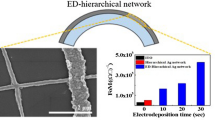
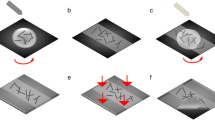
Abstract
Metal network based transparent conducting electrodes are essential for the future optoelectronic devices due to their mechanical flexibility and compatible with large-scale manufacturing. In this report, we investigated the morphological, optical, electrical, and flexible properties of an electrodeposited silver (Ag) mesh transparent conducting electrodes based on a self-cracking template. An overly coated Ag mesh (ED-TE Ag mesh) was prepared onto glass and PET substrates by the sequential deposition steps including thermal evaporation and electroplating methods. The self-cracking template was lift-off prior to the over coating of Ag by the electrodeposition step. The surface morphologies of ED-TE Ag meshes are smooth and well interconnected. The Ag mesh thickness and line width are typically increased with the electroplating time from 0 s to 30 s. The ED-TE Ag mesh shows higher optoelectronic performance with a larger figure of merit (2827 (Ω/sq)−1) than the individual evaporated Ag mesh (756 (Ω/sq)−1) and the ITO film (311 (Ω/sq)−1). Moreover, the low sheet resistance (1.01 Ω/sq) of the ED-TE Ag mesh is observed at 30 s. The ED-TE Ag mesh exhibits almost stable resistance to both concave and convex bending tests, even at a smaller radius of curvature (<2 mm). Thus, these electrodes are more suitable for many flexible device applications like solar cells, displays, etc.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hecht, D.S., Hu, L., Irvin, G.: Emerging transparent electrodes based on thin films of carbon nanotubes, graphene, and metallic nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 23, 1482–1513 (2011)
Rao, K.D.M., Hunger, C., Gupta, R., Kulkarni, G.U., Thelakkat, M.: A cracked polymer templated metal network as a transparent conducting electrode for ITO-free organic solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 15107–15110 (2014)
Bae, S., Kim, H., Lee, Y., Xu, X., Park, J.S., Zheng, Y., Balakrishnan, J., Lei, T., Kim, H.R., Song, Y.I., Kim, Y.J., Kim, K.S., Ozyilmaz, B., Ahn, J.H., Hong, B.H., Iijima, S.: Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 574–578 (2010)
Fortunato, E., Barquinha, P., Martins, R.: Oxide semiconductor thin-film transistors: a review of recent advances. Adv. Mater. 24, 2945–2986 (2012)
Ellmer, K.: Past achievements and future challenges in the development of optically transparent electrodes. Nat. Photonics 6, 809–817 (2012)
Jang, J., Lee, J.S., Hong, K.H., Lee, D.K., Song, S., Kim, K., Eo, Y.J., Yun, J., Chung, C.H.: Cu(In, Ga)Se2 thin film solar cells with solution processed silver nanowire composite window layers: buffer/window junctions and their effects. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 170, 60–67 (2017)
Kumar, A., Zhou, C.: The race to replace tin-doped indium oxide: which material will win? ACS Nano 4, 11–14 (2010)
Yang, L., Zhang, T., Zhou, H., Price, S.C., Wiley, B.J., You, W.: Solution-processed flexible polymer solar cells with silver nanowire electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 4075–4084 (2011)
Chung, C.H.: Lateral photocurrent method for directly measuring the sheet resistance of a junction partner for a chalcogenide light absorber in a thin-film solar cell. Phys. Rev. Appl. 17, 1 (2022)
Cho, K.S., Jang, J., Park, J.H., Lee, D.K., Song, S., Kim, K., Eo, Y.J., Yun, J.H., Gwak, J., Chung, C.H.: Optimal CdS buffer thickness to form high-quality CdS/Cu(In, Ga)Se2 junctions in solar cells without plasma damage and shunt paths. ACS Omega 5, 23983–23988 (2020)
Way, A., Luke, J., Evans, A.D., Li, Z., Kim, J.S., Durrant, J.R., Hin Lee, H.K., Tsoi, W.C.: Fluorine doped tin oxide as an alternative of indium tin oxide for bottom electrode of semi-transparent organic photovoltaic devices. AIP Adv. 9(8), 085220 (2019)
Geng, H.Z., Kim, K.K., So, K.P., Lee, Y.S., Chang, Y., Lee, Y.H.: Effect of acid treatment on carbon nanotube-based flexible transparent conducting films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 7758–7759 (2007)
Tenent, R.C., Barnes, T.M., Bergeson, J.D., Ferguson, A.J., To, B., Gedvilas, L.M., Heben, M.J., Blackburn, J.L.: UItrasmooth, large-area, high-uniformity, conductive transparent single-walled-carbon-nanotube films for photovoltaics produced by ultrasonic spraying. Adv. Mater. 21, 3210–3216 (2009)
Han, B., Pei, K., Huang, Y., Zhang, X., Rong, Q., Lin, Q., Guo, Y., Sun, T., Guo, C., Carnahan, D., Giersig, M., Wang, Y., Gao, J., Ren, Z., Kempa, K.: Uniform self-forming metallic network as a high-performance transparent conductive electrode. Adv. Mater. 26, 873–877 (2014)
Tenent, R.C., Barnes, T.M., Bergeson, J.D., Ferguson, A.J., To, B., Gedvilas, L.M., Heben, M.J., Blackburn, J.L.: Ultrasmooth, large-area, high-uniformity, conductive transparent single-walled-carbon-nanotube films for photovoltaics produced by ultrasonic spraying. Adv. Mater. 21, 3210–3216 (2009)
Kim, J., Yun, A.J., Park, B., Kim, J.: Recent progress in carbon electrodes for efficient and cost-benign perovskite optoelectronics. Electron. Mater. Lett. 18, 232–255 (2022)
Kim, K.S., Zhao, Y., Jang, H., Lee, S.Y., Kim, J.M., Kim, K.S., Ahn, J.H., Kim, P., Choi, J.Y., Hong, B.H.: Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature 457, 706–710 (2009)
Yu, H.K.: Copper micro-labyrinth with graphene skin: new transparent flexible electrodes with ultimate low sheet resistivity and superior stability. Nanomaterials 6, 161 (2016)
Kim, N., Kee, S., Lee, S.H., Lee, B.H., Kahng, Y.H., Jo, Y.R., Kim, B.J., Lee, K.: Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS nanofibrils induced by solution-processed crystallization. Adv. Mater. 26, 2268–2272 (2014)
Mengistie, D.A., Ibrahem, M.A., Wang, P.C., Chu, C.W.: Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS treated with formic acid for ITO-free polymer solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 2292–2299 (2014)
Cheong, H.G., Song, D.W., Park, J.W.: Transparent film heaters with highly enhanced thermal efficiency using silver nanowires and metal/metal-oxide blankets. Microelectron. Eng. 146, 11–18 (2015)
Hsu, P.C., Kong, D., Wang, S., Wang, H., Welch, A.J., Wu, H., Cui, Y.: Electrolessly deposited electrospun metal nanowire transparent electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 10593–10596 (2014)
Chee, S.S., Kim, H., Son, M., Ham, M.H.: Aspect ratio control of copper nanowire via solution process and its flexible transparent conductive electrode applications. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16, 404–410 (2020)
Hu, M., Gao, J., Dong, Y., Li, K., Shan, G., Yang, S., Li, R.K.Y.: Flexible transparent PES/silver nanowires/PET sandwich-structured film for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. Langmuir 28, 7101–7106 (2012)
Jung, E.D., Nam, Y.S., Seo, H., Lee, B.R., Yu, J.C., Lee, S.Y., Kim, J.Y., Park, J.U., Song, M.H.: Highly efficient flexible optoelectronic devices using metal nanowire-conducting polymer composite transparent electrode. Electron. Mater. Lett. 11, 906–914 (2015)
Yang, C., Merlo, J.M., Kong, J., **an, Z., Han, B., Zhou, G., Gao, J., Burns, M.J., Kempa, K., Naughton, M.J.: All-solution-processed, scalable, self-cracking ag network transparent conductor. Phys. Status Solidi A 215, 1–6 (2018)
Lee, S., Lee, J.S., Jang, J., Hong, K.H., Lee, D.K., Song, S., Kim, K., Eo, Y.J., Yun, J.H., Gwak, J., Chung, C.H.: Robust nanoscale contact of silver nanowire electrodes to semiconductors to achieve high performance chalcogenide thin film solar cells. Nano Energy 53, 675–682 (2018)
Yang, M.K., Lee, J.K.: CNT/AgNW multilayer electrodes on flexible organic solar cells. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16, 573–578 (2020)
Prabukumar, C., Bhat, K.U.: Beneficial effect of manganese(ii) ions on the morphology of polyol synthesised silver nanowires. Electron. Mater. Lett. 16, 264–275 (2020)
Lee, S., Jang, J., Park, T., Park, Y.M., Park, J.S., Kim, Y.K., Lee, H.K., Jeon, E.C., Lee, D.K., Ahn, B., Chung, C.H.: Electrodeposited silver nanowire transparent conducting electrodes for thin-film solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 6169–6175 (2020)
Cho, K.S., Kang, S., Oh, Y.J., Park, J.S., Lee, S., Wi, J.S., Park, J.H., Song, S., Kim, K., Eo, Y.J., Yun, J.H., Gwak, J., Cho, J.S., Chung, C.H.: Hierarchical silver network transparent conducting electrodes for thin-film solar cells. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 4, 823–830 (2022)
Han, Y., Lin, J., Liu, Y., Fu, H., Ma, Y., **, P., Tan, J.: Crackle template based metallic mesh with highly homogeneous light transmission for high-performance transparent EMI shielding. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–11 (2016)
Rao, K.D.M., Gupta, R., Kulkarni, G.U.: Fabrication of large area, high-performance, transparent conducting electrodes using a spontaneously formed crackle network as template. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 1, 1–7 (2014)
Kiruthika, S., Rao, K.D.M., Kumar, A., Gupta, R., Kulkarni, G.U.: Metal wire network based transparent conducting electrodes fabricated using interconnected crackled layer as template. Mater. Res. Express 1, 026301 (2014)
**an, Z., Han, B., Li, S., Yang, C., Wu, S., Lu, X., Gao, X., Zeng, M., Wang, Q., Bai, P., Naughton, M.J., Zhou, G., Liu, J.M., Kempa, K., Gao, J.: A practical ITO replacement strategy: sputtering-free processing of a metallic nanonetwork. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2, 1–6 (2017)
Cui, M., Zhang, X., Rong, Q., Nian, L., Shui, L., Zhou, G., Li, N.: High conductivity and transparency metal network fabricated by acrylic colloidal self-cracking template for flexible thermochromic device. Org. Electron. 83, 1–6 (2020)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the framework of the Research and Development Program of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER C2-2401-01), the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) that is funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Grant No. NRF-2021R1A2C1005815), and Regional Innovation Strategy (RIS) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE) (2021RIS-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
We declare that this manuscript is original and has not been published before and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
All authors have participated in (a) conception and design, or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (c) approval of the final version.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S., Arepalli, V.K., Yang, E. et al. High Performance and Flexible Electrodeposited Silver Mesh Transparent Conducting Electrodes Based on a Self-Cracking Template. Electron. Mater. Lett. 18, 440–446 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00358-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00358-4