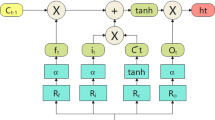
Abstract
With the purpose of improving the accuracy of the wind power short-term forecasting in an effective way, improved wavelet threshold denoising and principal component analysis (PCA) are applied to denoise and reduce the dimension of the original wind power data, the wind power data are reconstructed, and the quality of the information is effectively improved. Next, with the aim of decreasing the nonstationarity of the wind power signal, the reconstructed signal is decomposed in the frequency domain by ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD). In terms of the problem that the extreme learning machine (ELM) algorithm has low stability and accuracy when the quantity of hidden layer neurons is randomly determined, particle swarm optimization algorithm improved (IPSO) by differential evolution (DE) algorithm is introduced to improve the ELM, which is then used to build prediction models for wind power signals in different frequency domains, respectively, and a lower prediction error is achieved. Then, the Markov chain is employed to construct the dynamic combination prediction model, and the weights of different subsignal prediction models are adaptively determined. Compared with adding the prediction values of different subsignals directly, the higher prediction accuracy is demonstrated by the prediction scheme proposed in this paper. At last, actual wind farm operation data are applied to conduct a simulation experiment, and the superiority of the introduced prediction scheme is verified.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shoaib, M.; Siddiqui, I.; Rehman, S.; Khan, S.; Alhems, L.: Assessment of wind energy potential using wind energy conversion system. J. Clean Prod. 216, 346–360 (2019)
Bahrami, A.; Teimourian, A.; Okoye, C.O.; Khosravi, N.: Assessing the feasibility of wind energy as a power source in Turkmenistan; a major opportunity for Central Asia’s energy market. Energy 183, 415–427 (2019)
Zhao, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, A.; Xu, F.: An improved complex ICA based method for wind farm harmonic emission levels evaluation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 179, 106105 (2020)
Geng, H.; Liu, L.; Li, R.: Synchronization and Reactive Current Support of PMSG-Based Wind Farm during Severe Grid Fault. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 9, 1596–1604 (2018)
Notton, G.; Nivet, M.L.; Voyant, C.; Paoli, C.; Darras, C.; Motte, F.; Fouilloy, A.: Intermittent and stochastic character of renewable energy sources: Consequences, cost of intermittence and benefit of forecasting. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 87, 96–105 (2018)
Hong, Y.Y.; Rioflorido, C.L.P.P.: A hybrid deep learning-based neural network for 24-h ahead wind power forecasting. Appl. Energy 250, 530–539 (2019)
Wang, S.X.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; **, C.: Short-term wind power prediction based on improved small-world neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 31, 3173–3185 (2019)
Yu, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Ma, D.; Yu, M.; Wang, J.; Li, B.: Scene learning: Deep convolutional networks for wind power prediction by embedding turbines into grid space. Appl. Energy 238, 249–257 (2019)
Afshari-lgder, M.; Niknam, T.; Khooban, M.H.: Probabilistic wind power forecasting using a novel hybrid intelligent method. Neural Comput. Appl. 30, 473–485 (2018)
Mishra, S.P.; Dash, P.K.: Short-term prediction of wind power using a hybrid pseudo-inverse Legendre neural network and adaptive firefly algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 31, 2243–2268 (2019)
Jiao, R.; Huang, X.; Ma, X.; Han, L.; Tian, W.: A Model Combining Stacked Auto Encoder and Back Propagation Algorithm for Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting. IEEE Access 6, 17851–17858 (2018)
Li, L.L.; Zhao, X.; Tseng, M.L.; Tan, R.R.: Short-term wind power forecasting based on support vector machine with improved dragonfly algorithm. J. Clean Prod. 242, 118447 (2020)
Hong, D.Y.; Ji, T.Y.; Li, M.S.; Wu, Q.H.: Ultra-short-term forecast of wind speed and wind power based on morphological high frequency filter and double similarity search algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 104, 868–879 (2019)
Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Tang, Y.: Clustered hybrid wind power prediction model based on ARMA, PSO-SVM, and clustering methods. IEEE Access 8, 17071–17079 (2020)
Han, S.; Qiao, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.: Mid-to-long term wind and photovoltaic power generation prediction based on copula function and long short term memory network. Appl. Energy 239, 181–191 (2019)
Yin, H.; Ou, Z.; Huang, S.; Meng, A.: A cascaded deep learning wind power prediction approach based on a two-layer of mode decomposition. Energy 189, 116316 (2019)
Shahid, F.; Khan, A.; Zameer, A.; Arshad, J.; Safdar, K.: Wind power prediction using a three stage genetic ensemble and auxiliary predictor. Appl. Soft. Comput. 90, 106151 (2020)
Korprasertsak, N.; Leephakpreeda, T.: Robust short-term prediction of wind power generation under uncertainty via statistical interpretation of multiple forecasting models. Energy 180, 387–397 (2019)
Li, N.; He, F.; Ma, W.: Wind power prediction based on extreme learning machine with kernel mean p-power error loss. Energies 12, 673 (2019)
Yin, H.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ge, J.; Lai, L.L.; Vaccaro, A.; Meng, A.: An effective secondary decomposition approach for wind power forecasting using extreme learning machine trained by crisscross optimization. Energy Conv. Manag. 150, 108–121 (2017)
Hao, Y.; Tian, C.: A novel two-stage forecasting model based on error factor and ensemble method for multi-step wind power forecasting. Appl. Energy 238, 368–383 (2019)
Zhang, C.; Ding, M.; Wang, W.; Bi, R.; Miao, L.; Yu, H.; Liu, L.: An improved ELM model based on CEEMD-LZC and manifold learning for short-term wind power prediction. IEEE Access 7, 121472–121481 (2019)
Zhang, C.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Fu, W.; Peng, T.: A compound structure of ELM based on feature selection and parameter optimization using hybrid backtracking search algorithm for wind speed forecasting. Energy Conv. Manag. 143, 360–376 (2017)
Tan, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, H.: Ultra-short-term wind power prediction by Salp Swarm algorithm-based optimizing extreme learning machine. IEEE Access 8, 44470–44484 (2020)
Yang, H.F.; Chen, Y.P.P.: Representation learning with extreme learning machines and empirical mode decomposition for wind speed forecasting methods. Artif. Intell. 277, 103176 (2019)
Wu, Z.; **a, X.; **ao, L.; Liu, Y.: Combined model with secondary decomposition-model selection and sample selection for multi-step wind power forecasting. Appl. Energy 261, 114345 (2020)
Khan, M.; Liu, T.; Ullah, F.: A new hybrid approach to forecast wind power for large scale wind turbine data using deep learning with Tensorflow framework and principal component analysis. Energies 12, 2229 (2019)
Hu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Chu, J.; Yuan, L.; Pan, L.: Joint point-interval prediction and optimization of wind power considering the sequential uncertainties of stepwise procedure. Energies 12, 2205 (2019)
Tian, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, G.: Short-term wind power prediction based on empirical mode decomposition and improved extreme learning machine. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 13, 1841–1851 (2018)
Lu, P.; Ye, L.; Sun, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, T.: A new hybrid prediction method of ultra-short term wind power forecasting based on EEMD-PE and LSSVM optimized by the GSA. Energies 11, 697 (2018)
Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Du, J.; Cui, Y.: Ultra-short-term multistep wind power prediction based on improved EMD and reconstruction method using run-length analysis. IEEE Access 6, 31908–31917 (2018)
Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Fan, W.; Ma, P.: A new chaotic time series hybrid prediction method of wind power based on EEMD-SE and full-parameters continued fraction. Energy 138, 977–990 (2017)
Sun, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, J.: Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting on Multiple Scales Using VMD Decomposition, K-Means Clustering and LSTM Principal Computing. IEEE Access 7, 166917–166929 (2019)
Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; Hua, X.; Wang, Y.: Wind power prediction based on variational mode decomposition multi-frequency combinations. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 7, 281–288 (2019)
Dong, W.; Yang, Q.; Fang, X.: Multi-step ahead wind power generation prediction based on hybrid machine learning techniques. Energies 11, 1975 (2018)
Ouyang, T.; Zha, X.; Qin, L.: A combined multivariate model for wind power prediction. Energy Conv. Manag. 144, 361–373 (2017)
Liu, L.; Ji, T.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Q.: Short-term local prediction of wind speed and wind power based on singular spectrum analysis and locality-sensitive hashing. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 6, 317–329 (2018)
Ouyang, T.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Tang, Z.: Chaotic wind power time series prediction via switching data-driven modes. Renew. Energy 145, 270–281 (2020)
Chen, P.; Zhang, Q.: Classification of heart sounds using discrete time-frequency energy feature based on S transform and the wavelet threshold denoising. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 57, 101684 (2020)
Bayer, F.M.; Kozakevicius, A.J.; Cintra, R.J.: An iterative wavelet threshold for signal denoising. Signal Process. 162, 10–20 (2019)
Han, L.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, K.; Yang, X.: Online multilinear principal component analysis. Neurocomputing 275, 888–896 (2018)
Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, G.: Wind Speed Prediction of IPSO-BP Neural Network Based on Lorenz Disturbance. IEEE Access 6, 53168–53179 (2018)
Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.: Comparative study on three new hybrid models using Elman Neural Network and Empirical Mode Decomposition based technologies improved by Singular Spectrum Analysis for hour-ahead wind speed forecasting. Energy Conv. Manag. 147, 75–85 (2017)
Liu, H.; Mi, X.; Li, Y.: An experimental investigation of three new hybrid wind speed forecasting models using multi-decomposing strategy and ELM algorithm. Renew. Energy 123, 694–705 (2018)
Tian, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, G. Short-term wind speed prediction based on improved PSO algorithm optimized EM-ELM. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 41, 26–46 (2019)
Li, N.; He, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.: Wind Power Prediction of Kernel Extreme Learning Machine Based on Differential Evolution Algorithm and Cross Validation Algorithm. IEEE Access 8, 68874–68882 (2020)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the guest editors, assistant editors and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.L. supplied the main idea, simulated, and wrote the draft. H.Z. was in charge of technical checking and gave some suggestions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Zou, H. Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Based on Data Reconstruction and Improved Extreme Learning Machine. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 3669–3682 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05311-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05311-x