Abstract
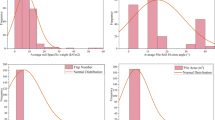
A commonly-encountered problem in foundation design is the reliable prediction of the pile bearing capacity (PBC). This study is planned to propose a feasible soft computing technique in this field i.e.; the Gaussian process regression (GPR) for the PBC estimation. The established database includes 296 number of dynamic pile load test in the field where the most influential factors on the PBC were selected as input variables. Several GPR models were designed and built. These models were assessed using three performance indices namely value account for (VAF), coefficient of determination (R2) and system error. To have a comparison, a genetic algorithm-based artificial neural network (GA-based ANN) model was also employed. It was found that the GPR-based model with VAF value of 86.41%, R2 of 0.84 and system error of 0.2006 is capable enough to predict the PBC and outperforms the GA-based ANN model. The results showed that the GPR can be utilized as a practical tool for the PBC estimation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Momeni, E.; Nazir, R.; Armaghani, D.J.; Maizir, H.: Application of artificial neural network for predicting shaft and tip resistances of concrete piles. Earth Sci. Res. J. 19, 85–93 (2015)
Mayerhof, G.G.: Bearing capacity and settlemtn of pile foundations. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 102, 196–228 (1976)
Momeni, E.; Maizir, H.; Gofar, N.; Nazir, R.: Comparative study on prediction of axial bearing capacity of driven piles in granular materials. J. Teknol. Sci. Eng. 61, 15–20 (2013). https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v61.1777
Milad, F.; Kamal, T.; Nader, H.; Erman, O.E.: New method for predicting the ultimate bearing capacity of driven piles by using Flap number. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 19, 611–620 (2015)
Nazir, R.; Momeni, E.; Gofar, N.; Maizir, H.: Numerical Modelling of skin resistance distribution with depth in driven pile. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 18, 2477–2488 (2013)
Rausche, F.; Goble, G.G.; Likins Jr.; G.E.: Dynamic determination of pile capacity. J. Geotech. Eng. 111, 367–383 (1985)
Dowlatshahi, M.B.; Derhami, V.; Nezamabadi-pour, H.: Ensemble of filter-based rankers to guide an epsilon-greedy swarm optimizer for high-dimensional feature subset selection. Information. 8, 152 (2017)
Dowlatshahi, M.B.; Derhami, V.; Nezamabadi-pour, H.: A novel three-stage filter-wrapper framework for miRNA subset selection in cancer classification. In: Informatics, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, p. 13 (2018)
Paniri, M.; Dowlatshahi, M.B.; Nezamabadi-pour, H.: MLACO: a multi-label feature selection algorithm based on ant colony optimization. Knowl. Based Syst. 192, 105285 (2020)
Hashemi, A.; Dowlatshahi, M.B.; Nezamabadi-pour, H.: MGFS: a multi-label graph-based feature selection algorithm via PageRank centrality. Expert Syst. Appl. 142, 113024 (2020)
Omidinasab, F.; Goodarzimehr, V.: A Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm for truss structures with discrete variables. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 6, 593–604 (2020)
Armaghani, D.J.; Asteris, P.G.; Askarian, B.; Hasanipanah, M.; Tarinejad, R.; Van Huynh, V.: Examining hybrid and single SVM models with different kernels to predict rock brittleness. Sustainability. 12, 2229 (2020)
Armaghani, D.J.; Asteris, P.G.; Fatemi, S.A.; Hasanipanah, M.; Tarinejad, R.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Van Huynh, V.: On the use of neuro-swarm system to forecast the pile settlement. Appl. Sci. 10, 1904 (2020)
Asteris, P.G.; Mokos, V.G.: Concrete compressive strength using artificial neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04663-2
Sarir, P.; Chen, J.; Asteris, P.G.; Armaghani, D.J.; Tahir, M.M.: Develo** GEP tree-based, neuro-swarm, and whale optimization models for evaluation of bearing capacity of concrete-filled steel tube columns. Eng. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00808-y
Cavaleri, L.; Asteris, P.G.; Psyllaki, P.P.; Douvika, M.G.; Skentou, A.D.; Vaxevanidis, N.M.: Prediction of surface treatment effects on the tribological performance of tool steels using artificial neural networks. Appl. Sci. 9, 2788 (2019)
Asteris, P.G.; Nozhati, S.; Nikoo, M.; Cavaleri, L.; Nikoo, M.: Krill herd algorithm-based neural network in structural seismic reliability evaluation. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 26, 1–8 (2018)
Huang, L.; Asteris, P.G.; Koopialipoor, M.; Armaghani, D.J.; Tahir, M.M.: Invasive weed optimization technique-based ANN to the prediction of rock tensile strength. Appl. Sci. 9, 5372 (2019)
Armaghani, D.J.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.D.; Karamani, C.; Skentou, A.; Zoumpoulaki, I.; Asteris, P.G.: Soft computing-based techniques for concrete beams shear strength. Proc. Struct. Integr. 17, 924–933 (2019)
Armaghani, D.J.; Mirzaei, F.; Shariati, M.; Trung, N.T.; Shariati, M.; Trnavac, D.: Hybrid ANN-based techniques in predicting cohesion of sandy-soil combined with fiber. Geomech. Eng. 20, 191–205 (2020)
Armaghani, D.J.; Mohamad, E.T.; Narayanasamy, M.S.; Narita, N.; Yagiz, S.: Development of hybrid intelligent models for predicting TBM penetration rate in hard rock condition. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 63, 29–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2016.12.009
Armaghani, D.J.; Koopialipoor, M.; Marto, A.; Yagiz, S.: Application of several optimization techniques for estimating TBM advance rate in granitic rocks. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2019.01.002
Harandizadeh, H.; Armaghani, D.J.; Mohamad, E.T.: Development of fuzzy-GMDH model optimized by GSA to predict rock tensile strength based on experimental datasets. Neural Comput. Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04803-z
Naghipour, M.; Niak, K.M.; Shariati, M.; Toghroli, A.: Effect of progressive shear punch of a foundation on a reinforced concrete building behavior. Steel Compos. Struct. 35, 279–294 (2020)
Bunawan, A.R.; Momeni, E.; Armaghani, D.J.; Rashid, A.S.A.: Experimental and intelligent techniques to estimate bearing capacity of cohesive soft soils reinforced with soil-cement columns. Measurement 124, 529–538 (2018)
Armaghani, D.J.; Mohamad, E.T.; Momeni, E.; Monjezi, M.; Narayanasamy, M.S.: Prediction of the strength and elasticity modulus of granite through an expert artificial neural network. Arab. J. Geosci. 9, 48 (2016)
Armaghani, D.; Momeni, E.; Abad, S.: Feasibility of ANFIS model for prediction of ground vibrations resulting from quarry blasting. Environ. Earth Sci. 74, 2845–2860 (2015)
Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Mitri, H.S.: Comparative performance of six supervised learning methods for the development of models of hard rock pillar stability prediction. Nat. Hazards. 79, 291–316 (2015)
Zhou, J.; Li, E.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Shi, X.; Yao, S.; Mitri, H.S.: Slope stability prediction for circular mode failure using gradient boosting machine approach based on an updated database of case histories. Saf. Sci. 118, 505–518 (2019)
Zhou, J.; Shi, X.; Li, X.: Utilizing gradient boosted machine for the prediction of damage to residential structures owing to blasting vibrations of open pit mining. J. Vib. Control. 22, 3986–3997 (2016)
Asteris, P.G.; Apostolopoulou, M.; Skentou, A.D.; Moropoulou, A.: Application of artificial neural networks for the prediction of the compressive strength of cement-based mortars. Comput. Concr. 24, 329–345 (2019)
Ghanizadeh, A.R.; Abbaslou, H.; Amlashi, A.T.; Alidoust, P.: Modeling of bentonite/sepiolite plastic concrete compressive strength using artificial neural network and support vector machine. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 13, 215–239 (2019)
Reddy, T.C.S.: Predicting the strength properties of slurry infiltrated fibrous concrete using artificial neural network. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 12, 490–503 (2018)
Chen, R.; Zhang, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, Z.: Prediction of shield tunneling-induced ground settlement using machine learning techniques. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 13, 1363–1378 (2019)
Safa, M.; Maleka, A.; Arjomand, M.-A.; Khorami, M.; Shariati, M.: Strain rate effects on soil-geosynthetic interaction in fine-grained soil. Geomech. Eng. 19, 533 (2019)
Singh, T.; Pal, M.; Arora, V.K.: Modeling oblique load carrying capacity of batter pile groups using neural network, random forest regression and M5 model tree. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 13, 674–685 (2019)
Ismail, A.: ANN-based empirical modelling of pile behaviour under static compressive loading. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 12, 594–608 (2018)
Asteris, P.G.; Nikoo, M.: Artificial bee colony-based neural network for the prediction of the fundamental period of infilled frame structures. Neural Comput. Appl. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-03965-1
Asteris, P.G.; Armaghani, D.J.; Hatzigeorgiou, G.D.; Karayannis, C.G.; Pilakoutas, K.: Predicting the shear strength of reinforced concrete beams using Artificial Neural Networks. Comput. Concr. 24, 469–488 (2019)
Momeni, E.; Poormoosavian, M.; Mahdiyar, A.; Fakher, A.: Evaluating random set technique for reliability analysis of deep urban excavation using Monte Carlo simulation. Comput. Geotech. 100, 203–215 (2018)
Li, E.; Zhou, J.; Shi, X.; Armaghani, D.J.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, P.: Develo** a hybrid model of salp swarm algorithm-based support vector machine to predict the strength of fiber-reinforced cemented paste backfill. Eng. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01014-x
Shariati, M.; Azar, S.M.; Arjomand, M.-A.; Tehrani, H.S.; Daei, M.; Safa, M.: Comparison of dynamic behavior of shallow foundations based on pile and geosynthetic materials in fine-grained clayey soils. Geomech. Eng. 19, 473 (2019)
Safa, M., Sari, P.A., Shariati, M., Suhatril, M., Trung, N.T., Wakil, K., Khorami, M.: Development of neuro-fuzzy and neuro-bee predictive models for prediction of the safety factor of eco-protection slopes. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 550, 124046 (2020)
Shariati, M.; Azar, S.M.; Arjomand, M.-A.; Tehrani, H.S.; Daei, M.; Safa, M.: Evaluating the impacts of using piles and geosynthetics in reducing the settlement of fine-grained soils under static load. Geomech. Eng. 20, 87–101 (2020)
Suhatril, M.; Osman, N.; Sari, P.A.; Shariati, M.; Marto, A.: Significance of surface eco-protection techniques for cohesive soils slope in Selangor, Malaysia. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 37, 2007–2014 (2019)
Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Mitri, H.S.: Evaluation method of rockburst: state-of-the-art literature review. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 81, 632–659 (2018)
Duan, J.; Asteris, P.G.; Nguyen, H.; Bui, X.-N.; Moayedi, H.: A novel artificial intelligence technique to predict compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete using ICA-XGBoost model. Eng. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01003-0
Fatehnia, M.; Amirinia, G.: A review of Genetic Programming and Artificial Neural Network applications in pile foundations. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 9, 2 (2018)
Luo, Z.; Hasanipanah, M.; Amnieh, H.B.; Brindhadevi, K.; Tahir, M.M.: GA-SVR: a novel hybrid data-driven model to simulate vertical load capacity of driven piles. Eng. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00858-2
Harandizadeh, H.; Armaghani, D.J.; Khari, M.: A new development of ANFIS–GMDH optimized by PSO to predict pile bearing capacity based on experimental datasets. Eng. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00849-3
Chen, W.; Sarir, P.; Bui, X.-N.; Nguyen, H.; Tahir, M.M.; Armaghani, D.J.: Neuro-genetic, neuro-imperialism and genetic programing models in predicting ultimate bearing capacity of pile. Eng. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00752-x
Momeni, E.; Nazir, R.; Armaghani, D.J.; Maizir, H.: Prediction of pile bearing capacity using a hybrid genetic algorithm-based ANN. Measurement 57, 122–131 (2014)
Shaik, S.; Krishna, K.S.R.; Abbas, M.; Ahmed, M.; Mavaluru, D.: Applying several soft computing techniques for prediction of bearing capacity of driven piles. Eng. Comput. 35, 1463–1474 (2019)
Mohanty, R.; Suman, S.; Das, S.K.: Prediction of vertical pile capacity of driven pile in cohesionless soil using artificial intelligence techniques. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 12, 1–8 (2016)
Samui, P.: Prediction of pile bearing capacity using support vector machine. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 5, 95–102 (2011)
Muduli, P.K.; Das, S.K.; Das, M.R.: Prediction of lateral load capacity of piles using extreme learning machine. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 7, 388–394 (2013)
Suman, S.; Das, S.K.; Mohanty, R.: Prediction of friction capacity of driven piles in clay using artificial intelligence techniques. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 10, 469–475 (2016)
Armaghani, D.J.; Faradonbeh, R.S.; Rezaei, H.; Rashid, A.S.A.; Amnieh, H.B.: Settlement prediction of the rock-socketed piles through a new technique based on gene expression programming. Neural Comput. Appl. 29, 1115–1125 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2618-8
Jebur, A.A.; Atherton, W.; Al Khaddar, R.M.; Loffill, E.: Artificial neural network (ANN) approach for modelling of pile settlement of open-ended steel piles subjected to compression load. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 1–23 (2018)
Nazir, R.; Momeni, E.; Marsono, K.; Prediction of bearing capacity for thin-wall spread foundations using ICA-ANN predictive model. In: Proc. Int. Conf. Civil, Struct. Transp. Eng. Ottawa, Ontario–May, pp. 4–5 (2015)
Acharyya, R.; Dey, A.: Assessment of bearing capacity for strip footing located near slo** surface considering ANN model. Neural Comput. Appl. 31, 8087–8100 (2019)
Harandizadeh, H.; Toufigh, M.M.; Toufigh, V.: Application of improved ANFIS approaches to estimate bearing capacity of piles. Soft Comput. 23, 9537–9549 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3517-
Rezaei, H.; Nazir, R.; Momeni, E.: Bearing capacity of thin-walled shallow foundations: an experimental and artificial intelligence-based study. J. Zhejiang Univ. A. 17, 273–285 (2016)
Momeni, E.; Armaghani, D.J.; Fatemi, S.A.; Nazir, R.: Prediction of bearing capacity of thin-walled foundation: a simulation approach. Eng. Comput. 34, 319–327 (2018)
Armaghani, D.J.; Raja, R.S.N.S.B.; Faizi, K.; Rashid, A.S.A.: Develo** a hybrid PSO–ANN model for estimating the ultimate bearing capacity of rock-socketed piles. Neural Comput. Appl. 28, 391–405 (2017)
Goh, A.T.C.: Back-propagation neural networks for modeling complex systems. Artif. Intell. Eng. 9, 143–151 (1995)
Goh, A.T.C.: Pile driving records reanalyzed using neural networks. J. Geotech. Eng. 122, 492–495 (1996)
Marto, A.; Hajihassani, M.; Momeni, E.: Bearing capacity of shallow foundation’s prediction through hybrid artificial neural networks. In: Appl. Mech. Mater.; Trans Tech Publ, pp. 681–686 (2014)
Benali, A.; Hachama, M.; Bounif, A.; Nechnech, A.; Karray, M.: A TLBO-optimized artificial neural network for modeling axial capacity of pile foundations. Eng. Comput. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00847-5
Soleimanbeigi, A.; Hataf, N.: Prediction of settlement of shallow foundations on reinforced soils using neural networks. Geosynth. Int. 13, 161–170 (2006)
Padmini, D.; Ilamparuthi, K.; Sudheer, K.P.: Ultimate bearing capacity prediction of shallow foundations on cohesionless soils using neurofuzzy models. Comput. Geotech. 35, 33–46 (2008)
Wardani, S.P.R.; Surjandari, N.S.; Jajaputra, A.A.: Analysis of ultimate bearing capacity of single pile using the artificial neural networks approach: a case study. In: Proc.; 18th Int. Conf. Soil Mech. Geotech. Engrg.; Paris, Fr.; pp. 837–840 (2013)
Ornek, M.; Laman, M.; Demir, A.; Yildiz, A.: Prediction of bearing capacity of circular footings on soft clay stabilized with granular soil. Soils Found. 52, 69–80 (2012)
Kiefa, M.A.A.: General regression neural networks for driven piles in cohesionless soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 124, 1177–1185 (1998)
Nawari, N.O.; Liang, R.; Nusairat, J.: Artificial intelligence techniques for the design and analysis of deep foundations. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 4, 1–21 (1999)
Pal, M.; Deswal, S.: Modeling pile capacity using support vector machines and generalized regression neural network. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 134, 1021–1024 (2008)
Shahin, M.A.: Intelligent computing for modeling axial capacity of pile foundations. Can. Geotech. J. 47, 230–243 (2010)
Shahin, M.A.; Jaksa, M.B.: Intelligent computing for predicting axial capacity of drilled shafts. In: Contemp. Top. Situ Testing, Anal. Reliab. Found.; pp. 26–33 (2009)
Mahesh, P.: Modeling pile capacity using generalized regression neural network. In: Proc.; Indian Geotech. Conf. Kochi, India, No. N-027, pp. 811–814 (2011)
Jianbin, Z.; Jiewen, T.; Yongqiang, S.: An ANN model for predicting level ultimate bearing capacity of PHC pipe pile. In: Earth Sp. 2010 Eng. Sci. Constr. Oper. Challenging Environ.; pp. 3168–3176 (2010)
Benali, A, Nechnech, A.: Prediction of the pile capacity in purely coherent soils using the approach of the artificial neural networks. In: Int. Semin. Innov. Valorization Civ. Eng. Constr. Mater. Rabat, Morocco, pp. 23–25 (2011)
Moayedi, H.; Hayati, S.: Artificial intelligence design charts for predicting friction capacity of driven pile in clay. Neural Comput. Appl. 31, 7429–7445 (2019)
ASTM D 4945-13: Standard test method for high strain testing of piles, American Society for Testing and Materials (2013)
Goble, G.G.; Rausche, F.; Moses, F.: Dynamics Studies on the Bearing Capacity of piles: Final Report to the Ohio Department of Highways, Cleveland, Ohio Case West. Reserv. Univ. (1970)
Fellenius, B.H.: Wave equation analysis and dynamic monitoring. Deep Found J. 1, 49–55 (1984)
Williams, C.K.I.; Rasmussen, C.E.: Gaussian processes for machine learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2006)
Li, J.J.; Jutzeler, A.; Faltings, B.; Winter, S.; Rizos, C.: Estimating urban ultrafine particle distributions with gaussian process models. Res. Locate 14, 145–153 (2014)
Kang, F.; Han, S.; Salgado, R.; Li, J.: System probabilistic stability analysis of soil slopes using Gaussian process regression with Latin hypercube sampling. Comput. Geotech. 63, 13–25 (2015)
Snelson, E.L.: Flexible and efficient Gaussian process models for machine learning. PhD thesis, Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit, University College London (2007)
Dowlatshahi, M.B.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H.: GGSA: a grou** gravitational search algorithm for data clustering. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 36, 114–121 (2014)
Swingler, K.: Applying neural networks: a practical guide. Academic Press, New York (1996)
Armaghani, D.J.; Mohamad, E.T.; Momeni, E.; Narayanasamy, M.S.: An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for predicting unconfined compressive strength and Young’s modulus: a study on Main Range granite. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 74, 1301–1319 (2015)
Mohamad, E.T.; Armaghani, D.J.; Momeni, E.; Yazdavar, A.H.; Ebrahimi, M.: Rock strength estimation: a PSO-based BP approach. Neural Comput. Appl. 30, 1635–1646 (2018)
Momeni, E.; Armaghani, D.J.; Hajihassani, M.; Amin, M.F.M.: Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength of rock samples using hybrid particle swarm optimization-based artificial neural networks. Measurement 60, 50–63 (2015)
Liu, J.; Yan, K.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.: Prediction of autogenous shrinkage of concretes by support vector machine. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 9, 169–177 (2016)
Moore, C.J.; Chua, A.J.K.; Berry, C.P.L.; Gair, J.R.: Fast methods for training Gaussian processes on large datasets. R. Soc. Open Sci. 3, 160125 (2016)
R. MATLAB, version 9.4. 0.813654 (R2018a), MathWorks R Natick, MA, USA (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momeni, E., Dowlatshahi, M.B., Omidinasab, F. et al. Gaussian Process Regression Technique to Estimate the Pile Bearing Capacity. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 8255–8267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04683-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04683-4