Abstract
Background
An ideal glucose-lowering drug is expected to not only improve glycemic control, but also have positive effects on weight, blood pressure, dyslipidemia, and also cardiovascular and renal outcomes.
Objective
To investigate and compare the impact of Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on glycemic and extraglycemic laboratory parameters and the parameters which affect this impact.
Methods
This retrospective study was conducted between January 2022 and December 2022. A total of 250 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) using SGLT2i were included in the study.
Results
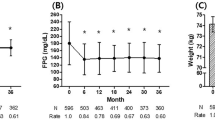
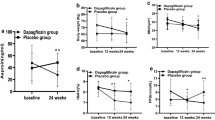
Patients had a mean age of 55.4 ± 9.6, and 53.6% (n = 134) were male. Among the patients, 19.6% (n = 49) used dapagliflozin and 80.4% (n = 201) used empagliflozin. Glucose, HbA1c, and triglyceride levels at 3 and 6 months showed significant reductions compared to baseline, while serum sodium and HDL-C levels showed significant increases (p < 0.001). Additionally, creatinine and serum potassium levels at 6 months were significantly higher than baseline, while LDL-C and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio levels were significantly lower. Empagliflozin users exhibited significantly higher creatinine levels only at 3. months, higher serum sodium levels only at 6. months, and lower HbA1c levels only at 6. months compared to dapagliflozin users.
Conclusion
While SGLT2i seem to provide positive effects on the lipid profile, as well as their well-recognized effects on glycemic parameters, there may be value in further evaluating renal safety and the long-term alterations in lipid profile.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Suppl 1):S13-s28.
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(2):255–323.
Davies MJ, D’alessio DA, Fradkin J, Kernan WN, Mathieu C, Mingrone G, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2018;61(12):2461–98.
Brown E, Heerspink HJL, Cuthbertson DJ, Wilding JPH. SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists: established and emerging indications. Lancet. 2021;398(10296):262–76.
Scheen AJ. An update on the safety of SGLT2 inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019;18(4):295–311.
Vallon V. The mechanisms and therapeutic potential of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:255–70.
Storgaard H, Gluud LL, Bennett C, Grøndahl MF, Christensen MB, Knop FK, et al. Benefits and harms of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(11): e0166125.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(24):2295–306.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–28.
Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, De Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(7):644–57.
Kosiborod M, Cavender MA, Fu AZ, Wilding JP, Khunti K, Holl RW, et al. Lower risk of heart failure and death in patients initiated on sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors versus other glucose-lowering drugs: The CVD-REAL study (Comparative effectiveness of cardiovascular outcomes in new users of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors). Circulation. 2017;136(3):249–59.
Raschi E, Poluzzi E, Fadini GP, Marchesini G, De Ponti F. Observational research on sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors: A real breakthrough? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(12):2711–23.
American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Suppl 1):S90-s102.
Bonora BM, Avogaro A, Fadini GP. Extraglycemic effects of SGLT2 inhibitors: A review of the evidence. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:161–74.
Basu D, Huggins LA, Scerbo D, Obunike J, Mullick AE, Rothenberg PL, et al. Mechanism of increased LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) and decreased triglycerides with SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2) inhibition. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(9):2207–16.
Szalat A, Perlman A, Muszkat M, Khamaisi M, Abassi Z, Heyman SN. Can SGLT2 inhibitors cause acute renal failure? Plausible role for altered glomerular hemodynamics and medullary hypoxia. Drug Saf. 2018;41(3):239–52.
Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, Koskinas KC, Casula M, Badimon L, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur Heart J. 2019;41(1):111–88.
Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ, Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2018;39(2):119–77.
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti Rosei E, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3021–104.
National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guideline for diabetes and CKD: 2012 update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;60(5):850–86.
Samadi A, Sabuncuoglu S, Samadi M, Isikhan SY, Chirumbolo S, Peana M, et al. A comprehensive review on oxysterols and related diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(1):110–36.
Thomas MC, Cherney DZI. The actions of SGLT2 inhibitors on metabolism, renal function and blood pressure. Diabetologia. 2018;61(10):2098–107.
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):323–34.
Mosenzon O, Wiviott SD, Cahn A, Rozenberg A, Yanuv I, Goodrich EL, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on development and progression of kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(8):606–17.
Wheeler DC, Stefánsson BV, Jongs N, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetic and non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a prespecified analysis from the DAPA-CKD trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(1):22–31.
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1577–89.
Patel A, Macmahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2560–72.
Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJL, Neal B, Perkovic V, Billot L, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(11):845–54.
Tang H, Li D, Zhang J, Li Y, Wang T, Zhai S, et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and risk of adverse renal outcomes among patients with type 2 diabetes: A network and cumulative meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19(8):1106–15.
Wu JH, Foote C, Blomster J, Toyama T, Perkovic V, Sundström J, et al. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events, death, and major safety outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016;4(5):411–9.
Häring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Weimer M, Meinicke T, Broedl UC, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(6):1650–9.
Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Swallow R, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, et al. Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16(2):147–58.
Fadini GP, Bonora BM, Zatti G, Vitturi N, Iori E, Marescotti MC, et al. Effects of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on HDL cholesterol, particle size, and cholesterol efflux capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16(1):42.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Ezgi Sahin; Methodology: Ezgi Sahin; Formal analysis and investigation: Elif Ezirmik, Fatma Akyol, Bahar Guler Filiz; Writing—original draft preparation: Deniz Yilmaz; Writing—review and editing: Deniz Yilmaz; Funding acquisition: Deniz Yilmaz; Resources: Ezgi Sahin; Supervision: Deniz Yılmaz.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Dr. Sadi Konuk Training and Research Hospital (Decision date: 21.02.2022, decision no: 2022–04-14).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yilmaz, D., Sahin, E., Akyol, F. et al. The effects of sodium-glucose cotransporters type 2 inhibitors on glycemic and extraglycemic laboratory parameters. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-023-01307-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-023-01307-z