Abstract
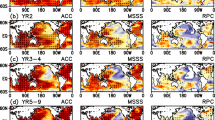
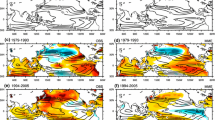
Using the hindcasts provided by the Ensemble-Based Predictions of Climate Changes and Their Impacts (ENSEMBLES) project for the period of 1980-2005, the forecast capability of spring climate in China is assessed mainly from the aspects of precipitation, 2-m air temperature, and atmospheric circulations. The ENSEMBELS can reproduce the climatology and dominant empirical orthogonal function (EOF) modes of precipitation and 2-m air temperature, with some differences arising from different initialization months. The multi-model ensemble (MME) forecast of interannual variability is of good performance in some regions such as eastern China with February initialization. The spatial patterns of the MME interannual and inter-member spreads for precipitation and 2-m air temperature are consistent with those of the observed interannual spread, indicating that internal dynamic processes have major impacts on the interannual anomaly of spring climate in China. We have identified two coupled modes between inter-member anomalies of the 850-hPa vorticity in spring and sea surface temperature (SST) both in spring and at a lead of 2 months, of which the first mode shows a significant impact on the spring climate in China, with an anomalous anticyclone located over Northwest Pacific and positive precipitation and southwesterly anomalies in eastern China. Our results also suggest that the SST at a lead of two months may be a predictor for the spring climate in eastern China. A better representation of the ocean-atmosphere interaction over the tropical Pacific, Northwest Pacific, and Indian Ocean can improve the forecast skill of the spring climate in eastern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, R. F., G. J. Huffman, A. Chang, et al., 2003: The version-2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). J. Hydrometeor., 4, 1147–1167, doi: 10.1175/1525-7541(2003)004<1147:TVGP-CP>2.0.CO;2.
Bai, X. X., C. Y. Li, and L. Li, 2012: Numerical simulation study of the Madden-Julian Oscillation influences on spring precipitation in China. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 70, 986–1003, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2012.083. (in Chinese)
Chen, J. P., Z. P. Wen, R. G. Wu, et al., 2014: Interdecadal changes in the relationship between southern China winter- spring precipitation and ENSO. Climate Dyn., 43, 1327–1338, doi: 10.1007/s00382-013-1947-x.
Chen, L., and O. W. Frauenfeld, 2014: A comprehensive evaluation of precipitation simulations over China based on CMIP5 multimodel ensemble projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 119, 5767–5786, doi: 10.1002/2013JD021190.
Chen, Q. Y., Y. Q. Yu, and Y. F. Guo, 1997: Simulation of East Asian summer monsoon with IAP CGCM. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 461–472, doi: 10.1007/s00376-997-0064-3.
Chen, S. F., R. G. Wu, and Y. Liu, 2015: Dominant modes of interannual variability in Eurasian surface air temperature during boreal spring. J. Climate, 29, 1109–1125, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0524.1.
Chowdary, J. S., S. P. **e, J. J. Luo, et al., 2011: Predictability of Northwest Pacific climate during summer and the role of the tropical Indian Ocean. Climate Dyn., 36, 607–621, doi: 10.10 07/s00382-009-0686-5.
Deser, C., and M. S. Timlin, 1997: Atmosphere-ocean interaction on weekly timescales in the North Atlantic and Pacific. J. Climate, 10, 393–408, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<0393:AOIOWT>2.0.CO;2.
Ding, Y. H., Q. Q. Li, W. J. Li, et al., 2004: Advance in seasonal dynamical prediction operation in China. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 62, 598–612, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2004.059. (in Chinese)
Doblas-Reyes, F. J., R. Hagedorn, and T. N. Palmer, 2005: The rationale behind the success of multi-model ensembles in seasonal forecasting—II. Calibration and combination. Tellus A, 57, 234–252, doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0870.2005.00104.x.
Doblas-Reyes, F. J., A. Weisheimer, T. N. Palmer, et al., 2010: Forecast Quality Assessment of the ENSEMBLES Seasonal-to-Decadal Stream 2 Hindcasts. ECMWF Technical Memorandum 621, ECMWF, Reading UK, 1-45, doi: 10.21957/10x9tmf12.
Du, Y., S. P. **e, G. Huang, et al., 2009: Role of air-sea interaction in the long persistence of El Niño-induced north Indian Ocean warming. J. Climate, 22, 2023–2038, doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2590.1.
Fan, Y., K. Fan, and B. Q. Tian, 2016: Has the prediction of the South China Sea summer monsoon improved since the late 1970s? J. Meteor. Res., 30, 833–852, doi: 10.1007/s13351-016-6052-8.
Feng, J., and J. P. Li, 2011: Influence of El Niño Modoki on spring rainfall over South China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 116, D13102, doi: 10.1029/2010JD015160.
Feng, J. Q., L. J. Yu, and D. X. Hu, 2014: Influence of Indian Ocean subtropical dipole on spring rainfall over China. Int. J. Climatol., 34, 954–963, doi: 10.1002/joc.3732.
Feng, L., T. J. Zhou, B. Wu, et al., 2011: Projection of future precipitation change over China with a high-resolution global atmospheric model. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 28, 464–476, doi: 10.1007/s00376-010-0016-1.
Huang, B. Y., V. F. Banzon, E. Freeman, et al., 2014: Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature version 4 (ERSST. v4). Part I: Upgrades and intercomparisons. J. Climate, 28, 911–930, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00006.1.
Huang, D. Q., J. Zhu, Y. C. Zhang, et al., 2013: Uncertainties on the simulated summer precipitation over Eastern China from the CMIP5 models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 118, 9035–9047, doi: 10.1002/jgrd.50695.
Huang, G., K. M. Hu, and S. P. **e, 2010: Strengthening of tropical Indian Ocean teleconnection to the Northwest Pacific since the mid-1970s: An atmospheric GCM study. J. Climate, 23, 5294–5304, doi: 10.1175/2010JCLI3577.1.
Jia, X. J., J. Y. Lee, H. Lin, et al., 2014: Interdecadal change in the Northern Hemisphere seasonal climate prediction skill: Part I. The leading forced mode of atmospheric circulation. Climate Dyn., 43, 1595–1609, doi: 10.1007/s00382-013-1988-1.
Jiang, D. B., H. J. Wang, and X. M. Lang, 2005: Evaluation of East Asian climatology as simulated by seven coupled models. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 22, 479–495, doi: 10.1007/BF02918482.
Kanamitsu, M., W. Ebisuzaki, J. Woollen, et al., 2002: NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 83, 1631–1644, doi: 10.1175/BAMS-83-11-1631.
Kosaka, Y., S. P. **e, N. C. Lau, et al., 2013: Origin of seasonal predictability for summer climate over the Northwestern Pacific. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 7574–7579, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215582110.
Krishnamurti, T. N., C. M. Kishtawal, T. E. La Row, et al., 1999: Improved weather and seasonal climate forecasts from multimodel superensemble. Science, 285, 1548–1550, doi: 10.1126/science.285.5433.1548.
Kumar, V., and T. N. Krishnamurti, 2012: Improved seasonal precipitation forecasts for the Asian monsoon using 16 atmosphere-ocean coupled models. Part I: Climatology. J. Climate, 25, 39–64, doi: 10.1175/2011JCLI4125.1.
Li, C. F., R. Y. Lu, and B. W. Dong, 2012: Predictability of the western North Pacific summer climate demonstrated by the coupled models of ENSEMBLES. Climate Dyn., 39, 329–346, doi: 10.1007/s00382-011-1274-z.
Li, C. F., R. Y. Lu, and B. W. Dong, 2014: Predictability of the western North Pacific summer climate associated with different ENSO phases by ENSEMBLES multi-model seasonal forecasts. Climate Dyn., 43, 1829–1845, doi: 10.1007/s00382-013-2010-7.
Liu, W., B. Y. Huang, P. W. Thorne, et al., 2015: Extended reconstructed sea surface temperature version 4 (ERSST. v4): Part II. Parametric and structural uncertainty estimations. J. Climate, 28, 931–951, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00007.1.
Ma, J., S. P. **e, and H. M. Xu, 2017a: Intermember variability of the summer Northwest Pacific subtropical anticyclone in the ensemble forecast. J. Climate, 30, 3927–3941, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0638.1.
Ma, J., S. P. **e, and H. M. Xu, 2017b: Contributions of the north pacific meridional mode to ensemble spread of ENSO prediction. J. Climate, 30, 9167–9181, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0182.1.
Miao, C. Y., Q. Y. Duan, L. Yang, et al., 2012: On the applicability of temperature and precipitation data from CMIP3 for China. PLoS One, 7, e44659, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044659.
Qiu, Y., W. J. Cai, X. G. Guo, et al., 2009: Dynamics of late spring rainfall reduction in recent decades over southeastern China. J. Climate, 22, 2240–2247, doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2809.1.
Rajeevan, M., C. K. Unnikrishnan, and B. Preethi, 2012: Evaluation of the ENSEMBLES multi-model seasonal forecasts of Indian summer monsoon variability. Climate Dyn., 38, 2257–2274, doi: 10.1007/s00382-011-1061-x.
Si, D., Y. H. Ding, and Y. J. Liu, 2009: Evaluation of Meiyu prediction in the Yangtze-Huaihe region by coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation model (BCC_CM1.0). Acta Meteor. Sinica, 67, 947–960, doi: 10.11676/qxxb2009.092. (in Chinese)
Stockdale, T. N., O. Alves, G. Boer, et al., 2010: Understanding and predicting seasonal-to-interannual climate variability — The producer perspective. Proced. Environ. Sci., 1, 55–80, doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2010.09.006.
Taylor, K. E., 2001: Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 106, 7183–7192, doi: 10.1029/2000JD900719.
van der Linden, P., and J. F. B. Mitchell, 2009: ENSEMBLES: Climate Change and Its Impacts: Summary of Research and Results from the ENSEMBLES Project. Met Office Hadley Centre, FitzRoy Road, Exeter EX1 3PB, UK, 160 pp.
Wallace, J. M., C. Smith, and C. S. Bretherton, 1992: Singular value decomposition of wintertime sea surface temperature and 500-mb height anomalies. J. Climate, 5, 561–576, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1992)005<0561:SVDOWS>2.0.CO;2.
Wang, B., R. G. Wu, and X. H. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian tele-connection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<1517:PEATHD>2.0.CO;2.
Wang, B., R. G. Wu, and T. Li, 2003: Atmosphere-warm ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian-Australian monsoon variation. J. Climate, 16, 1195–1211, doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)16<1195:AOIAII>2.0.CO;2.
Wang, B., Q. H. Ding, X. H. Fu, et al., 2005: Fundamental challenge in simulation and prediction of summer monsoon rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L15711, doi: 10.1029/2005 GL022734.
Wang, B., J. Y. Lee, I. S. Kang, et al., 2009: Advance and prospectus of seasonal prediction: Assessment of the APCC/Cli-PAS 14-model ensemble retrospective seasonal prediction (1980-2004). Climate Dyn., 33, 93–117, doi: 10.1007/s00382-008-0460-0.
Weisheimer, A., F. J. Doblas-Reyes, T. N. Palmer, et al., 2009: ENSEMBLES: A new multi-model ensemble for seasonal-to-annual predictions—skill and progress beyond DEMETER in forecasting tropical Pacific SSTs. Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L21711, doi: 10.1029/2009GL040896.
Wilks, D. S., 1995: Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences: An Introduction. 2nd Ed., Academic Press, New York, 467 pp.
Wu, R. G., and B. P. Kirtman, 2007: Observed relationship of spring and summer East Asian rainfall with winter and spring Eurasian snow. J. Climate, 20, 1285–1304, doi: 10.1175/JCLI4068.1.
Wu, X. F., and J. Y. Mao, 2016: Interdecadal modulation of EN-SO-related spring rainfall over South China by the Pacific decadal oscillation. Climate Dyn., 47, 3203–3220, doi: 10.1007/s00382-016-3021-y.
**e, S. P., K. M. Hu, J. Hafner, et al., 2009: Indian Ocean capacitor effect on Indo-western Pacific climate during the summer following El Niño. J. Climate, 22, 730–747, doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2544.1.
Xu, C. H., Y. Luo, and Y. Xu, 2010: Assessment and projection for spatial-temporal distribution of precipitation in China based on global climate models. Adv. Climate Change Res., 6, 398–404, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2010.06.002. (in Chinese)
Xu, Y., and C. H. Xu, 2012: Preliminary assessment of simulations of climate changes over china by CMIP5 multi-models. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett., 5, 489–494, doi: 10.1080/16742 834.2012.11447041.
You, Y. J., and X. J. Jia, 2018: Interannual variations and prediction of spring precipitation over China. J. Climate, 31, 655–670, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0233.1.
Yu, R. C., W. Li, X. H. Zhang, et al., 2000: Climatic features related to eastern China summer rainfalls in the NCAR CCM3. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 503–518, doi: 10.1007/s00376-000-0014-9.
Zhang, R. H., and A. Sumi, 2002: Moisture circulation over East Asia during El Niño episode in northern winter, spring and autumn. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 80, 213–227, doi: 10.2151/jmsj.80.213.
Zhou, T. J., and R. C. Yu, 2006: Twentieth-century surface air temperature over China and the globe simulated by coupled climate models. J. Climate, 19, 5843–5858, doi: 10.1175/JCLI3952.1.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the ENSEMBLES project for providing the model outputs. We also acknowledge the organizations that provided the observations for this study: the NCEP Reanalysis Derived data, NOAA_ERSST_V4 data, and GPCP precipitation data, which are provided by the NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD, Boulder, Colorado, USA (at https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/). The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive and thoughtful comments, which have helped improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41575077, 41490643, and 41805051), National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0604102), Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and Startup Found for Introduced Talents of Nan**g University of Information Science & Technology (2017r057).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Xu, H., Ma, J. et al. Assessment of the Capability of ENSEMBLES Hindcasts in Predicting Spring Climate in China. J Meteorol Res 33, 307–322 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8131-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-019-8131-0