Abstract
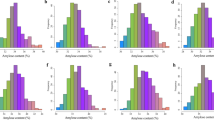
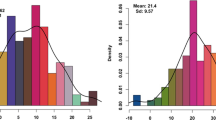
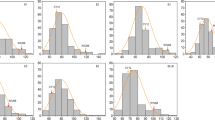
Iron and zinc deficiency is a major problem among large populations in rice-consuming countries. Development micronutrient dense rice varieties with high yield is a key target area in breeding programmes and QTL map** studies using backcross inbred lines to transfer beneficial genes from wild relatives is one of the potential strategy. In this study, 136 BC4F10 backcross inbred lines (BILs) from BPT5204 x Oryza rufipogon WR119 were field evaluated for 3 years for nine yield related traits. Grain Fe and Zn were estimated using ED-XRF. In all, 11 major QTLs with phenotypic variance from 10 to 16.8% were identified for Fe, Zn, and 5 yield related traits. O. rufipogon alleles were trait-enhancing in 18% of all QTLs and an allele at qFe2.1 increased iron concentration. Major effect QTLs qFe1.1 for grain Fe and qZn5.1, qZn8.1, and qZn10.1 for grain Zn explained 11 to 16% PVE, qZn8.1 and qZn10.1 were co-located with QTLs for grain yield related traits. Seven chromosomal regions showed QTLs for more than two traits. QTLs were associated with several high priority candidate genes for grain Fe, Zn and yield. One elite BIL [IET 24775 RP4920-Bio51B] was tested in AICRIP bio fortification trials for 4 years [2014–2017], and three BILs [IET 28715 RP4920-Bio61-1B], [IET28706 RP4920-Bio83B] and [IET28695 RP4920-Bio88B] are evaluated for 2 years of trials. The significant BILs and QTLs are useful in rice bio fortification and for gene discovery.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Authors declare data and materials of this study are available as supplementary material.
Abbreviations
- BM:
-
Biomass
- BY:
-
Bulk yield
- DFF:
-
Days to 50% flowering
- EAR:
-
Estimated average requirement
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- MAGIC:
-
Multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross
- NPN:
-
Number of productive tillers per plant
- PH:
-
Plant height
- PW:
-
Panicle weight
- RCBD:
-
Randomized complete block design
- TN:
-
Number of tillers per plant
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- YLDP:
-
Yield per plant
References
Adeva C, Yun Y-T, Shim K-C, Luong NH, Lee H-S, Kang J-W, Kim H-J, Ahn S-N (2023) QTL map** of mineral element contents in rice using introgression lines derived from an interspecific cross. Agronomy 13:76. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010076
Agarwal S, Venkata TVGN, Kotla A, Mangrauthia SK, Neelamraju S (2014) Expression patterns of QTL based and other candidate genes in Madhukar×Swarna RILs with contrasting levels of iron and zinc in unpolished rice grains. Gene 546:430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.05.069
Agarwal S, Mangrauthia SK, Sarla N (2018) Genomic approaches for micronutrients bio fortification of rice. In: Mohammad AH, Takehiro K, David B, Lam-Son PT, Toru F (eds) Plant micronutrient use efficiency-molecular and genomic perspectives in crop plants, pp 245–260. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812104-7.00014-9
Akinwale MG, Gregorio G, Nwilene F, Akinyele BO, Ogunbayo SA, Odiyi AC (2011) Heritability and correlation coefficient analysis for yield and its components in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Afr J Plant Sci 5:207–212
Andaya VC, Mackill DJ (2003) QTLs conferring cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice using recombinant inbred lines from a japonica x indica cross. Theor Appl Genet 106:1084–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1126-7
Anuradha K, Agarwal S, Batchu AK, Babu AP, Swamy M, Longvah T, Sarla N (2012a) Evaluating rice germplasm for iron and zinc concentration in brown rice and seed dimensions. J Phytol 4:19–25
Anuradha K, Agarwal S, Rao YV, Rao KV, Viraktamath BC, Sarla N (2012b) Map** QTLs and candidate genes for iron and zinc concentrations in unpolished rice of Madhukar × Swarna RILs. Gene 508:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.07.054
Anusha G, Rao DS, Jaldhani V, Beulah P, Neeraja CN, Gireesh C, Anantha MS, Suneetha K, Santhosha R, Prasad AS, Sundaram RM, Madhav MS, Fiyaz A, Brajendra P, Tuti MD, Bhave MH, Krishna KV, Ali J, Subrahmanyam D, Senguttuvel P (2021) Grain Fe and Zn content, heterosis, combining ability and its association with grain yield in irrigated and aerobic rice. Sci Rep 11:10579
Aoyama T, Kobayashi T, Takahashi M, Nagasaka S, Usuda K, Kakei Y, Ishimaru Y, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2009) OsYSL18 is a rice iron (III)-deoxymugineic acid transporter specifically expressed in reproductive organs and phloem of lamina joints. Plant Mol Biol 70:681–692
Babu A, Kumari K, Swamy B, Reddy ChS, Ramesha M, Sarla N (2017) Marker aided selection of yield-enhancing QTL yld2.1 into restorer KMR3 and fine map** a genomic region on chromosome 2. J Exp Agric Int 17:1–14. https://doi.org/10.9734/jeai/2017/34039
Bollinedi H, Yadav AK, Vinod KK, Gopala Krishnan S, Bhowmick PK, Nagarajan M, Neeraja CN, Ellur RK, Singh AK (2020) Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Marker-Trait Associations (MTAs) Governing the Localization of Fe and Zn in the Rice Grain. Front Genet 11:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00213
Briat JF, Dubos C, Gaymard F (2015) Iron nutrition, biomass production, and plant product quality. Trends Plant Sci 20:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.07.005
Calayugan MIC, Formantes AK, Amparado A, Descalsota-Empleo GI, Nha CT, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Swe ZM, Hernandez JE, Borromeo TH, Lalusin AG, Mendioro MS, Diaz MGQ, Viña CBD, Reinke R, Swamy BPM (2020) Genetic analysis of agronomic traits and grain iron and zinc concentrations in a doubled haploid population of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Rep 10:2283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59184-z
Cheng SH, Zhuang JY, Fan YY, Du JH, Cao LY (2007) Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: a super-domesticate in China. Annuals of Botany 100:959–966. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm121
Dai GJ, Cheng SH, Hua ZT, Zhang ML, Jiang HB, Feng Y, Shen XH, Su YA, He N, Ma ZB, Ma XQ, Hou SG, Wang YR (2015) Map** quantitative trait loci for nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency in rice (Oryza sativa L.) at different nitrogen fertilizer levels. Genet Mol Res 14:10404–10414. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.September.8.1
Descalsota GIL, Swamy BPM, Zaw H, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Amparado A, Mauleon R, Chadha-Mohanty P, Arocena EC, Raghavan C, Leung H, Hernandez JE, Lalusin AB, Mendioro MS, Diaz MGQ, Reinke R (2018) Genome-wide association map** in a rice magic plus population detects qtls and genes useful for biofortification. Front Plant Sci 9:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01347
Dixit S, Singh UM, Abbai R, Ram T, Singh VK, Paul A, Virk PS, Kumar A (2019) Identification of genomic region(s) responsible for high iron and zinc content in rice. Sci Rep 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43888-y
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Duan P, Xu J, Zeng D, Zhang B, Geng M, Zhang G, Huang K, Huang L, Xu R, Ge S, Qian Q, Li Y (2017) Natural variation in the promoter of GSE5 contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Mol Plant 10:685–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.03.009
Dufey I, Mathieu AS, Draye X, Lutts S, Bertin P (2015) Construction of an integrated map through comparative studies allows the identification of candidate regions for resistance to ferrous iron toxicity in rice. Euphytica 203:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1255-5
Feng Z, Wu C, Wang C, Roh J, Zhang L, Chen J, Zhang S, Zhang H, Yang C, Hu J, You X, Liu X, Yang X, Guo X, Zhang X, Wu F, Terzaghi W, Kim SK, Jiang L, Wan J (2016) SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice. J Exp Bot 67:4241–4253. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw204
FAO Stats (2018). http://www.fao.org/statistics/en/
Garcia-Oliveira AL, Tan L, Fu Y, Sun C (2009) Genetic identification of quantitative trait loci for contents of mineral nutrients in rice grain. J Integr Plant Biol 51:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00730.x
Garcia-Oliveira AL, Chander S, Ortiz R, Menkir A, Gedil M (2018) Genetic basis and breeding perspectives of grain iron and zinc enrichment in cereals. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00937
Gong HB, Zeng SY, Xue X, Zhang YF, Chen ZX, Zuo S, Li C, Lin TZ, **g DD, Yu B, Qian HF, Pan XB, Sheng SL (2017) Fine map** of a novel wax crystal-sparse leaf3 gene in rice. J Integ Agric 16:497–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61470-3
Haritha G, Vishnukiran T, Venkateswara Rao Y, Gowthami C, Divya B, Sarla N, Subrahmanyam D (2019) Characterization of Oryza nivara introgression lines: a potential prebreeding resource to improve net photosynthetic rate in elite cultivars of rice. Photosynthetica 57:47–60. https://doi.org/10.32615/ps.2019.003
Hotz C, Brown KH (2004) International Zinc Nutrition Consultative Group (IZiNCG) Technical Document 1: Assessment of the risk of zinc deficiency in populations and options for its control. Food Nutr Bull 25:S94–S200
Hu J, Wang Y, Fang Y, Zeng L, Xu J, Yu H, Shi Z, Pan J, Zhang D, Kang S, Zhu L, Dong G, Guo L, Zeng D, Zhang G, **e L, **ong G, Li J, Qian Q (2015) A rare allele of GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 8:1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.07.002
Hurrell R, Egli I (2010) Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. Am J Clin Nutr 91:1461–1467. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2010.28674F
Hussain K, Yingxing Z, Anley W, Riaz A, Abbas A, Rani MH, Hong W, ** of quantitative trait loci for grain size in introgression line derived from Oryza rufipogon. Rice Sci 27:246–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2020.04.007
Ishikawa R, Iwata M, Taniko K, Monden G, Miyazaki N, Orn C, Tsujimura Y, Yoshida S, Ma JF, Ishii T (2017) Detection of quantitative trait loci controlling grain zinc concentration using Australian wild rice, Oryza meridionalis, a potential genetic resource for biofortification of rice. PLoS ONE 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187224
Jia B, Zhao X, Qin Y, Irfan M, Kim TH, Wang B, Wang S, Sohn JK (2019) Quantitative trait loci map** of panicle traits in rice. Mol Biol Res Commun 8:9–15. https://doi.org/10.22099/mbrc.2019.31550.1366
Kader MA, Biswas PS, Aditya TL, Anisuzzaman M, Hore TK, Haq ME (2020) Zinc enriched high yielding rice variety BRRI dhan84 for dry season rice growing areas of Bangladesh. Asian Plant Res J 6:6–13. https://doi.org/10.9734/aprj/2020/v6i130117
Kappara S, Neelamraju S, Ramanan R (2018) Down regulation of a heavy metal transporter gene influences several domestication traits and grain Fe-Zn content in rice. Plant Sci 276:208–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.09.003
Kaur R, Chakraborty A, Bhunia RK, Bhattacharyya J, Basu A, Sen SK, Ghosh AK (2017) Wsi18 promoter from wild rice genotype, Oryza nivara, shows enhanced expression under soil water stress in contrast to elite cultivar, IR20. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 26:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-016-0355-9
Kaur A, Neelam K, Kitazumi A, Kaur K, Sharma P, Mangat GS, de los Reyes BG, Brar DS, Singh K, (2020) Novel cis-acting regulatory elements in wild Oryza species impart improved rice bran quality by lowering the expression of phospholipase D alpha1 enzyme (OsPLDα1). Mol Biol Rep 47:401–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05144-4
Kim SR, Ramos JM, Hizon RJM, Ashikari M, Virk PS, Torres EA, Nissila E, Jena KK (2018) Introgression of a functional epigenetic OsSPL14 WFP allele into elite indica rice genomes greatly improved panicle traits and grain yield. Sci Rep 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21355-4
Kiranmayi SL, Manorama K, Tripura Venkata VGN, Radhika K, Cheralu C, Roja V, Sarla N (2014) Identification of markers associated with iron and zinc concentration in recombinant inbred lines of brown rice. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 74:423–429. https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-6906.2014.00865.7
Kitomi Y, Hanzawa E, Kuya N, Inoue H, Hara N, Kawai S, Kanno N, Endo M, Sugimoto K, Yamazaki T, Sakamoto S, Sentoku N, Wu J, Kanno H, Mitsuda N, Toriyama K, Sato T, Uga Y (2020) Root angle modifications by the DRO1 homolog improve rice yields in saline paddy fields. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:21242–21250. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2005911117
Li J, Zhang M, Sun J, Mao X, Wang J, Liu H, Zheng H, Li X, Zhao H, Zou D (2020) Heavy metal stress-associated proteins in rice and arabidopsis:genome-wide identification, phylogenetics, duplication, and expression profiles analysis. Front Genet 11:1–21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00477
Liu Q, Harberd NP, Fu X (2016) Squamosa promoter binding protein-like transcription factors: targets for improving cereal grain yield. Mol Plant 9:765–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.04.008
Lou J, Chen L, Yue G, Lou Q, Mei H, ** of grain quality traits in rice. J Cereal Sci 50:145–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2009.04.005
McCouch SR, Sweeney M, Li J, Jiang H, Thomson M, Septiningsih E, Edwards J, Moncada P, **ao J, Garris A, Tai T, Martinez C, Tohme J, Sugiono M, McClung A, Yuan LP, Ahn SN (2007) Through the genetic bottleneck: O. rufipogon as a source of trait-enhancing alleles for O. sativa. Euphytica 154:317–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9210-8
Mishra A, Shamim M, Siddiqui MW, Singh A, Srivastava D, Singh KN (2020) Genotypic variation in spatial distribution of fe in rice grains in relation to phytic acid content and ferritin gene expression. Rice Sci 27:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2020.04.005
Montoya M, Vallejo A, Recio J, Guardia G, Alvarez JM (2020) Zinc–nitrogen interaction effect on wheat biofortification and nutrient use efficiency. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 183:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201900339
Muthayya S, Rah JH, Sugimoto JD, Roos FF, Kraemer K, Black RE (2013) The global hidden hunger indices and maps: an advocacy tool for action. PLoS ONE 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067860
Naik SM, Raman AK, Nagamallika M, Venkateshwarlu C, Singh SP, Kumar S, Singh SK, Tomizuddin A, Das SP, Prasad K, Izhar T, Mandal NP, Singh NK, Yadav S, Reinke R, Swamy BPM, Virk P, Kumar A (2020) Genotype × environment interactions for grain iron and zinc content in rice. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10454
Ozyildirim S, Baltaci SB (2022) Cardiovascular diseases and zinc. Biol Trace Elem Res 201:1615–1626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03292-6
Perera I, Fukushima A, Akabane T, Horiguchi G, Seneweera S, Hirotsu N (2019) Expression regulation of myo-inositol 3-phosphate synthase 1 (INO1) in determination of phytic acid accumulation in rice grain. Sci Rep 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51485-2
Pradhan SK, Pandit E, Pawar S, Naveenkumar R, Barik SR, Mohanty SP, Nayak DK, Ghritlahre SK, Sanjiba Rao D, Reddy JN, Patnaik SSC (2020) Linkage disequilibrium map** for grain Fe and Zn enhancing QTLs useful for nutrient dense rice breeding. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-2262-4
Qamar ZU, Hameed A, Ashraf M, Rizwan M, Akhtar M (2019) Development and molecular characterization of low phytate basmati rice through induced mutagenesis, hybridization, backcross, and marker assisted breeding. Front Plant Sci 10:1525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01525
Qiao W, Qi L, Cheng Z, Su L, Li J, Sun Y, Ren J, Zheng X, Yang Q (2016) Development and characterization of chromosome segment substitution lines derived from Oryza rufipogon in the genetic background of O. sativa spp. indica cultivar 9311. BMC Genom 17:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2987-5
Rana N, Rahim MS, Kaur G, Bansal R, Kumawat S, Roy J, Deshmukh R, Sonah H, Sharma TR (2019) Applications and challenges for efficient exploration of omics interventions for the enhancement of nutritional quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1685454
Samtiya M, Aluko RE, Dhewa T (2020) Plant food anti-nutritional factors and their reduction strategies: an overview. Food Prod Process Nutr 2:1–14
Sanjeeva Rao D, Neeraja CN, Madhu Babu P, Nirmala B, Suman K, Rao LVS, Surekha K, Raghu P, Longvah T, Surendra P, Kumar R, Babu VR, Voleti SR (2020) Zinc biofortified rice varieties: challenges, possibilities, and progress in India. Front Nutr 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00026
Senguttuvel P, Padmavathi G, Jasmine C, Sanjeeva Rao D, Neeraja CN, Jaldhani V, Beulah P, Gobinath R, Aravind Kumar J, Sai Prasad SV, Subba Rao LV, Hariprasad AS, Sruthi K, Shivani D, Sundaram RM, Govindaraj M (2023) Rice biofortification: breeding and genomic approaches for genetic enhancement of grain zinc and iron contents. Front Plant Sci 14:1138408
Shi CL, Dong NQ, Guo T, Ye WW, Shan JX, Lin HX (2020) A quantitative trait locus GW6 controls rice grain size and yield through the gibberellin pathway. Plant J 103:1174–1188. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14793
Singh U, Praharaj CS, Chaturvedi SK, Bohra A (2016) Biofortification: introduction, approaches, limitations, and challenges. Biofortification Food Crops. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2716-8
Surapaneni M, Balakrishnan D, Mesapogu S, Addanki KR, Yadavalli VR, Tripura Venkata VGN, Neelamraju S (2017) Identification of major effect QTLs for agronomic traits and CSSLs in rice from swarna/Oryza nivara derived backcross inbred lines. Front Plant Sci 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01027
Swamy BPM, Sarla N (2008) Yield-enhancing quantitative trait loci (QTLs) from wild species. Biotechnol Adv 26:106–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.09.005
Swamy BPM, Sarla N (2011) Meta-analysis of yield QTLs derived from inter-specific crosses of rice reveals consensus regions and candidate genes. Plant Mol Biol Report 29:663–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0274-1
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Ashok Reddy G, Viraktamath BC, Sarla N (2014) Map** and introgression of QTL for yield and related traits in two backcross populations derived from Oryza sativa cv. Swarna and two accessions of O. nivara. J Genet 93:643–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-014-0420-x
Swamy BPM, Rahman MA, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Amparado A, Manito C, Chadha-Mohanty P, Reinke R, Slamet-Loedin IH (2016) Advances in breeding for high grain Zinc in Rice. Rice. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-016-0122-5
Swamy BPM, Descalsota GIL, Nha CT, Amparado A, Inabangan-Asilo MA, Manito C, Tesoro F, Reinke R (2018a) Identification of genomic regions associated with agronomic and biofortification traits in DH populations of rice. PLoS ONE 13:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201756
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Anuradha K, Batchu AK, Longvah T, Sarla N (2018b) QTL analysis for grain iron and zinc concentrations in two O.nivara derived backcross populations. Rice Sci 25:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2018.06.003
Tan L, Qu M, Zhu Y, Peng C, Wang J, Gao D, Chen C (2020) Zinc transporter5 and zinc transporter9 function synergistically in zinc/cadmium uptake1. Plant Physiol 183:1235–1249. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.01569
Thalapati S, Batchu AK, Neelamraju S, Ramanan R (2012) Os11Gsk gene from a wild rice, Oryza rufipogon improves yield in rice. Funct Integr Genomics 12:277–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-012-0265-4
Thalapati S, Guttikonda H, Nannapaneni ND, Adari PB, Surendhar Reddy C, Swamy BPM, Batchu AK, Basava RK, Viraktamath BC, Neelamraju S (2014) Heterosis and combining ability in rice as influenced by introgressions from wild species Oryza rufipogon including qyld2.1 sub-QTL into the restorer line KMR3. Euphytica 202:81–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1222-1
Toxqui L, Vaquero MP (2015) Chronic iron deficiency as an emerging risk factor for osteoporosis: a hypothesis. Nutrients 7:2324–2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7042324
United Nations Environment Programme (2021) Food systems hold key to ending world hunger. Available at: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/food-s
Uttam GA, Suman K, Jaldhani V, Babu PM, Rao DS, Sundaram RM, Neeraja CN (2022) Identification of genomic regions associated with high grain Zn content in polished rice using genoty**-by-sequencing (GBS). Plants 12(1):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010144
Wairich A, Ricachenevsky FK, Lee S (2022) A tale of two metals: Biofortification of rice grains with iron and zinc. Front Plant Sci 13:944624. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.944624
Weng X, Wang L, Wang J, Hu Y, Du H, Xu C, **ng Y, Li X, **ao J, Zhang Q (2014) Grain number, plant height, and heading Date7 is a central regulator of growth, development, and stress response. Plant Physiol 164:735–747. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.231308
Wheeler E, Ferrel RE (1971) A method for Phytic acid determination in wheat and wheat fractions. Cereal Chem 48:312–320
World production volume of milled rice (2020) Available online at: https://www.statista.com/aboutus/our-research-commitment/1239/m-shahbandeh
WorldHealthOrganization(2021)Malnutrition. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/ detail/malnutrition. Accessed Nov 2023
Yadavalli VR, Balakrishnan D, Surapaneni M, Addanki K, Mesapogu S, Beerelli K, Desiraju S, Voleti SR, Neelamraju S (2022) Map** QTLs for yield and photosynthesis-related traits in three consecutive backcross populations of Oryza sativa cultivar Cottondora Sannalu (MTU1010) and Oryza rufipogon. Planta 256(4):71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-022-03983-3
Yan B, Liu R, Li Y, Wang Y, Gao G, Zhang Q, Liu X, Jiang G, He Y (2014) QTL analysis on rice grain appearance quality, as exemplifying the typical events of transgenic or backcrossing breeding. Breed Sci 64:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.64.231
Yang Z, Wu Y, Li Y, Ling HQ, Chu C (2009) OsMT1a, a type 1 metallothionein, plays the pivotal role in zinc homeostasis and drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 70:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9466-1
Yin C, Li H, Li S, Xu L, Zhao Z, Wang J (2015) Genetic dissection on rice grain shape by the two-dimensional image analysis in one japonica × indica population consisting of recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 128:1969–1986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2560-7
Young MF, Luo H, Suchdev PS (2023) The challenge of defining the global burden of iron deficiency anaemia. Lancet Haematol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(23)00168-0
Yugandhar P, Basava RK, Desiraju S, Voleti SR, Sharma RP, Neelamraju S (2017) Identifying markers associated with yield traits in Nagina22 rice mutants grown in low phosphorus field or in alternate wet/dry conditions. Aust J Crop Sci 11:548–556. https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.17.11.05.p372
Zhang F, Wu XN, Zhou HM, Wang DF, Jiang TT, Sun YF, Cao Y, Pei WX, Bin SS, Xu GH (2014) Overexpression of rice phosphate transporter gene OsPT6 enhances phosphate uptake and accumulation in transgenic rice plants. Plant Soil 384:259–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2168-8
Zhang Z, Hu W, Shen G, Liu H, Hu Y, Zhou X, Liu T, **ng Y (2017) Alternative functions of Hd1 in repressing or promoting heading are determined by Ghd7 status under long-day condition. Sci Rep 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05873-1
Zhang YY, Stockmann R, Ng K, Ajlouni S (2021) Opportunities for plant-derived enhancers for iron, zinc, and calcium bioavailability: a review. Comp Rev Food Sci Food Saf 20(1):652–685
Zhou W, Wang X, Zhou D, Ouyang Y, Yao J (2017) Overexpression of the 16-kDa α-amylase/trypsin inhibitor RAG2 improves grain yield and quality of rice. Plant Biotechnol J 15:568–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12654
Zhu YJ, Fan YY, Wang K, Huang DR, Liu WZ, Ying JZ, Zhuang JY (2017) Rice Flowering Locus T 1 plays an important role in heading date influencing yield traits in rice. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05302-3
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge ICAR-NPFFGM project 3019 (NPTC/FG/05/2672/33) Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India for the financial support to carry out the research work. The initial BC4F3 map** population was developed by BPM Swamy and carried forward by A Prasad Babu in DBT funded Network Project on Functional Genomics of Rice sub project Yield (BT/AB/FG -2(PHII- IA/2009) at IIRR. GC thanks Dr. P. Sudhakar and Dr. A. Krishna Satya, Department of Biotechnology, Acharya Nagarjuna University for Ph.D registration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GC: Investigation; Methodology; Writing—original draft. DB: Methodology; Data curation; Software; Formal analysis; Validation; Writing—review & editing. SBM: Investigation. SKM: Project administration; Writing—review & editing. SRD, CN: Investigation, methodology, writing- review and editing, supervision, validation. RMS: supervision, writing- review and editing, validation. Sarla Neelamraju: Conceptualization; Funding acquisition; Resources; Supervision; Project administration; Validation; Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13562_2023_869_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary file 1 (DOC 364 kb). Supplementary Table 1. Details of the polymorphic markers between BPT5204 and O. rufipogon used in QTL map**. Supplementary Table 2. Single Marker Analysis for grain Fe Zn and yield related traits. Supplementary Table 3. QTLs for grain Fe, Zn and yield related traits across 3 years. Supplementary Table 4. Novel and consistent QTLs identified at same marker interval across 2 years. Supplementary Table 5. AICRIP data of elite high grain Zn BILs in comparison with checks.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chandu, G., Balakrishnan, D., Munnam, S.B. et al. Map** QTLs for grain iron, zinc, and yield traits in advanced backcross inbred lines of Samba mahsuri (BPT5204)/Oryza rufipogon. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 33, 68–84 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-023-00869-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-023-00869-7