Abstract
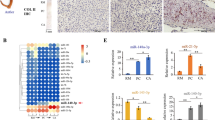
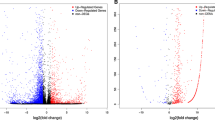
Transforming growth factor (TGF-β) plays a pivotal role in angiogenesis. The purpose of this study was to explore the microRNA-mediated regulation of TGF-β receptor-II (TGFBR2) expression during rapid antler growth and proliferation of antler cells in sika deer. Deep sequencing–based expression analysis of miRNAs on the antler tip tissue was performed. Then, two bioinformatics software were used to analyze TGFBR2 3′-UTR sequence for predicting the matched and differentially expressed miRNAs in different tissues of the antler. The results indicated that miRNA-19a and miRNA-19b exhibited the highest upregulation among differentially expressed miRNAs. We also found that the TGFBR2 3′-UTR contains a binding site for miRNA-19a and miRNA-19b by transfection of wild-type and mutant dual-luciferase reporter vectors into antler cartilage cells. Meanwhile, overexpression of miRNA-19a and miRNA-19b significantly inhibited the proliferation of cartilage cells in vitro, and decreased the expression level of TGFBR2 protein. Furthermore, the expression levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and TGF-β2, which were associated with TGFBR2, reduced after transfection of cartilage cells with miRNA-19a and miRNA-19b. Our results indicate the significant roles of miRNA-19a and miRNA-19b in proliferation of antler cells and its potential application.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derynck R, Zhang YE (2003) Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 425:577–584
Dews M, Fox JL, Hultine S et al (2010) The.Myc-MiR-17-92Axis Blunts TGFβ Signaling and Production of Multiple TGF-βDependent Antiangiogenic Factors. Cancer Research 70:8233–8246
Faucheux C, Nesbitt SA, Horton MA, Price JS (2001) Cells in regenerating deer antler cartilage provide a microenvironment that supports osteoclast differentiation. J Exp Biol 204:443–455
Fricke F, Mussack V, Buschmann D et al (2019) TGFBR2-dependent alterations of microRNA profiles in extra cellular vesicles and parental colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol 19
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Haj-Salem I, Fakhfakh R, Bérubé JC et al (2015) MicroRNA-19a enhances proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells by targeting TGFβR2 gene in severe asthma. Allergy 70:212–219
Yu-Shuai Han, Expression and regulation of TGF-β family and their receptors in sika deer antler, master thesis of Jilin University, (2011) 23–30
Han X, Liu M, Hu W et al (2019) Identification of MicroRNA-148a-3p with a role in transcriptional regulation of TGF-β2 and its relationship with antler cell proliferation. Int J Agric Biol 22:435–442
Heldin CH, Landstrom M, Moustakas A (2009) Mechanism of TGFbeta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchyma transition. Current Opinionin Cell Biology 21:166–176
Herranz SM, Cohen (2010) MicroRNAs and gene regulatory networks: managing the impact of noise in biological systems. Genes Dev 24:1339–1344
Hu W, Li T, Wu L et al (2014a) Identification of microRNA-18a as a novel regulator of the insulin-like growth factor-1 in the proliferation and regeneration of deer antler [J]. Biotechnol Lett 36:703–710
Hu W, Li T, Hu R et al (2014b) MicroRNA let-7a and let-7f as novel regulatory factors of the sika deer (Cervus nippon) IGF-1R gene. Growth Factor 32:27–33
Hu W, Mu L, Hu R et al (2015) microRNA-18b modulates insulin-like growth factor-1 expression in deer antler cell proliferation by directly targeting its 3′ Untranslated region [J]. DNA Cell Biol 34(4):282–289
Huang SS, Huang JS (2005) TGF-beta control of cell proliferation. J Cell Biochem 96:447–462
Lakner AM, Steuerwald NM, Walling TL et al (2012) Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis[J]. Hep-atology 56(1):300–310
Li C (2012) Deer antler regeneration: a stem cell-based epimorphic process, birth defects research. Part C, Embryo Today : reviews 96:51–62
Li C, Suttie JM, Clark DE (2004) Morphological observation of antler regeneration in red deer (Cervus elaphus). J Morphol 262:731–740
Li C, Zhao H, Liu Z, McMahon C (2014) Deer antler--a novel model for studying organ regeneration in mammals. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 56:111–122
Liu M, Han X, Hu W et al (2018) Post-transcriptional regulation of miRNA-15a and miRNA-15b on VEGFR gene and deer antler cell proliferation. Turkish Journal of Biochemistry 44:354–362
Liu M, Han X, Hu W et al (2019) The effects of CRISPR-Cas9 knockout of the TGF-β1 gene on antler cartilage cells in Vitro. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters 24:44
Luo K (2017) Signaling cross talk between TGF-β/Smad and other signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9:a022137
Ma L, Yang Z-Q, Ding J-L et al (2019) Function and regulation of transforming growth factor β1 signalling in antler chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Cell Proliferation:e12637
Mestdagh P, Boström A-K (2010) The miR-17-92 microRNA cluster regulates multiple components of the TGFβ-pathway in neuroblastoma [J]. Mol Cell 40(5):762–773
Mestdagh P, Boström A-K, Impens F et al (2010) The mi R-17-92 micro RNA cluster regulates multiple components of the TGF-β pathway in neuroblastoma. Molecular Cell 40:762–773
Oeztuerk-Winder F, Guinot A, Ochalek A et al (2012) Regulation of human lung alveolar multipotent cells by a novel p38α MAPK/mi R-17-92 axis. EMBOJ 31(16):3431–3441
Pan WL, Chopp M, Fan B et al (2019) Ablation of the microRNA-17-92 cluster in neural stem cells diminishes adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive function. FASEB J 33:5257–5267
Shen J, Li S, Chen D (2014) TGF-β signaling and the development of osteoarthritis. Bone Res 2:73–79
Tang Y, Urs S, Boucher J et al (2010) Notch and transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) signaling pathways cooperatively regulate vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 285:17556–17563
Vander Ark A, Cao J, Li X (2018) TGF-β receptors: In and beyond TGF-β signaling. 52:112–120
Wei HU, Meng X, Lu T et al (2013) MicroRNA-1 inhibits the proliferation of chinese sika deer-derived cartilage cells by binding to the 3′-untranslated region of IGF-1. Mol Med Rep 8:523–528
Wrana JJL, Attisano L, Wieser R et al (1994) Mechanism of activation of the TGF-beta receptor. Nature 370:341–347
**ao FJ, Zhang D, Wu Y et al (2019) miRNA-17-92 protects endothelial cells from erastin-induced ferroptosis through targeting the A20-ACSL4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 515:448–454
Zimmerman CM, Padgett RW (2000) Transforming growth factor beta signaling mediators and modulators. Gene 249:17–30
Zou M, Wang F, Gao R et al (2016) Autophagy inhibition of hsa-miR-19a-3p/19b-3p by targeting TGF-β R II during TGF-β1-induced fibrogenesis in hu- man cardiac fibroblasts. Sci Rep 21:24747
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 31572372 and 30972083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by: Shuiqiao Yuan
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Chen, D., Han, X. et al. MiRNA-19a and miRNA-19b regulate proliferation of antler cells by targeting TGFBR2. Mamm Res 65, 339–348 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-019-00469-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13364-019-00469-8