mackay TF, Frankham R (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics. Trends Genet 12:280
Feng SG, He RF, Jiang MY, Lu JJ, Shen XX, Liu JJ, Wang ZA, Wang HZ (2016) Genetic diversity and relationships of medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium revealed by start codon targeted (SCoT) markers. Sci Hortic 201:118–123
Fu X, Ning G, Gao L, Bao M (2008) Genetic diversity of Dianthus accessions as assessed using two molecular marker systems (SRAPs and ISSRs) and morphological traits. Sci Hortic 117:263–270
Gaikwad AM, Katwate SM, Nimbalkar CA (2002) Evaluation of Chrysanthemum cultivars for growth and yield. South Indian Hortic 50:624–628
Ghafouri F, Rahimmalek M (2018) Genetic structure and variation in different Iranian myrtle (Myrtus communis L.) populations based on morphological, phytochemical and molecular markers. Ind Crops Prod 123:489–499
Han J, Hu N, Li YG, Shang FD (2007) Genetic diversity of Chrysanthemum cultivars revealed by AFLP analysis. Acta Hortic Sin 34:1041
Hassanein AMA, Al-Soqeer AA (2017) Morphological and genetic diversity of Moringa oleifera and Moringa peregrina genotypes. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 59:251–261
Kulkarni BS, Reddy BS (2004) Vegetative growth, flower yield and quality of different Chrysanthemum cultivars. J Ornam Hortic 7:32–36
Kumar S, Sharma R, Kumar V, Vyas GK, Rathore A (2013) Combining molecular-marker and chemical analysis of Capparis deciduas (Capparaceae) in the Thar desert of Western Rajasthan (India). Rev Biol Trop 61:311–320
Kumar S, Kumar M, Yadav HK, Sharma S (2017) Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflora Tzvelev) germplasm based on RAPD markers. J Environ Biol 38:457
Li T, Li Y, Ning H, Sun X, Zheng C (2013) Genetic diversity assessment of Chrysanthemum germplasm using conserved DNA-derived polymorphism markers. Sci Hortic 162:271–277
Martí C, Uberhuaga E, Pérez C (2002) Application of RAPD markers in the characterisation of Chrysanthemum varieties and the assessment of somaclonal variation. Euphytica 127:247–253
Mohammadi SA, Prasanna BM (2003) Analysis of genetic diversity in crop plants-salient statistical tools and considerations. Crop Sci 43:1235–1248
Mokhtari N, Rahimmalek M, Talebi M, Khorrami M (2013) Assessment of genetic diversity among and within Carthamus species using sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers. Plant Syst Evol 299:1285–1294
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Naz S, Shehzadi I, Shahzadi K, Ilyas S (2015) Assessment of genetic variability in different Chrysanthemum varieties of Pakistan using RAPD markers. J Anim Plant Sci 25:554–560
Palai SK, Rout GR (2011) Characterization of new variety of Chrysanthemum by using ISSR markers. Hortic Bras 29:613–617
Robarts DW, Wolfe AD (2014) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers: a potential resource for studies in plant molecular biology. Appl Plant Sci 2:1400017
Roein Z, Asil MH, Sabouri A, Dadras AR (2014) Genetic structure of Chrysanthemum genotypes from Iran assessed by AFLP markers and phenotypic traits. Plant Syst Evol 300:493–503
Roein Z, Hassanpour Asil M, Sabouri A (2015) Identification of AFLP markers associated with flowering time and ornamental traits in Chrysanthemum. Iran J Genet Plant Breed 4:37–47
Shao QS, Guo QS, Deng YM, Guo HP (2010) A comparative analysis of genetic diversity in medicinal Chrysanthemum morifolium based on morphology, ISSR and SRAP markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 38:1160–1169
Solouki M, Mehdikhani H, Zeinali H, Emamjomeh AA (2008) Study of genetic diversity in chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) based on morphological traits and molecular markers. Sci Hortic 117:281–287
Soriano JM, Villegas D, Aranzana MJ, Moral LFG, Royo C (2016) Genetic structure of modern durum wheat cultivars and mediterranean landraces matches with their agronomic performance. PLoS One 11:e0160983
Talebi M, Rahimmalek M, Norouzi M (2015) Genetic diversity of Thymus daenensis subsp. daenensis using SRAP markers. Biologia 70:453–459
**e WG, Zhang XQ, Cai HW, Liu W, Peng Y (2010) Genetic diversity analysis and transferability of cereal EST-SSR markers to orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.). Biochem Syst Ecol 38:740–749
Yao MZ, Chen L, Liang YR (2008) Genetic diversity among tea cultivars from China, Japan and Kenya revealed by ISSR markers and its implication for parental selection in tea breeding programmes. Plant Breed 127:166–172
Zhang F, Chen S, Chen F, Fang W, Chen Y, Li F (2011a) SRAP-based map** and QTL detection for inflorescence-related traits in Chrysanthemum (Dendranthema morifolium). Mol Breed 27:11–23
Zhang F, Chen S, Chen F, Fang W, Deng Y, Chang Q, Liu P (2011b) Genetic analysis and associated SRAP markers for flowering traits of Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium). Euphytica 177:15–24
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Mohammad Reza Shafie at the National Research Center of Ornamental Plants, Mahallat, Iran, for providing the genetic materials used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Inhwa Yeam.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodaei, M., Rahimmalek, M. & Arzani, A. Genetic diversity of Iranian Chrysanthemum morifolium cultivars using morphological traits and sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 60, 753–765 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00137-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00137-5