Abstract
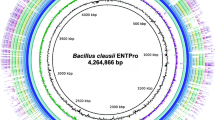
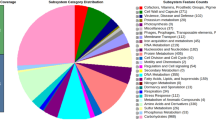
In this study, we report on whole genome sequence analysis of clinically documented, commercial probiotic Bacillus clausii 088AE and genome features contributing to probiotic properties. The whole genome sequence of B. clausii 088AE generated a single scaffold of 4,598,457 bp with 44.74 mol% G + C. This assembled genome sequence annotated by the RAST resulted in 4371 coding genes, 75 tRNAs, and 22 rRNAs. Gene ontology classification indicated 39.5% proteins with molecular function, 44.24% cellular component, and 16.25% proteins involved in biological processes. In taxonomic analysis, B. clausii 088AE shared 99% identity with B. clausii DSM 8716. The gene sequences related to safety and genome stability such as antibiotic resistance (840), virulence factors (706), biogenic amines (1), enterotoxin (0), emetic toxin (0), lanthipeptides (4), prophage (4) and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) sequences (11), were identified and evaluated for safety and functions. The absence of functional prophage sequences and the presence of CRISPR indicated an advantage in genome stability. Moreover, the presence of genome features contributing to probiotic characteristics such as acid, and bile salt tolerance, adhesion to the gut mucosa, and environmental resistance ensure the strains survivability when consumed as a probiotic. In conclusion, the absence of risks associated with sequences/genes in the B. clausii 088AE genome and the presence of essential probiotic traits confirm the strain to be safe for use as a probiotic.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data collected to write this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation, to any qualified researcher.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adelskov J, Patel BKC (2016) A molecular phylogenetic framework for Bacillus subtilis using genome sequences and its application to Bacillus subtilis subspecies stecoris strain D7XPN1, an isolate from a commercial food-waste degrading bioreactor. 3 Biotech 6:96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0408-8
Ahire JJ (2012) Studies on probiotic microorganism(s) and its biogenic metabolite(s). Dissertation, North Maharashtra University, India
Ahire JJ, Kashikar MS, Madempudi RS (2020) Survival and germination of Bacillus clausii UBBC07 spores in in vitro human gastrointestinal tract simulation model and evaluation of clausin production. Front Microbiol 11:1010. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01010
Ahire JJ, Kashikar MS, Madempudi RS (2021) Comparative accounts of probiotic properties of spore and vegetative cells of Bacillus clausii UBBC07 and in silico analysis of probiotic function. 3 Biotech 11(3):116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02668-0
Aleksey VZ, Guillaume M, Daniela P, Michael R, Steven LS, James AY (2013) The MaSuRCA genome assembler. Bioinformatics 21:2669–2677. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt476
Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA (2011) BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom 12:402. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-402
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Amitai G, Sorek R (2016) CRISPR–Cas adaptation: insights into the mechanism of action. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2015.14
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, Wishart DS (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W16-21. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw387
Bennedsen M, Stuer-Lauridsen B, Danielsen M, Johansen E (2011) Screening for antimicrobial resistance genes and virulencefactors via genome sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2785–2787. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02493-10
Benoni G, Marcer V, Cuzzolin L, Raimo F (1984) Antibiotic administration and oral bacterial therapy in infants. Chemioterapia 3:291–294
Blin K, Wolf T, Chevrette MG, Lu X, Schwalen CJ, Kautsar SA, Suarez Duran HG, de Los Santos ELC, Kim HU, Nave M, Dickschat JS, Mitchell DA, Shelest E, Breitling R, Takano E, Lee SY, Weber T, Medema MH (2017) antiSMASH 4.0—improvements in chemistry prediction and gene cluster boundary identification. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W36–W41. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx319
Chen L, **ong Z, Sun L, Yang J, ** Q (2012) VFDB 2012 update: toward the genetic diversity and molecular evolution of bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res 40(Database issue):D641–D645. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr989
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2012) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 22nd Informational supplement: M100-S22
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2016) Methods for antimicrobial dilution and disk susceptibility testing of infrequently isolated or fastidious bacteria, 3rd edn.Wayne, p M45
Cotter PD, Hill C (2003) Surviving the acid test:responses of Gram-positive bacteria to low pH. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:429–453. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.67.3.429-453.2003
Couvin D, Bernheim A, Toffano-Nioche C, Touchon M, Michalik J, Néron B, Rocha EPC, Vergnaud G, Gautheret D, Pourcel C (2018) CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W246–W251. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky425
Darmon E, David RFL (2014) Bacterial genome instability. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 78(1):1–39. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00035-13
Dimitriu T, Kurilovich E, Łapińska U, Severinov K, Pagliara S, Szczelkun MD, Westra ER (2022) Bacteriostatic antibiotics promote CRISPR-Cas adaptive immunity by enabling increased spacer acquisition. Cell Host Microbe 30(1):31-40.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2021.11.014
Duranti S, Lugli GA, Mancabelli L, Turroni F, Milani C, Mangifesta M, Ferrario C, Anzalone R, Viappiani A, van Sinderen D, Ventura M (2017) Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes among human gut-derived bifidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e02894-e2916. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02894-16
FDA-GRAS (2016) Subpart E—Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) Notice Source: 81 FR 55048. https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-B/part-170/subpart-E
EFSA (2007) Opinion of the Scientific Committee. Introduction of a Qualified Presumption of Safety (QPS) approach for assessment of selected microorganisms referred to EFSA. EFSA J 587:1–16. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2007.587
EFSA (2012) EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP); Guidance on the assessment of bacterial susceptibility to antimicrobials of human and veterinary importance. EFSA J 10(6):2740. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2740
EFSA (2016) Update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 4: suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2016. EFSA J 14:4522. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2016.4522
EFSA/ECDC (2018) EFSA/ECDC The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2016. EFSA J 6:5182. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5182
EFSA-FEEDAP (2018) EFSA-FEEDAP Guidance on the characterisation of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms. EFSA J 16(3):5206. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5206
Fagerlund A, Lindbäck T, Storset AK, Granum PE, Hardy SP (2008) Bacillus cereus Nhe is a pore-forming toxin with structural and functional properties similar to the ClyA (HlyE, SheA) family of haemolysins, able to induce osmotic lysis in epithelia. Microbiol 154:693–704. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2007/014134-0
FAO/WHO (2002) Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London
Ghelardi E, Abreu Y, Abreu AT, Marzet CB, Álvarez Calatayud G, Perez M, Moschione Castro AP (2022) Current progress and future perspectives on the use of Bacillus clausii. Microorganisms 10(6):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061246
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
GRN 971 (2023) Generally recognized as safe (GRAS) notification Bacillus clausii 088AE (MCC 0538), Notice (GRN) No. 971. https://www.fda.gov/media/151721/download
Guo FB, Wei W, Wang XL, Lin H, Ding H, Huang J, Rao N (2012) Coevolution of genomic islands and their bacterial hosts revealed through phylogenetic analyses of 17 groups of homologous genomic islands. Genet Mol Res 11:3735–3743. https://doi.org/10.4238/2012.October.15.5
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR, Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S, Calder PC (2014) The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:506–514. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66
Hille F, Richter H, Wong SP, Bratovič M, Ressel S, Charpentier E (2018) The biology of CRISPR-Cas: backward and forward. Cell 172(6):1239–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.032
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C (2012) Effects of b-alanine supplementation on exercise performance: a meta-analysis. Amino Acids 43:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1200-z
Jackson SA, Schoeni JL, Vegge C, Pane M, Stahl B, Bradley M, Goldman VS, Burguière P, Atwater JB, Sanders ME (2019) Improving end-user trust in the quality of commercial probiotic products. Front Microbiol 10:739. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00739
Jia B, Raphenya AR, Alcock B, Waglechner N, Guo P, Tsang K, Lago B, Dave B, Pereira S, Sharma A, Doshi S, Courtot M, Lo R, Williams L, Frye J, Elsayegh T, Sardar D, Westman E, Pawlowski A, Johnson T, Brinkman F, Wright G, McArthur A (2017) CARD: expansion and model-centric curation of the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D566–D573. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1004
Khatri I, Gaurav S, Srikrishna S (2019) Composite genome sequence of Bacillus clausii, a probiotic commercially available as Enterogermina®, and insights into its probiotic properties. BMC Microbiol 19:307. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1680-7
Koransky JR, Allen SD, Dowell VRJ (1978) Use of ethanol for selective isolation of sporeforming microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:762–765. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.35.4.762-765.1978
Lakshmi SG, Jayanthi N, Saravanan M, Ratna Sudha M (2017) Safety assessment of Bacillus clausii UBBC07, a spore forming probiotic. Toxicol Rep 4:62–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2016.12.004
Leplae R, Lima-Mendez G, Toussaint A (2009) ACLAME: a classification of mobile genetic elements, update 2010. Nucleic Acids Res 38(suppl_1):D57–D61. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp938
Li B, Zhan M, Evivie SE, ** D, Zhao L, Chowdhury S, Sarker SK, Huo G, Liu F (2018) Evaluating the safety of potential probiotic Enterococcus durans KLDS6.0930 using whole genome sequencing and oral toxicity study. Front Microbiol 9:1943. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01943
Linares DM, Del Río B, Ladero V, Martínez N, Fernández M, Martín MC, Alvarez MA (2012) Factors influencing biogenic amines accumulation in dairy products. Front Microbiol 3:180. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00180
Liu L, Chen X, Skogerbø G, Zhang P, Chen R, He S, Huang DW (2012) The human microbiome: a hot spot of microbial horizontal gene transfer. Genomics 100:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2012.07.012
Logan NA, Berge O, Bishop AH, Busse HJ, De Vos P, Fritze D, Heyndrickx M, Kämpfer P, Rabinovitch L, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Seldin L, Ventosa A (2009) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of aerobic, endosporeforming bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2114–2121. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.013649-0
Maity C, Gupta AK (2021) Therapeutic efficacy of probiotic Alkalihalobacillus clausii 088AE in antibiotic-associated diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial. Heliyon 7(9):e07993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07993
Maity C, Bagkar P, Dixit Y, Tiwari A (2022) Alkalihalobacillus clausii 088AE as a functional and medical food ingredient: assessment of in vitro protein digestibility and food calorie reduction. Int J Food Sci Technol 57(6):3440–3455. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.15668
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(62)80066-7
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Hans-Peter K, Markus G (2014) Taxonomic use of DNA G+C content and DNA–DNA hybridization in the genomic age. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:352–356. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.056994-0
Merenstein D, Pot B, Leyer G, Ouwehand AC, Preidis GA, Elkins CA, Hill C, Lewis ZT, Shane AL, Zmora N, Petrova MI, Collado MC, Morelli L, Montoya GA, Szajewska H, Tancredi DJ, Sanders ME (2023) Emerging issues in probiotic safety: 2023 perspectives. Gut Microbes 15(1):2185034. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2023.2185034
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35(suppl_2):W182-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm321
Neelamraju J, Madempudi RS (2015) Bacillus clausii - The probiotic of choice in the treatment of diarrhoea. J Yoga Phys 5:4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2157-7595.1000211
Newsom S, Parameshwaran HP, Martin L, Rajan R (2021) The CRISPR-cas mechanism for adaptive immunity and alternate bacterial functions fuels diverse biotechnologies. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:619763. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.619763
Orna MM, Davenport ER, Gilad Y (2013) Taxonomic classification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes using short sequencing reads: evaluation of effective study designs. PLoS ONE 8(1):e53608. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053608
Owen RJ, Hill LR, Lapage SP (1969) Determination of DNA base compositions from melting profiles in dilute buffers. Biopolymers 7:503–516. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.1969.360070408
Pakbin B, Brück WM, Rossen JWA (2021) Virulence factors of enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli: a review. Int J Mol Sci 22(18):9922. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22189922
Petti CA (2007) Detection and identification of microorganisms by gene amplification and sequencing. Clin Infect Dis 44:1108–1114. https://doi.org/10.1086/512818
Pieniz S, de Moura TM, Cassenego AP, Andreazza R, Frazzon AP, de Oliveira Camargo FA, Brandelli A (2015) Evaluation of resistance genes and virulence factors in a food isolated Enterococcus durans with potential probiotic effect. Food Control 51:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.11.012
Price CE, Reid SJ, Driessen AJ, Abratt VR (2006) The Bifidobacterium longum NCIMB 702259T ctr gene codes for a novel cholate transporter. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:923–926. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.72.1.923-926.2006
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs BM, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35(21):7188–7196. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm864
Rozman V, Petr ML, Tomaz A, Bojana BM (2020) Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria used as probiotics or starter cultures based on integration of phenotypic and in silico data. Int J Food Microbiol 314:108388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108388
Sabat AJ, van Zanten E, Akkerboom V, Wisselink G, van Slochteren K, de Boer RF, Hendrix R, Friedrich AW, Rossen JWA, Kooistra-Smid AMDM (2017) Targeted next-generation sequencing of the 16S–23S rRNA region for culture-independent bacterial identification - increased discrimination of closely related species. Sci Rep 7:3434. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03458-6
Salvetti E, Orru L, Capozzi V, Martina A, Lamontanara A, Keller D, Cash H, Felis GE, Cattivelli L, Torriani S, Spano G (2016) Integrate genome-based assessment of safety for probiotic strains: Bacillus coagulans GBI-30, 6086 as a case study. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:4595–4605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7416-9
Saroj D, Gupta AK (2020) Genome based safety assessment for Bacillus coagulans strain LBSC (DSM 17654) for probiotic application. Int J Food Microbiol 318:108523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108523
Schildkraut CL, Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol 4:430–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(62)80100-4
Siguier P, Pérochon J, Lestrade L, Mahillon J, Chandler M (2006) ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 34(suppl_1):D32–D36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj014
Štšepetova J, Taelma H, Smidt I, Hütt P, Lapp E, Aotäht E, Mändar R (2017) Assessment of phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic susceptibility of vaginal Lactobacillus sp. J Appl Microbiol 123:524–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13497
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44(14):6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
UniProt Consortium (2014) UniProt: a hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res 43(D1):D204–D212
Weisblum B (1995) Erythromycin resistance by ribosome modification. Antimicrob Agents Chem 39:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.39.3.577
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. VL Rathi, and Mr. MM Kabra, Advanced Enzyme Technologies Limited for providing the laboratory facilities.
Funding
This study was funded by Advanced Enzyme Technologies, Limited, Thane, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: DBS; Methodology: DBS; Formal analysis and investigation: DBS, RS and JJA; Writing—original draft preparation: DBS, RS, and JJA; Resources: DBS; Supervision: DBS. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The paper does not contain any study on human participants or animals.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saroj, D.B., Ahire, J.J. & Shukla, R. Genetic and phenotypic assessments for the safety of probiotic Bacillus clausii 088AE. 3 Biotech 13, 238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03662-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03662-4