Abstract
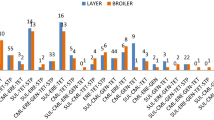
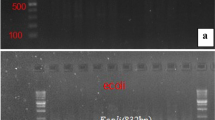
Antibiotics in animal farms play a significant role in the proliferation and spread of antibiotic-resistant genes (ARGs) and antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB). The dissemination of antibiotic resistance from animal facilities to the nearby environment has become an emerging concern. The present study was focused on the isolation and molecular identification of Escherichia coli (E. coli) isolates from broiler chicken meat and further access their antibiotic-resistant profile against different antibiotics. Broiler chicken meat samples were collected from 44 retail poultry slaughter shops in Prayagraj district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Standard bacteriological protocols were followed to first isolate the E. coli, and molecular characterization was performed with genus-specific PCR. Phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic-resistant profiles of all confirmed 154 E. coli isolates were screened against 09 antibiotics using the disc diffusion and PCR-based method for selected resistance genes. In antibiotic sensitivity testing, the isolates have shown maximum resistance potential against tetracycline (78%), ciprofloxacin (57.8%), trimethoprim (54.00%) and erythromycin (49.35%). E. coli bacterial isolates have shown relative resistant to amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (43.00%) and against ampicillin (44.15%). Notably, 64.28% E. coli bacteria were found to be multidrug resistant. The results of PCR assays exposed that tetA and blaTEM genes were the most abundant genes harboured by 83 (84.0%) and 82 (82.0%) out of all 99 targeted E. coli isolates, followed by 48.0% for AmpC (CITM) gene and cmlA (23.00%) for chloramphenicol resistance. It is notable that most of the isolates collected from chicken meat samples were multidrug resistant (> 3 antibiotics), with more than 80% of them carrying tetracycline (tetA) and beta-lactam gene (blaTEM). This study highlights the high risk associated with poultry products due to MDR-E. coli and promote the limited use of antibiotics in poultry farms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are contained within the article.
References
Andrew Selaledi L, Mohammed Hassan Z, Manyelo TG, Mabelebele M (2020) The current status of the alternative use to antibiotics in poultry production: An African perspective. Antibiotics 9:594. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090594
Apata DF (2009) Antibiotic resistance in poultry. Int J Poult Sci 8:404–408. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijps.2009.404.408
Arsène MMJ, Davares AKL, Viktorovna PI, Andreevna SL, Sarra S, Khelifi I, Sergueïevna DM (2022) The public health issue of antibiotic residues in food and feed: causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Vet World 15:662–671. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2022.662-671
Badr H, Reda RM, Hagag NM, Kamel E, Elnomrosy SM, Mansour AI, Shahein MA, Ali SF, Ali HR (2022) Multidrug-resistant and genetic characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing E. Coli recovered from chickens and humans in Egypt. Animals 12:346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030346
Bhardwaj K, Shenoy MS, Baliga S (2021) Research note: characterization of antibiotic resistant phenotypes and linked genes of Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae from healthy broiler chickens, Karnataka. India Poult Sci 100:101094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2021.101094
Bhushan C, Khurana A, Sinha R, Nagaraju R (2017) Antibiotic resistance in poultry environment: spread of resistance from poultry farm to agricultural field. In: Shankar A (ed) Centre for science and environment, New Delhi, India, pp 1–36
Bower PA, Scopel CO, Jensen ET, Depas MM, McLellan SL (2005) Detection of genetic markers of fecal indicator bacteria in Lake Michigan and determination of their relationship to Escherichia coli densities using standard microbiological methods. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8305–8313. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.12.8305-8313.2005
Brower CH, Mandal S, Hayer S, Sran M, Zehra A, Patel SJ, Kaur R, Chatterjee L, Mishra S, Singh DBR (2017) The prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in poultry chickens and variation according to farming practices in Punjab. India Environ Health Perspect 125:077015. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP292
da Costa PM, Loureiro L, Matos AJF (2013) Transfer of multidrug-resistant bacteria between intermingled ecological niches: the interface between humans, animals and the environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:278–294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10010278
Darwish WS, Eldaly EA, El-Abbasy MT, Ikenaka Y, Nakayama S, Ishizuka M (2013) Antibiotic residues in food: The African Scenario. Jpn J Vet Res 61(Suppl):S13-22
de Mesquita Souza Saraiva M, Lim K, do Monte DFM, Givisiez PEN, Alves LBR, de Freitas Neto OC, Kariuki S, Júnior AB, de Oliveira CJB, Gebreyes WA (2022) Antimicrobial resistance in the globalized food chain: a one health perspective applied to the poultry industry. Braz J Microbiol 53:465–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-021-00635-8
Debbarma M, Deka D, ChaaTolenkhomba T, Rajesh JB (2022) Microbiological contamination of retail meat from Mizoram (India) with special reference to molecular detection and multidrug resistance of Escherichia coli. Indian J Vet Sci Biotechnol 18(2):32–35
Diarra MS, Malouin F (2014) Antibiotics in Canadian poultry productions and anticipated alternatives. Front Microbiol 5:282. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00282
Eeswaran R, Nejadhashemi AP, Faye A, Min D, Prasad PVV, Ciampitti IA (2022) Current and future challenges and opportunities for livestock farming in West Africa: perspectives from the case of senegal. Agronomy 12:1818. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081818
FAO (2020) Meat market review: overview of global meat market developments in 2019
FAO, WHO (2013) Codex alimentarius commission, procedural manual. Joint FAO/WHO food standard programme, FAO: Rome, Italy, WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 21–24
Farhoumand P, Hassanzadazar H, Soltanpour MS, Aminzare M, Abbasi Z (2020) Prevalence, genoty** and antibiotic resistance of listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia Coli in fresh beef and chicken meats marketed in Zanjan. Iran Iran J Microbiol 12(6):537–546. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijm.v12i6.5028
Fatoba DO, Amoako DG, Abia ALK, Essack SY (2022) Transmission of antibiotic-resistant escherichia coli from chicken litter to agricultural soil. Front Environ Sci 9:751732. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.751732
Gonzalez Ronquillo M, Angeles Hernandez JC (2017) Antibiotic and synthetic growth promoters in animal diets: review of impact and analytical methods. Food Control 72:255–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.03.001
Hossain Mridha MdK, Islam MdS, Uddin MdS, Rahman ATMM, Ud-Daula A, Islam MdA, Rubaya R, Bhuiya AA, Alim MdA, Jahan N, Li J, Alam J (2023) Isolation, identification and genetic characterization of antibiotic resistant Escherichia Coli from frozen chicken meat obtained from supermarkets at Dhaka City in Bangladesh. Antibiotics 12:41. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010041
İnat G, Sırıken B, Çiftci A, Erol İ, Başkan C, Yıldırım T (2023) Molecular characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamases-producing Enterobacteriaceae species in ground beef and chicken meat. Int J Food Microbiol 398:110228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110228
Jakaria A, Islam MA, Khatun MM (2013) Prevalence, characteristics and antibiogram profiles of escherichia coli isolated from apparently healthy chickens in Mymensingh, Bangladesh. Microbes Health 1:27–29. https://doi.org/10.3329/mh.v1i1.13710
Karamova K, Danilova N, Selivanovskaya S, Galitskaya P (2022) The impact of chicken manure biochar on antibiotic resistance genes in chicken manure composting. Agriculture 12:1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12081158
Koju P, Shrestha R, Shrestha A, Tamrakar S, Rai A, Shrestha P, Madhup SK, Katuwal N, Shrestha A, Shrestha A, Shrestha S (2022) Antimicrobial resistance in E. Coli isolated from chicken cecum samples and factors contributing to antimicrobial resistance in Nepal. Tropical Med 7:249. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7090249
Kottawatta K, Van Bergen M, Abeynayake P, Wagenaar J, Veldman K, Kalupahana R (2017) Campylobacter in broiler chicken and broiler meat in Sri Lanka: influence of semi-automated vs. wet market processing on campylobacter contamination of broiler neck skin samples. Foods 6:105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods6120105
Lin Y, Watts DB, Santen E, Cao G (2018) Influence of poultry litter on crop productivity under different field conditions: a meta-analysis. Agron J 110:807–818. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2017.09.0513
Lundborg CS, Tamhankar AJ (2017) Antibiotic residues in the environment of South East Asia. BMJ 358:j2440. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j2440
Marshall BM, Levy SB (2011) Food Animals and antimicrobials: impacts on human health. Clin Microbiol Rev 24:718–733. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00002-11
Muaz K, Riaz M, Akhtar S, Park S, Ismail A (2018) Antibiotic residues in chicken meat: global prevalence, threats, and decontamination strategies: a review. J Food Prot 81:619–627. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-086
Mund MD, Khan UH, Tahir U, Mustafa BE, Fayyaz A (2017) Antimicrobial drug residues in poultry products and implications on public health: a review. Int J Food Prop 20:1433–1446. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1212874
Murray M, Salvatierra G, Dávila-Barclay A, Ayzanoa B, Castillo-Vilcahuaman C, Huang M, Pajuelo MJ, Lescano AG, Cabrera L, Calderón M, Berg DE, Gilman RH, Tsukayama P (2021) Market chickens as a source of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia Coli in a peri-urban community in Lima. Peru Front Microbiol 12:635871. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.635871
Nawaz Z, Aslam B, Zahoor MA, Siddique AB, Rafique A, Aslam R, Qamar MU, Ali S, Mubeen MU (2021) Frequency of extended spectrum beta lactamase producing escherichia coli in fresh and frozen meat. Pak Vet J 41(1):102–106. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2020.059
Ngogang MP, Ernest T, Kariuki J, Mouliom Mouiche MM, Ngogang J, Wade A, van der Sande MAB (2020) Microbial contamination of chicken litter manure and antimicrobial resistance threat in an urban area setting in Cameroon. Antibiotics 10:20. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010020
Nisha A (2008) Antibiotic residues - a global health hazard. Vet World 2:375. https://doi.org/10.5455/vetworld.2008.375-377
Ofori P, Asamoah G, Amoah B, Agyeman KOA, Yeboah E (2021) Combined application of poultry litter biochar and NPK fertilizer improves cabbage yield and soil chemical properties. Open Agriculture 6:356–368. https://doi.org/10.1515/opag-2021-0217
Olesen I, Hasman H, Aarestrup FM (2004) Prevalence of beta-lactamases among ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolated from food animals in Denmark. Microb Drug Resist 10(4):334–340
Parvin Mst S, Talukder S, Ali MdY, Chowdhury EH, Rahman MdT, Islam MdT (2020) Antimicrobial resistance pattern of Escherichia Coli isolated from frozen chicken meat in Bangladesh. Pathogens 9:420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9060420
Rahman MdM, Husna A, Elshabrawy HA, Alam J, Runa NY, Badruzzaman ATM, Banu NA, Al Mamun M, Paul B, Das S, Rahman MM, Mahbub-E-Elahi ATM, Khairalla AS, Ashour HA (2020) Isolation and molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant escherichia coli from chicken meat. Sci Rep 10:21999. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78367-2
Rahman M, Fliss I, Biron E (2022) Insights in the development and uses of alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters in poultry and swine production. Antibiotics 11:766. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060766
Roth N, Käsbohrer A, Mayrhofer S, Zitz U, Hofacre C, Domig KJ (2019) The application of antibiotics in broiler production and the resulting antibiotic resistance in Escherichia Coli: a global overview. Poult Sci 98:1791–1804. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pey539
Saha O, Hoque MN, Islam OK, Rahaman MdM, Sultana M, Hossain MA (2020) Multidrug-resistant avian pathogenic Escherichia Coli strains and association of their virulence genes in Bangladesh. Microorganisms 8:1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081135
Sary K, Fairbrother JM, Arsenault J, de Lagarde M, Boulianne M (2019) Antimicrobial resistance and virulence gene profiles among Escherichia Coli Isolates from retail chicken carcasses in Vietnam. Foodborne Pathog and Dis 16:298–306. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2018.2555
Sahu R, Saxena P (2023) New Delhi, India: centre for science and environment, centre for science and environment, India, Antibiotics in chicken meat. PML/PR-48/2014. Available online: https://cdn.cseindia.org/userfiles/Antibiotics%20in%20Chicken_Lab%20Report_Final%2029%20July.pdf. Accessed 31 Jan 2023
Shareef A, Jamel ZT, Yonis KM (2009) Detection of antibiotic residues in stored poultry products. Iraqi J Vet Sci 23:45–48
Shawa M, Furuta Y, Paudel A, Kabunda O, Mulenga E, Mubanga M, Kamboyi H, Zorigt T, Chambaro H, Simbotwe M, Hangombe B, Higashi H (2022) Clonal relationship between multidrug-resistant Escherichia Coli ST69 from poultry and humans in Lusaka. Zambia. FEMS Microbiol Lett 368(21–24):fnac004. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnac004
Shrestha A, Bajracharya AM, Subedi H, Turha RS, Kafle S, Sharma S, Neupane S, Chaudhary DK (2017) Multidrug resistance and extended spectrum beta lactamase producing gram negative bacteria from chicken meat in Bharatpur Metropolitan. Nepal BMC Res Notes 10:574. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-017-2917-x
Sudarmadi AAM, Prajitno S, Widodo ADW (2020) Antibiotic Resistance in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus from Retail Chicken Meat in Surabaya, Indonesia. Biomol Health Sci J 3(2):109–113. https://doi.org/10.20473/bhsj.v3i2.22170
Telli AE, Biçer Y, Telli N, Güngör C, Turkal G, Onmaz NE (2022) Pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. in chicken rinse carcasses: Isolation and genoty** by ERIC-PCR. Pak Vet J 42(4):493498. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2022.049
Uddin MB, Alam MN, Hasan M, Hossain SMB, Debnath M, Begum R, Samad MA, Hoque SF, Chowdhury MSR, Rahman MM, Hossain MM, Hassan MM, Lundkvist Å, Järhult JD, El Zowalaty ME, Ahmed SSU (2022) Molecular detection of colistin resistance mcr-1 gene in multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli Isolated from chicken. Antibiotics (basel) 11(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010097
Ulomi WJ, Mgaya FX, Kimera Z, Matee MI (2022) Determination of sulphonamides and tetracycline residues in liver tissues of broiler chicken sold in Kinondoni and Ilala Municipalities, Dar Es Salaam. Tanzania Antibiotics 11:1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11091222
Van TT, Chin J, Chapman T, Tran LT, Coloe PJ (2008) Safety of raw meat and shellfish in Vietnam: an analysis of Escherichia coli isolations for antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. Int J Food Microbiol 124(3):217–223
Wallinga D (2018) Turkey is bad on antibiotics—pork and beef, even worse. Available online: https://www.nrdc.org/experts/david-wallinga-md/analysis-high-intensity-antibiotics-us-beef-pork. Accessed 22 Sep 2021
Wang Y, Lyu N, Liu F, Liu WJ, Bi Y, Zhang Z, Ma S, Cao J, Song X, Wang A, Zhang G, Hu Y, Zhu B, Gao GF (2021) More diversified antibiotic resistance genes in chickens and workers of the live poultry markets. Environ Int 153:106534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2021.106534
Wibisono FJ, Sumiarto B, Kusumastuti TA (2018) Economic losses estimation of pathogenic Escherichia coli infection in Indonesian poultry farming. Buletin Peternak. https://doi.org/10.21059/buletinpeternak.v42i4.37505
Yang Y, Ashworth AJ, Willett C, Cook K, Upadhyay A, Owens PR, Ricke SC, DeBruyn JM, Moore PA Jr (2019) Review of antibiotic resistance, ecology, dissemination, and mitigation in U.S. broiler poultry systems. Front Microbiol 10:2639. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02639
Zellweger RM, Carrique-Mas J, Limmathurotsakul D, Day NPJ, Thwaites GE, Baker S (2017) Southeast Asia antimicrobial resistance network a current perspective on antimicrobial resistance in Southeast Asia. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:2963–2972. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkx260
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the respective departments and institution for their support in conducting this research.
Funding
The work has been supported by the Uttar Pradesh Council of Agricultural Research, Lucknow, India (15/VT/AH&D/RF/2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PT, JAL and VT were involved in conceptualization; AJ, AK, SS and AKP were involved in methodology; AKP and VT performed validation and VT and RS were involved in writing. All authors have read and agreed to publish.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was carried out under the permission of the laboratory biosafety guideline from Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences, Prayagraj, India. Animal ethics approval was taken (IAEC/LAF/SHUATS/PROTOCOL/02) on March 05, 2021.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jaiswal, A., Khan, A., Yogi, A. et al. Isolation and molecular characterization of multidrug‑resistant Escherichia coli from chicken meat. 3 Biotech 14, 107 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03950-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03950-7