Abstract
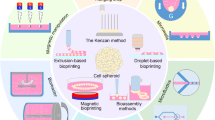
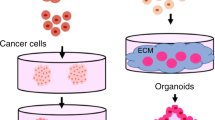
The significance of 3D cell culture—i.e., the maintenance of cell characteristics by mimicking the natural environment—has been increasing, and various 3D cell culture methods have been proposed. 3D cell culture is a widely used cell spheroid culture method, which is a representative method of matrix-free 3D cell culture. In contrast with that in conventional 2D cell culture, cells aggregate in a spherical shape with abundant cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions that more closely resemble the in vivo environment in a 3D culture. In a cell spheroid culture, the viability and functionality of spheroids change based on the cell type and morphology, and their controllable characteristics differ depending on the fabrication method used. Moreover, the mass production and size controllability of spheroids are dependent on the fabrication method used; therefore, the spheroid utilization method is also different. In this review, representative cell spheroid fabrication methods are examined, and the possibility of standardization is discussed so that these methods can be widely used. In addition, the biomedical applications of spheroids and their potential for future development are explored.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, A.: Cell culture: biology’s new dimension. Nature 424, 870–872 (2003)
Tibbitt, M.W., Anseth, K.S.: Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 103, 655–663 (2009)
Fennema, E., Rivron, N., Rouwkema, J., van Blitterswijk, C., de Boer, J.: Spheroid culture as a tool for creating 3D complex tissues. Trends Biotechnol. 31, 108–115 (2013)
Jensen, C., Teng, Y.: Is it time to start transitioning from 2D to 3D cell culture? Front Mol. Biosci. 7, 33 (2020)
Lauschke, V.M., Hendriks, D.F., Bell, C.C., Andersson, T.B., Ingelman-Sundberg, M.: Novel 3D culture systems for studies of human liver function and assessments of the hepatotoxicity of drugs and drug candidates. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 29, 1936–1955 (2016)
Pinto, B., Henriques, A.C., Silva, P.M.A., Bousbaa, H.: Three-dimensional spheroids as in vitro preclinical models for cancer research. Pharmaceutics 12, 1186 (2020)
Moroni, L., de Wijn, J.R., van Blitterswijk, C.A.: Integrating novel technologies to fabricate smart scaffolds. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed 19, 543–572 (2008)
Stratton, S., Shelke, N.B., Hoshino, K., Rudraiah, S., Kumbar, S.G.: Bioactive polymeric scaffolds for tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 1, 93–108 (2016)
Lu, T., Li, Y., Chen, T.: Techniques for fabrication and construction of three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 337–350 (2013)
Nunes, A.S., Barros, A.S., Costa, E.C., Moreira, A.F., Correia, I.J.: 3D tumor spheroids as in vitro models to mimic in vivo human solid tumors resistance to therapeutic drugs. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 116, 206–226 (2019)
Lin, R.Z., Chang, H.Y.: Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol. J. 3, 1172–1184 (2008)
Cui, X., Hartanto, Y., Zhang, H.: Advances in multicellular spheroids formation. J. R Soc. Interface 14, 20160877 (2017)
Kim, S.J., Kim, E.M., Yamamoto, M., Park, H., Shin, H.: Engineering Multi-Cellular Spheroids for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9, e2000608 (2020)
Tostoes, R.M., Leite, S.B., Serra, M., Jensen, J., Bjorquist, P., Carrondo, M.J., Brito, C., Alves, P.M.: Human liver cell spheroids in extended perfusion bioreactor culture for repeated-dose drug testing. Hepatology 55, 1227–1236 (2012)
Gionet-Gonzales, M.A., Leach, J.K.: Engineering principles for guiding spheroid function in the regeneration of bone, cartilage, and skin. Biomed. Mater. 13, 034109 (2018)
Bartosh, T.J., Ylostalo, J.H., Mohammadipoor, A., Bazhanov, N., Coble, K., Claypool, K., Lee, R.H., Choi, H., Prockop, D.J.: Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into 3D spheroids enhances their antiinflammatory properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 107, 13724–13729 (2010)
Siegel, R.L., Miller, K.D., Fuchs, H.E., Jemal, A.: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin 72, 7–33 (2022)
Chatzinikolaidou, M.: Cell spheroids: the new frontiers in in vitro models for cancer drug validation. Drug Discov. Today 21, 1553–1560 (2016)
Park, I.S., Chung, P.S., Ahn, J.C.: Enhancement of ischemic wound healing by spheroid grafting of human adipose-derived stem cells treated with low-level light irradiation. PLoS ONE 10, e0122776 (2015)
Laschke, M.W., Menger, M.D.: Life is 3D: boosting spheroid function for tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 35, 133–144 (2017)
Guo, L., Ge, J., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Zhao, R.C., Wu, Y.: Three-dimensional spheroid-cultured mesenchymal stem cells devoid of embolism attenuate brain stroke injury after intra-arterial injection. Stem Cells Dev. 23, 978–989 (2014)
Evans, M.J., Kaufman, M.H.: Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292, 154–156 (1981)
Takayama, K., Kawabata, K., Nagamoto, Y., Kishimoto, K., Tashiro, K., Sakurai, F., Tachibana, M., Kanda, K., Hayakawa, T., Furue, M.K., Mizuguchi, H.: 3D spheroid culture of hESC/hiPSC-derived hepatocyte-like cells for drug toxicity testing. Biomaterials 34, 1781–1789 (2013)
Ong, C.S., Fukunishi, T., Zhang, H., Huang, C.Y., Nashed, A., Blazeski, A., DiSilvestre, D., Vricella, L., Conte, J., Tung, L., Tomaselli, G.F., Hibino, N.: Biomaterial-free three-dimensional bioprinting of cardiac tissue using human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 7, 4566 (2017)
Mironov, V., Visconti, R.P., Kasyanov, V., Forgacs, G., Drake, C.J., Markwald, R.R.: Organ printing: tissue spheroids as building blocks. Biomaterials 30, 2164–2174 (2009)
Madrigal, M., Rao, K.S., Riordan, N.H.: A review of therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell secretions and induction of secretory modification by different culture methods. J. Transl. Med. 12, 260 (2014)
Wechsler, M.E., Rao, V.V., Borelli, A.N., Anseth, K.S.: Engineering the MSC secretome: a hydrogel focused approach. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10, e2001948 (2021)
Ingelman-Sundberg, M.: Pharmacogenomic biomarkers for prediction of severe adverse drug reactions. N. Engl J. Med. 358, 637–639 (2008)
Olson, H., Betton, G., Robinson, D., Thomas, K., Monro, A., Kolaja, G., Lilly, P., Sanders, J., Sipes, G., Bracken, W., Dorato, M., Van Deun, K., Smith, P., Berger, B., Heller, A.: Concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in humans and in animals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 32, 56–67 (2000)
Rowe, C., Gerrard, D.T., Jenkins, R., Berry, A., Durkin, K., Sundstrom, L., Goldring, C.E., Park, B.K., Kitteringham, N.R., Hanley, K.P., Hanley, N.A.: Proteome-wide analyses of human hepatocytes during differentiation and dedifferentiation. Hepatology 58, 799–809 (2013)
Anada, T., Fukuda, J., Sai, Y., Suzuki, O.: An oxygen-permeable spheroid culture system for the prevention of central hypoxia and necrosis of spheroids. Biomaterials 33, 8430–8441 (2012)
Raghavan, S., Mehta, P., Horst, E.N., Ward, M.R., Rowley, K.R., Mehta, G.: Comparative analysis of tumor spheroid generation techniques for differential in vitro drug toxicity. Oncotarget 7(13), 16948 (2016)
Dean, D.M., Napolitano, A.P., Youssef, J., Morgan, J.R.: Rods, tori, and honeycombs: the directed self-assembly of microtissues with prescribed microscale geometries. FASEB J 21, 4005–4012 (2007)
De Lora, J.A., Velasquez, J.L., Carroll, N.J., Freyer, J.P., Shreve, A.P.: Centrifugal generation of droplet-based 3D cell cultures. SLAS Technol. 25, 436–445 (2020)
Kim, W., Gwon, Y., Park, S., Kim, H., Kim, J.: Therapeutic strategies of three-dimensional stem cell spheroids and organoids for tissue repair and regeneration. Bioact Mater 19, 50–74 (2023)
Ro, J., Kim, J., Cho, Y.K.: Recent advances in spheroid-based microfluidic models to mimic the tumour microenvironment. Analyst 147, 2023–2034 (2022)
Moshksayan, K., Kashaninejad, N., Warkiani, M.E., Lock, J.G., Moghadas, H., Firoozabadi, B., Saidi, M.S., Nguyen, N.T.: Spheroids-on-a-chip: Recent advances and design considerations in microfluidic platforms for spheroid formation and culture. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 263, 151–176 (2018)
Kim, G., Jung, Y., Cho, K., Lee, H.J., Koh, W.G.: Thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel substrates micropatterned with poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel for adipose mesenchymal stem cell spheroid formation and retrieval. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 115, 111128 (2020)
Hong, H.J., Cho, J.M., Yoon, Y.J., Choi, D., Lee, S., Lee, H., Ahn, S., Koh, W.G., Lim, J.Y.: Thermoresponsive fiber-based microwells capable of formation and retrieval of salivary gland stem cell spheroids for the regeneration of irradiation-damaged salivary glands. J. Tissue Eng. 13, 20417314221085644 (2022)
Cho, C.Y., Chiang, T.H., Hsieh, L.H., Yang, W.Y., Hsu, H.H., Yeh, C.K., Huang, C.C., Huang, J.H.: Development of a novel hanging drop platform for engineering controllable 3D microenvironments. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 327 (2020)
Aijian, A.P., Garrell, R.L.: Digital microfluidics for automated hanging drop cell spheroid culture. J. Lab Autom. 20, 283–295 (2015)
Drewitz, M., Helbling, M., Fried, N., Bieri, M., Moritz, W., Lichtenberg, J., Kelm, J.M.: Towards automated production and drug sensitivity testing using scaffold-free spherical tumor microtissues. Biotechnol. J. 6, 1488–1496 (2011)
Sun, B., Zhao, Y., Wu, W., Zhao, Q., Li, G.: A superhydrophobic chip integrated with an array of medium reservoirs for long-term hanging drop spheroid culture. Acta Biomater. 135, 234–242 (2021)
Ganguli, A., Mostafa, A., Saavedra, C., Kim, Y., Le, P., Faramarzi, V., Feathers, R.W., Berger, J., Ramos-Cruz, K.P., Adeniba, O., Diaz, G.J.P., Drnevich, J., Wright, C.L., Hernandez, A.G., Lin, W., Smith, A.M., Kosari, F., Vasmatzis, G., Anastasiadis, P.Z., Bashir, R.: Three-dimensional microscale hanging drop arrays with geometric control for drug screening and live tissue imaging. Sci. Adv. 7(17), 1323 (2021)
Kim, H., Roh, H., Kim, H., Park, J.K.: Droplet contact-based spheroid transfer technique as a multi-step assay tool for spheroid arrays. Lab Chip 21, 4155–4165 (2021)
Costa, E.C., de Melo-Diogo, D., Moreira, A.F., Carvalho, M.P., Correia, I.J.: Spheroids formation on non-adhesive surfaces by liquid overlay technique: considerations and practical approaches. Biotechnol. J. 13, 1700417 (2018)
Dalen, H., Burki, H.: Some observations on the three-dimensional growth of L5178Y cell colonies in soft agar culture. Exp. Cell Res. 65, 433–438 (1971)
Su, G., Zhao, Y., Wei, J., Han, J., Chen, L., **ao, Z., Chen, B., Dai, J.: The effect of forced growth of cells into 3D spheres using low attachment surfaces on the acquisition of stemness properties. Biomaterials 34, 3215–3222 (2013)
Kuroda, Y., Wakao, S., Kitada, M., Murakami, T., Nojima, M., Dezawa, M.: Isolation, culture and evaluation of multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring (Muse) cells. Nat. Protoc. 8, 1391–1415 (2013)
Pereira, P.M.R., Berisha, N., Bhupathiraju, N., Fernandes, R., Tome, J.P.C., Drain, C.M.: Cancer cell spheroids are a better screen for the photodynamic efficiency of glycosylated photosensitizers. PLoS ONE 12, e0177737 (2017)
Bhang, S.H., Cho, S.W., La, W.G., Lee, T.J., Yang, H.S., Sun, A.Y., Baek, S.H., Rhie, J.W., Kim, B.S.: Angiogenesis in ischemic tissue produced by spheroid grafting of human adipose-derived stromal cells. Biomaterials 32, 2734–2747 (2011)
Massai, D., Isu, G., Madeddu, D., Cerino, G., Falco, A., Frati, C., Gallo, D., Deriu, M.A., Labate, F.D., G., Quaini, F., Audenino, A., Morbiducci, U.: A versatile bioreactor for dynamic suspension cell culture application to the culture of cancer cell spheroids. PLoS ONE 11, 0154610 (2016)
Shin, H.S., Lee, S., Hong, H.J., Lim, Y.C., Koh, W.G., Lim, J.Y.: Stem cell properties of human clonal salivary gland stem cells are enhanced by three-dimensional priming culture in nanofibrous microwells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 9, 74 (2018)
Shin, H.S., Hong, H.J., Koh, W.G., Lim, J.Y.: Organotypic 3D culture in nanoscaffold microwells supports salivary gland stem-cell-based organization. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 4, 4311–4320 (2018)
Ip, B.C., Leary, E., Knorlein, B., Reich, D., Van, V., Manning, J., Morgan, J.R.: 3D Microtissues mimic the architecture, estradiol synthesis, and gap junction intercellular communication of the avascular granulosa. Toxicol. Sci. 186, 29–42 (2022)
Prince, E., Kheiri, S., Wang, Y., Xu, F., Cruickshank, J., Topolskaia, V., Tao, H., Young, E.W.K., McGuigan, A.P., Cescon, D.W., Kumacheva, E.: Microfluidic arrays of breast tumor spheroids for drug screening and personalized cancer therapies. Adv. Healthc. Mater 11, e2101085 (2022)
Torisawa, Y.S., Chueh, B.H., Huh, D., Ramamurthy, P., Roth, T.M., Barald, K.F., Takayama, S.: Efficient formation of uniform-sized embryoid bodies using a compartmentalized microchannel device. Lab Chip 7, 770–776 (2007)
Patra, B., Chen, Y.H., Peng, C.C., Lin, S.C., Lee, C.H., Tung, Y.C.: A microfluidic device for uniform-sized cell spheroids formation, culture, harvesting and flow cytometry analysis. Biomicrofluidics 7, 54114 (2013)
Ruppen, J., Cortes-Dericks, L., Marconi, E., Karoubi, G., Schmid, R.A., Peng, R., Marti, T.M., Guenat, O.T.: A microfluidic platform for chemoresistive testing of multicellular pleural cancer spheroids. Lab Chip 14, 1198–1205 (2014)
Kang, S.-M.: Recent advances in microfluidic-based microphysiological systems. BioChip J. 16, 13–26 (2022)
Kim, C., Chung, S., Kim, Y.E., Lee, K.S., Lee, S.H., Oh, K.W., Kang, J.Y.: Generation of core-shell microcapsules with three-dimensional focusing device for efficient formation of cell spheroid. Lab Chip 11, 246–252 (2011)
Ronteix, G., Jain, S., Angely, C., Cazaux, M., Khazen, R., Bousso, P., Baroud, C.N.: High resolution microfluidic assay and probabilistic modeling reveal cooperation between T cells in tumor killing. Nat. Commun. 13, 3111 (2022)
Segers, V.F., Lee, R.T.: Stem-cell therapy for cardiac disease. Nature 451, 937–942 (2008)
Lagasse, E., Connors, H., Al-Dhalimy, M., Reitsma, M., Dohse, M., Osborne, L., Wang, X., Finegold, M., Weissman, I.L., Grompe, M.: Purified hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into hepatocytes in vivo. Nat. Med. 6, 1229–1234 (2000)
Suryaprakash, S., Lao, Y.-H., Cho, H.-Y., Li, M., Ji, H.Y., Shao, D., Hu, H., Quek, C.H., Huang, D., Mintz, R.L., Bagó, J.R., Hingtgen, S.D., Lee, K.-B., Leong, K.W.: Engineered mesenchymal stem cell/nanomedicine spheroid as an active drug delivery platform for combinational glioblastoma therapy. Nano Lett. 19, 1701–1705 (2019)
Yap, K.K., Dingle, A.M., Palmer, J.A., Dhillon, R.S., Lokmic, Z., Penington, A.J., Yeoh, G.C., Morrison, W.A., Mitchell, G.M.: Enhanced liver progenitor cell survival and differentiation in vivo by spheroid implantation in a vascularized tissue engineering chamber. Biomaterials 34, 3992–4001 (2013)
Lin, Y.-J., Lee, Y.-W., Chang, C.-W., Huang, C.-C.: 3D Spheroids of Umbilical Cord Blood MSC-Derived Schwann Cells Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 604946 (2020)
Ko, J.Y., Park, J.W., Kim, J., Im, G.I.: Characterization of adipose-derived stromal/stem cell spheroids versus single-cell suspension in cell survival and arrest of osteoarthritis progression. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 109, 869–878 (2021)
Li, L.K., Huang, W.C., Hsueh, Y.Y., Yamauchi, K., Olivares, N., Davila, R., Fang, J., Ding, X., Zhao, W., Soto, J., Hasani, M., Novitch, B., Li, S.: Intramuscular delivery of neural crest stem cell spheroids enhances neuromuscular regeneration after denervation injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13, 205 (2022)
Zimmermann, J.A., McDevitt, T.C.: Pre-conditioning mesenchymal stromal cell spheroids for immunomodulatory paracrine factor secretion. Cytotherapy 16, 331–345 (2014)
Xu, Y., Shi, T., Xu, A., Zhang, L.: 3D spheroid culture enhances survival and therapeutic capacities of MSC s injected into ischemic kidney. J. Cell Mol. Med. 20, 1203–1213 (2016)
Whitehead, J., Griffin, K.H., Gionet-Gonzales, M., Vorwald, C.E., Cinque, S.E., Leach, J.K.: Hydrogel mechanics are a key driver of bone formation by mesenchymal stromal cell spheroids. Biomaterials 269, 120607 (2021)
Yang, W.Y., Chen, L.C., Jhuang, Y.T., Lin, Y.J., Hung, P.Y., Ko, Y.C., Tsai, M.Y., Lee, Y.W., Hsu, L.W., Yeh, C.K., Hsu, H.H., Huang, C.C.: Injection of hybrid 3D spheroids composed of podocytes, mesenchymal stem cells, and vascular endothelial cells into the renal cortex improves kidney function and replenishes glomerular podocytes. Bioeng. Trans. Med. 6, e10212 (2021)
Genovese, P., Patel, A., Ziemkiewicz, N., Paoli, A., Bruns, J., Case, N., Zustiak, S.P., Garg, K.: Co-delivery of fibrin-laminin hydrogel with mesenchymal stem cell spheroids supports skeletal muscle regeneration following trauma. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 15, 1131–1143 (2021)
Hsu, S.H., Hsieh, P.S.: Self-assembled adult adipose-derived stem cell spheroids combined with biomaterials promote wound healing in a rat skin repair model. Wound Repair Regen 23, 57–64 (2015)
Ezquer, F., Morales, P., Quintanilla, M.E., Santapau, D., Lespay-Rebolledo, C., Ezquer, M., Herrera-Marschitz, M., Israel, Y.: Intravenous administration of anti-inflammatory mesenchymal stem cell spheroids reduces chronic alcohol intake and abolishes binge-drinking. Sci. Rep. 8, 4325 (2018)
Friedrich, J., Seidel, C., Ebner, R., Kunz-Schughart, L.A.: Spheroid-based drug screen: considerations and practical approach. Nat. Protoc. 4, 309–324 (2009)
Ranganath, S.H., Levy, O., Inamdar, M.S., Karp, J.M.: Harnessing the mesenchymal stem cell secretome for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Cell Stem Cell 10, 244–258 (2012)
Velasco, V., Shariati, S.A., Esfandyarpour, R.: Microtechnology-based methods for organoid models. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 6, 76 (2020)
Leedale, J.A., Kyffin, J.A., Harding, A.L., Colley, H.E., Murdoch, C., Sharma, P., Williams, D.P., Webb, S.D., Bearon, R.N.: Multiscale modelling of drug transport and metabolism in liver spheroids. Interface Focus 10, 20190041 (2020)
Almazroo, O.A., Miah, M.K., Venkataramanan, R.: Drug Metabolism in the Liver. Clin. Liver Dis. 21, 1–20 (2017)
Huang, D., Zhang, X., Fu, X., Zu, Y., Sun, W., Zhao, Y.: Liver spheroids on chips as emerging platforms for drug screening. Eng. Regen. 2, 246–256 (2022)
Bhise, N.S., Manoharan, V., Massa, S., Tamayol, A., Ghaderi, M., Miscuglio, M., Lang, Q., Shrike Zhang, Y., Shin, S.R., Calzone, G., Annabi, N., Shupe, T.D., Bishop, C.E., Atala, A., Dokmeci, M.R., Khademhosseini, A.: A liver-on-a-chip platform with bioprinted hepatic spheroids. Biofabrication 8, 014101 (2016)
Foster, A.J., Chouhan, B., Regan, S.L., Rollison, H., Amberntsson, S., Andersson, L.C., Srivastava, A., Darnell, M., Cairns, J., Lazic, S.E., Jang, K.J., Petropolis, D.B., Kodella, K., Rubins, J.E., Williams, D., Hamilton, G.A., Ewart, L., Morgan, P.: Integrated in vitro models for hepatic safety and metabolism: evaluation of a human Liver-Chip and liver spheroid. Arch. Toxicol. 93, 1021–1037 (2019)
Lee, G., Kim, H., Park, J.Y., Kim, G., Han, J., Chung, S., Yang, J.H., Jeon, J.S., Woo, D.H., Han, C., Kim, S.K., Park, H.J., Kim, J.H.: Generation of uniform liver spheroids from human pluripotent stem cells for imaging-based drug toxicity analysis. Biomaterials 269, 120529 (2021)
Choi, N.Y., Lee, M.-Y., Jeong, S.: Recent Advances in 3D-Cultured Brain Tissue Models Derived from Human iPSCs. BioChip Journal, (2022).
Lee, H.K., Velazquez Sanchez, C., Chen, M., Morin, P.J., Wells, J.M., Hanlon, E.B., **a, W.: Three dimensional human neuro-spheroid model of alzheimer’s disease based on differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE 11, e0163072 (2016)
Tuffin, J., Chesor, M., Kuzmuk, V., Johnson, T., Satchell, S.C., Welsh, G.I., Saleem, M.A.: GlomSpheres as a 3D co-culture spheroid model of the kidney glomerulus for rapid drug-screening. Commun. Biol. 4, 1–14 (2021)
**itore, P., Sasidharan, K., Ekstrand, M., Prill, S., Linden, D., Romeo, S.: Human Multilineage 3D Spheroids as a Model of Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 1629 (2019)
Lau, A.N., Vander Heiden, M.G.: Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 4(4), 17–40 (2020)
Nath, S., Devi, G.R.: Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Ther. 163, 94–108 (2016)
Zanoni, M., Piccinini, F., Arienti, C., Zamagni, A., Santi, S., Polico, R., Bevilacqua, A., Tesei, A.: 3D tumor spheroid models for in vitro therapeutic screening: a systematic approach to enhance the biological relevance of data obtained. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–11 (2016)
Bae, J., Han, S., Park, S.: Recent Advances in 3D Bioprinted Tumor Microenvironment. BioChip J. 14, 137–147 (2020)
LaBarbera, D.V., Reid, B.G., Yoo, B.H.: The multicellular tumor spheroid model for high-throughput cancer drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug. Discov. 7, 819–830 (2012)
Lee, K.H., Kim, T.H.: Recent advances in multicellular tumor spheroid generation for drug screening. Biosensors (Basel) 11, 445 (2021)
Li, Y., Kumacheva, E.: Hydrogel microenvironments for cancer spheroid growth and drug screening. Sci. Adv. 4, eaas8998 (2018)
Gunti, S., Hoke, A.T.K., Vu, K.P., London, N.R., Jr.: Organoid and spheroid tumor models: techniques and applications. Cancers (Basel) 13, 874 (2021)
Boucherit, N., Gorvel, L., Olive, D.: 3D Tumor models and their use for the testing of immunotherapies. Front. Immunol. 11, 603640 (2020)
Stock, K., Estrada, M.F., Vidic, S., Gjerde, K., Rudisch, A., Santo, V.E., Barbier, M., Blom, S., Arundkar, S.C., Selvam, I., Osswald, A., Stein, Y., Gruenewald, S., Brito, C., van Weerden, W., Rotter, V., Boghaert, E., Oren, M., Sommergruber, W., Chong, Y., de Hoogt, R., Graeser, R.: Capturing tumor complexity in vitro: Comparative analysis of 2D and 3D tumor models for drug discovery. Sci. Rep. 6, 28951 (2016)
Yip, D., Cho, C.H.: A multicellular 3D heterospheroid model of liver tumor and stromal cells in collagen gel for anti-cancer drug testing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 433, 327–332 (2013)
Lu, S., Cuzzucoli, F., Jiang, J., Liang, L.G., Wang, Y., Kong, M., Zhao, X., Cui, W., Li, J., Wang, S.: Development of a biomimetic liver tumor-on-a-chip model based on decellularized liver matrix for toxicity testing. Lab Chip 18, 3379–3392 (2018)
Skardal, A., Devarasetty, M., Rodman, C., Atala, A., Soker, S.: Liver-tumor hybrid organoids for modeling tumor growth and drug response in vitro. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43, 2361–2373 (2015)
Song, Y., Kim, S.H., Kim, K.M., Choi, E.K., Kim, J., Seo, H.R.: Activated hepatic stellate cells play pivotal roles in hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemoresistance and migration in multicellular tumor spheroids. Sci. Rep. 6, 36750 (2016)
Chen, Y., Sun, W., Kang, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Zhang, H., Hu, P.: Microfluidic co-culture of liver tumor spheroids with stellate cells for the investigation of drug resistance and intercellular interactions. Analyst 144, 4233–4240 (2019)
Barrera-Rodriguez, R., Fuentes, J.M.: Multidrug resistance characterization in multicellular tumour spheroids from two human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 15, 47 (2015)
Huber, J.M., Amann, A., Koeck, S., Lorenz, E., Kelm, J.M., Obexer, P., Zwierzina, H., Gamerith, G.: Evaluation of assays for drug efficacy in a three-dimensional model of the lung. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 142, 1955–1966 (2016)
Longati, P., Jia, X., Eimer, J., Wagman, A., Witt, M.R., Rehnmark, S., Verbeke, C., Toftgard, R., Lohr, M., Heuchel, R.L.: 3D pancreatic carcinoma spheroids induce a matrix-rich, chemoresistant phenotype offering a better model for drug testing. BMC Cancer 13, 95 (2013)
Wen, Z., Liao, Q., Hu, Y., You, L., Zhou, L., Zhao, Y.: A spheroid-based 3-D culture model for pancreatic cancer drug testing, using the acid phosphatase assay. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 46, 634–642 (2013)
Yeon, S., Da No, Y., Lee, S.H., Nam, S.W., Oh, I.H., Lee, J., Kuh, H.J.: Application of concave microwells to pancreatic tumor spheroids enabling anticancer drug evaluation in a clinically relevant drug resistance model. PLoS ONE 8, e73345 (2013)
Hou, S., Tiriac, H., Sridharan, B.P., Scampavia, L., Madoux, F., Seldin, J., Souza, G.R., Watson, D., Tuveson, D., Spicer, T.P.: Advanced development of primary pancreatic organoid tumor models for high-throughput phenotypic drug screening. SLAS Discov. 23, 574–584 (2018)
Wong, C.W., Han, H.W., Tien, Y.W., Hsu, S.H.: Biomaterial substrate-derived compact cellular spheroids mimicking the behavior of pancreatic cancer and microenvironment. Biomaterials 213, 119202 (2019)
Gong, X., Lin, C., Cheng, J., Su, J., Zhao, H., Liu, T., Wen, X., Zhao, P.: Generation of multicellular tumor spheroids with microwell-based agarose scaffolds for drug testing. PLoS ONE 10, e0130348 (2015)
Yu, L., Chen, M.C., Cheung, K.C.: Droplet-based microfluidic system for multicellular tumor spheroid formation and anticancer drug testing. Lab Chip 10, 2424–2432 (2010)
Sun, Q., Tan, S.H., Chen, Q.S., Ran, R., Hui, Y., Chen, D., Zhao, C.X.: Microfluidic formation of coculture tumor spheroids with stromal cells as a novel 3D tumor model for drug testing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 4, 4425–4433 (2018)
Ho, W.Y., Yeap, S.K., Ho, C.L., Rahim, R.A., Alitheen, N.B.: Development of Multicellular Tumor Spheroid (MCTS) Culture from Breast Cancer Cell and a High Throughput Screening Method Using the MTT Assay. Plos One 7, (2012).
Chen, Y., Gao, D., Liu, H., Lin, S., Jiang, Y.: Drug cytotoxicity and signaling pathway analysis with three-dimensional tumor spheroids in a microwell-based microfluidic chip for drug screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 898, 85–92 (2015)
Folkesson, E., Niederdorfer, B., Nakstad, V.T., Thommesen, L., Klinkenberg, G., Lægreid, A., Flobak, Å.: High-throughput screening reveals higher synergistic effect of MEK inhibitor combinations in colon cancer spheroids. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–14 (2020)
Hoffmann, O.I., Ilmberger, C., Magosch, S., Joka, M., Jauch, K.W., Mayer, B.: Impact of the spheroid model complexity on drug response. J. Biotechnol. 205, 14–23 (2015)
Däster, S., Amatruda, N., Calabrese, D., Ivanek, R., Turrini, E., Droeser, R.A., Zajac, P., Fimognari, C., Spagnoli, G.C., Iezzi, G.: Induction of hypoxia and necrosis in multicellular tumor spheroids is associated with resistance to chemotherapy treatment. Oncotarget 8, 1725 (2017)
Alzeeb, G., Arzur, D., Trichet, V., Talagas, M., Corcos, L., Le Jossic-Corcos, C.: Gastric cancer cell death analyzed by live cell imaging of spheroids. Sci. Rep. 12, 1488 (2022)
Balmana, M., Diniz, F., Feijao, T., Barrias, C.C., Mereiter, S., Reis, C.A.: Analysis of the Effect of Increased alpha2,3-Sialylation on RTK Activation in MKN45 Gastric Cancer Spheroids Treated with Crizotinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 722 (2020)
Jang, M., Koh, I., Lee, S.J., Cheong, J.H., Kim, P.: Droplet-based microtumor model to assess cell-ECM interactions and drug resistance of gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 7, 41541 (2017)
Tofani, L.B., Abriata, J.P., Luiz, M.T., Marchetti, J.M., Swiech, K.: Establishment and characterization of an in vitro 3D ovarian cancer model for drug screening assays. Biotechnol. Prog. 36, e3034 (2020)
Raghavan, S., Ward, M.R., Rowley, K.R., Wold, R.M., Takayama, S., Buckanovich, R.J., Mehta, G.: Formation of stable small cell number three-dimensional ovarian cancer spheroids using hanging drop arrays for preclinical drug sensitivity assays. Gynecol. Oncol. 138, 181–189 (2015)
Tofani, L.B., Sousa, L.O., Luiz, M.T., Abriata, J.P., Marchetti, J.M., Leopoldino, A.M., Swiech, K.: Generation of a three-dimensional in vitro ovarian cancer co-culture model for drug screening assays. J. Pharm. Sci. 110, 2629–2636 (2021)
Gunay, G., Kirit, H.A., Kamatar, A., Baghdasaryan, O., Hamsici, S., Acar, H.: The effects of size and shape of the ovarian cancer spheroids on the drug resistance and migration. Gynecol. Oncol. 159, 563–572 (2020)
Filipiak-Duliban, A., Brodaczewska, K., Kajdasz, A., Kieda, C.: Spheroid culture differentially affects cancer cell sensitivity to drugs in melanoma and RCC models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 1166 (2022)
An, H.J., Kim, H.S., Kwon, J.A., Song, J., Choi, I.: Adjustable and versatile 3D tumor spheroid culture platform with interfacial elastomeric wells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 6924–6932 (2020)
Rausch, M., Blanc, L., De Souza Silva, O., Dormond, O., Griffioen, A.W., Nowak-Sliwinska, P.: Characterization of renal cell carcinoma heterotypic 3D co-cultures with immune cell subsets. Cancers (Basel) 13, 2551 (2021)
Ho, V.H., Guo, W.M., Huang, C.L., Ho, S.F., Chaw, S.Y., Tan, E.Y., Ng, K.W., Loo, J.S.: Manipulating magnetic 3D spheroids in hanging drops for applications in tissue engineering and drug screening. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2, 1430–1434 (2013)
Brodaczewska, K.K., Bielecka, Z.F., Maliszewska-Olejniczak, K., Szczylik, C., Porta, C., Bartnik, E., Czarnecka, A.M.: Metastatic renal cell carcinoma cells growing in 3D on polyDlysine or laminin present a stemlike phenotype and drug resistance. Oncol. Rep. 42, 1878–1892 (2019)
Khademhosseini, A., Langer, R.: A decade of progress in tissue engineering. Nat. Protoc. 11, 1775–1781 (2016)
Kim, M., Hwang, D.G., Jang, J.: 3D pancreatic tissue modeling in vitro: advances and prospects. BioChip J. 14, 84–99 (2020)
Chen, G.P., Ushida, T., Tateishi, T.: Scaffold design for tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2, 67–77 (2002)
Tan, Y., Richards, D., Coyle, R.C., Yao, J., Xu, R., Gou, W., Wang, H., Menick, D.R., Tian, B., Mei, Y.: Cell number per spheroid and electrical conductivity of nanowires influence the function of silicon nanowired human cardiac spheroids. Acta Biomater. 51, 495–504 (2017)
Lee, H.J., Koh, W.G.: Hydrogel micropattern-incorporated fibrous scaffolds capable of sequential growth factor delivery for enhanced osteogenesis of hMSCs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 9338–9348 (2014)
Heidariyan, Z., Ghanian, M.H., Ashjari, M., Farzaneh, Z., Najarasl, M., Larijani, M.R., Piryaei, A., Vosough, M., Baharvand, H.: Efficient and cost-effective generation of hepatocyte-like cells through microparticle-mediated delivery of growth factors in a 3D culture of human pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials 159, 174–188 (2018)
Guvendiren, M., Burdick, J.A.: Engineering synthetic hydrogel microenvironments to instruct stem cells. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 24, 841–846 (2013)
Wei, J., **a, T., Chen, W., Ran, P., Chen, M., Li, X.: Glucose and lipid metabolism screening models of hepatocyte spheroids after culture with injectable fiber fragments. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 14, 774–788 (2020)
Ahmad, T., Lee, J., Shin, Y.M., Shin, H.J., Madhurakat Perikamana, S.K., Park, S.H., Kim, S.W., Shin, H.: Hybrid-spheroids incorporating ECM like engineered fragmented fibers potentiate stem cell function by improved cell/cell and cell/ECM interactions. Acta Biomater. 64, 161–175 (2017)
Yamada, M., Hori, A., Sugaya, S., Yajima, Y., Utoh, R., Yamato, M., Seki, M.: Cell-sized condensed collagen microparticles for preparing microengineered composite spheroids of primary hepatocytes. Lab Chip 15, 3941–3951 (2015)
Mansouri, M., Beemer, S., Kothapalli, C.R., Rhoades, T., Fodor, P.S., Das, D., Leipzig, N.D.: Generation of oxygenating fluorinated methacrylamide chitosan microparticles to increase cell survival and function in large liver spheroids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 4899–4913 (2022)
Baraniak, P.R., Cooke, M.T., Saeed, R., Kinney, M.A., Fridley, K.M., McDevitt, T.C.: Stiffening of human mesenchymal stem cell spheroid microenvironments induced by incorporation of gelatin microparticles. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 11, 63–71 (2012)
Rathnam, C., Yang, L., Castro-Pedrido, S., Luo, J., Cai, L., Lee, K.B.: Hybrid SMART spheroids to enhance stem cell therapy for CNS injuries. Sci. Adv. 7, 2281 (2021)
Cui, H., Wang, X., Wesslowski, J., Tronser, T., Rosenbauer, J., Schug, A., Davidson, G., Popova, A.A., Levkin, P.A.: Assembly of multi-spheroid cellular architectures by programmable droplet merging. Adv. Mater. 33, e2006434 (2021)
Polonchuk, L., Surija, L., Lee, M.H., Sharma, P., Ming, L.C., et al.: Towards engineering heart tissues from bioprinted cardiac spheroids. Biofabrication 13, 045009 (2021)
Kim, T.Y., Kofron, C.M., King, M.E., Markes, A.R., Okundaye, A.O., Qu, Z.L., Mende, U., Choi, B.R.: Directed fusion of cardiac spheroids into larger heterocellular microtissues enables investigation of cardiac action potential propagation via cardiac fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 13, e0196714 (2018)
Lindberg, G.C.J., Cui, X., Durham, M., Veenendaal, L., Schon, B.S., Hooper, G.J., Lim, K.S., Woodfield, T.B.F.: Probing multicellular tissue fusion of cocultured spheroids-A 3D-bioassembly model. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 8, e2103320 (2021)
Tran, C., Damaser, M.S.: Stem cells as drug delivery methods: Application of stem cell secretome for regeneration. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 82–83, 1–11 (2015)
Chang, C., Yan, J., Yao, Z.C., Zhang, C., Li, X.W., Mao, H.Q.: Effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived paracrine signals and their delivery strategies. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10, 2001689 (2021)
Carter, K., Lee, H.J., Na, K.S., Fernandes-Cunha, G.M., Blanco, I.J., Djalilian, A., Myung, D.: Characterizing the impact of 2D and 3D culture conditions on the therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cell secretome on corneal wound healing in vitro and ex vivo. Acta Biomater. 99, 247–257 (2019)
**e, L., Mao, M., Zhou, L., Zhang, L., Jiang, B.: Signal factors secreted by 2D and spheroid mesenchymal stem cells and by cocultures of mesenchymal stem cells derived microvesicles and retinal photoreceptor neurons. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2730472 (2017)
Kumar, L.P., Kandoi, S., Misra, R., Vijayalakshmi, S., Rajagopal, K., Verma, R.S.: The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 46, 1–9 (2019)
Fernandes-Cunha, G.M., Na, K.S., Putra, I., Lee, H.J., Hull, S., Cheng, Y.C., Blanco, I.J., Eslani, M., Djalilian, A.R., Myung, D.: Corneal wound healing effects of mesenchymal stem cell secretome delivered within a viscoelastic gel carrier. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 8, 478–489 (2019)
Dinh, P.C., Paudel, D., Brochu, H., Popowski, K.D., Gracieux, M.C., Cores, J., Huang, K., Hensley, M.T., Harrell, E., Vandergriff, A.C., George, A.K., Barrio, R.T., Hu, S., Allen, T.A., Blackburn, K., Caranasos, T.G., Peng, X., Schnabel, L.V., Adler, K.B., Lobo, L.J., Goshe, M.B., Cheng, K.: Inhalation of lung spheroid cell secretome and exosomes promotes lung repair in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 11, 1064 (2020)
Joshi, J., Abnavi, M.D., Kothapalli, C.R.: Synthesis and secretome release by human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell spheroids within three-dimensional collagen hydrogels: Integrating experiments and modelling. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 13, 1923–1937 (2019)
Miranda, J.P., Camoes, S.P., Gaspar, M.M., Rodrigues, J.S., Carvalheiro, M., Barcia, R.N., Cruz, P., Cruz, H., Simoes, S., Santos, J.M.: The secretome derived from 3D-cultured umbilical cord tissue MSCs counteracts manifestations typifying rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 10, 18 (2019)
Redondo-Castro, E., Cunningham, C.J., Miller, J., Brown, H., Allan, S.M., Pinteaux, E.: Changes in the secretome of tri-dimensional spheroid-cultured human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro by interleukin-1 priming. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 9, 11 (2018)
Chouw, A., Facicilia, G., Sartika, C.R., Faried, A., Milanda, T.: Factors Influencing the Therapeutic Potential of the MSC-derived Secretome. Regen. Eng. Trans. Med. 9, 1–10 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) (grant numbers NRF-2020R1C1C1013227, 2021R1A6A1A03038996), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and the Gachon University Research Fund of 2020 (GCU-202208970001).
Funding
Ministry of Science and ICT, South Korea, NRF-2020R1C1C1013227, Hyun Jong Lee, NRF-2021R1A6A1A03038996, Hyun Jong Lee, Gachon University, GCU-202208970001, Hyun Jong Lee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.Y., Hong, H.J. & Lee, H.J. Fabrication of Cell Spheroids for 3D Cell Culture and Biomedical Applications. BioChip J 17, 24–43 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00086-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00086-9