Abstract
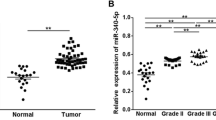
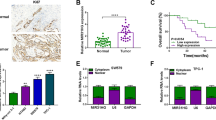
microRNA-137 expression is downregulated in several tumors. To date, its expression and function in human thyroid cancer remain unexplored. The aim of this study is to identify its expression, function, and molecular mechanism in thyroid cancer. microRNA-137 (miR-137) downregulation was observed in thyroid cancer tissues compared with normal thyroid tissues. miR-137 mimics downregulated B-CPAP cell proliferation, colony formation ability, and invasion, with suppressed expression of cyclin E, MMP2, p-ERK, and p-AKT. miR-137 inhibitor transfection in TPC-1 cell line showed the opposite effects. With prediction software and luciferase reporter assay, we found that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) was a target of miR-137. Transfection of miR-137 mimic suppressed EGFR protein and messenger RNA (mRNA) expression. EGFR small interfering RNA (siRNA) abrogated the role of miR-137 inhibitor on cyclin E, MMP2, p-ERK, and p-AKT. In addition, we found a negative correlation of EGFR and miR-137 in thyroid cancer tissues. In conclusion, the present study showed that miR-137 downregulation is associated with malignant progression of thyroid cancer. miR-137 inhibits growth and invasion by targeting EGFR in thyroid cancer cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R et al. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29.
Griffith OL et al. Biomarker panel diagnosis of thyroid cancer: a critical review. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008;8(9):1399–413.
Sipos JA, Mazzaferri EL. Thyroid cancer epidemiology and prognostic variables. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2010;22(6):395–404.
Lu J et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435(7043):834–8.
Yanaihara N et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(3):189–98.
Takamizawa J et al. Reduced expression of the let-7 microRNAs in human lung cancers in association with shortened postoperative survival. Cancer Res. 2004;64(11):3753–6.
Visone R et al. Specific microRNAs are downregulated in human thyroid anaplastic carcinomas. Oncogene. 2007;26(54):7590–5.
Zhao S, Li J. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces the migration of thyroid follicular carcinoma cells through the microRNA-17/PTK6/ERK1/2 pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119148.
Dettmer M et al. Comprehensive microRNA expression profiling identifies novel markers in follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 2013;23(11):1383–9.
Weber F et al. A limited set of human microRNA is deregulated in follicular thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(9):3584–91.
Han Y et al. miR-137 suppresses the invasion and procedure of EMT of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 through targeting CtBP1. Hum Cell. 2015.
Kang N et al. Silencing of miR-137 by aberrant promoter hypermethylation in surgically resected lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2015;89(2):99–103.
Guo J et al. miR-137 suppresses cell growth in ovarian cancer by targeting AEG-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441(2):357–63.
Zhu X et al. miR-137 inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting Cdc42 and Cdk6. FEBS Lett. 2013;587(1):73–81.
Chen Q et al. miR-137 is frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer and is a negative regulator of Cdc42. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56(7):2009–16.
Liu M et al. miR-137 targets Cdc42 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2011;128(6):1269–79.
Hao S et al. miR-137 inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells by targeting PAK2. Exp Dermatol. 2015.
Sun Y et al. miR-124, miR-137 and miR-340 regulate colorectal cancer growth via inhibition of the Warburg effect. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(4):1346–52.
Althoff K et al. MiR-137 functions as a tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma by downregulating KDM1A. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(5):1064–73.
Sun G et al. Overexpressed miRNA-137 inhibits human glioma cells growth by targeting Rac1. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013;28(4):327–34.
Bi Y et al. miR-137 impairs the proliferative and migratory capacity of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting paxillin. Hum Cell. 2014;27(3):95–102.
Liu LL et al. FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137 suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 2014;5(13):5113–24.
Steponaitiene R et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 is a frequent event in gastric carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 2015.
Zheng X et al. MicroRNA library-based functional screening identified miR-137 as a suppresser of gastric cancer cell proliferation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015;141(5):785–95.
Lee JM et al. A contrasting function for miR-137 in embryonic mammogenesis and adult breast carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 2015;6(26):22048–59.
**u Y et al. MicroRNA-137 upregulation increases bladder cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting PAQR3. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109734.
Liang W et al. Down-regulation of SOSTDC1 promotes thyroid cancer cell proliferation via regulating cyclin A2 and cyclin E2. Oncotarget. 2015.
Kalhori V, Tornquist K. MMP2 and MMP9 participate in S1P-induced invasion of follicular ML-1 thyroid cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;404:113–22.
Tian X et al. Relationship between protein expression of VEGF-C, MMP-2 and lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer. J Int Med Res. 2008;36(4):699–703.
Dong QZ et al. Derlin-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cancer cell invasion via EGFR-ERK-mediated up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(3):954–64.
Kharman-Biz A et al. Expression of activator protein-1 (AP-1) family members in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:441.
Cheng SP et al. Leptin enhances migration of human papillary thyroid cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 2011;26(5):1265–71.
Gule MK et al. Targeted therapy of VEGFR2 and EGFR significantly inhibits growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer in an orthotopic murine model. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2281–91.
Rebai M et al. Association of EGFR and HER2 polymorphisms with risk and clinical features of thyroid cancer. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2009;13(6):779–84.
Schiff BA et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in anaplastic thyroid cancer, and the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib inhibits the growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(24):8594–602.
Deng D et al. miR-137 acts as a tumor suppressor in astrocytoma by targeting RASGRF1. Tumour Biol. 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Li, X., Dong, J. et al. microRNA-137 is downregulated in thyroid cancer and inhibits proliferation and invasion by targeting EGFR. Tumor Biol. 37, 7749–7755 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4611-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4611-8