Abstract
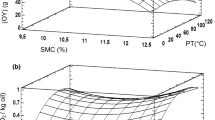
Seed oil expression is an important economic venture in rural Nigeria. The traditional techniques of carrying out the operation is not only energy sap** and time consuming but also wasteful. In order to reduce the tedium involved in the expression of oil from moringa oleifera seed and develop efficient equipment for carrying out the operation, the oil point pressure of the seed was determined under different processing conditions using a laboratory press. The processing conditions employed were moisture content (4.78, 6.00, 8.00 and 10.00 % wet basis), heating temperature (50, 70, 85 and 100 °C) and heating time (15, 20, 25 and 30 min). Results showed that the oil point pressure increased with increase in seed moisture content, but decreased with increase in heating temperature and heating time within the above ranges. Highest oil point pressure value of 1.1239 MPa was obtained at the processing conditions of 10.00 % moisture content, 50 °C heating temperature and 15 min heating time. The lowest oil point pressure obtained was 0.3164 MPa and it occurred at the moisture content of 4.78 %, heating temperature of 100 °C and heating time of 30 min. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) showed that all the processing variables and their interactions had significant effect on the oil point pressure of moringa oleifera seed at 1 % level of significance. This was further demonstrated using Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Tukey’s test and Duncan’s Multiple Range Analysis successfully separated the means and a multiple regression equation was used to express the relationship existing between the oil point pressure of moringa oleifera seed and its moisture content, processing temperature, heating time and their interactions. The model yielded coefficients that enabled the oil point pressure of the seed to be predicted with very high coefficient of determination.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeeko KA, Ajibola OO (1990) Processing factors affecting yield and quality of mechanically expressed groundnut oil. J Agric Eng Res 45:31–43
Ajibola OO, Owolarafe OK, Fasina OO, Adeeko KA (1993) Expression of oil from sesame seeds. Can Agric Eng 35:83–88
Ajibola OO, Adetunji SO, Owolarafe OK (2000) Oil point pressure of sesame seed. Ife J Technol 9:57–62
Ajibola OO, Okunade DA, Owolarafe OK (2002) Oil point pressure of soya bean. J Food Process Eng 25:407–416
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
Aregbesola OA, Olatunde GA, Esuola SS, Owolarafe OK (2012) Oil point pressure of Indian almond kernels. Int Agrophysics 26:225–228
Dedio W, Dornell DG (1977) Factor affecting the pressure extraction of oil from flaxseed. J Am Oil Chem Soc 54(8):313–320
Eilert U, Wolters B, Nahrstedt A (1981) The antibiotic principle of seeds of Moringa oleifera and Moringa stenopetada tala. J Med Plants 42:55–61
Farabode MO, Favier JF (1997) New insight into the mechanics of seed-oil expression. J Agric Eng Technol 5:9–24
Khan LM, Hanna MA (1983) Expression of oil from oilseeds – a review. J Agric Eng Res 28:495–505
Morton JF (1991) The horseradish, Moringa pterygosperma (moringaceae) – a boom to arid land economy. Botany 34:276–283
Mrema GC, McNulty PB (1985) Mathematical model of mechanical oil expression from oil seeds. J Agric Eng Res 31:361–370
Norris FA (1964) Extraction of Fat and Oil. Bailey’s industrial Oil and Fat. Wiley Press, New York
Ogunshina BS, Owolarafe OK, Olatunde GA (2008) Oil point pressure of cashew (Anacardium occidentale) kernels. Int Agrophysics 22:53–59
Olatunde GA, Owolarafe OK (2011) Effects of processing conditions on oil point pressure of neem seed. Proc Niger Inst Agric Eng 32:412–420
Owolarafe OK, Adegunloye AT, Ajibola OO (2003) The Effects of some processing conditions on oil point pressure of locust bean. J Food Process Eng 26(51):489–497
Oyinlola A, Adekoya LO (2004) Development of a laboratory model screw press for peanut oil expression. J Food Eng 64:221–227
Ram J (1994) Moringa – a highly nutritious vegetable tree. Tropical Rural and Island/Atoll Development Experimental Station (TRIADES), Technical Bulletin No. 2
Rusinek R, Rybczynski R, Tys J, Gawrysiak-Witulska M, Nogala-Kalucka M, Siger A (2012) The process parameters for nonb-typical seeds during simulated cold deep oil expression. Czech J Food Sci 30(2):126–134
Sanford SD, James MW, Parag SS, Claudia W, Marlen AV, Glen RM (2009) Feedstock and Biodiesel Chracteristics Report. RenewableEnergy Group Inc. Ames, Iowa, USA, www.regfuel.com
Sivala K, Bhole NG, Mukherjee R (1991) Effect of moisture content on rice bran oil expression. J Agric Eng Res 42:77–84
Sukumaran CR, Singh B (1989) Compression of a bed of rapeseeds - the oil point. J Agric Eng Res 42:77–88
Tunde-Akintunde TY (2010) Determination of oil point pressure for melon seeds. J Food Process Eng 33:179–189
Tunde-Akintunde TY, Akintude BO, Igbeka JC (2001) Effects of processing factors on yield and quality of mechanically expressed soya bean oil. J Agric Eng Technol 9:39–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aviara, N.A., Musa, W.B., Owolarafe, O.K. et al. Effect of processing conditions on oil point pressure of moringa oleifera seed. J Food Sci Technol 52, 4499–4506 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1498-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1498-0