Abstract
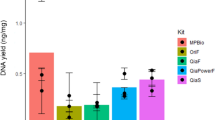
Genetic sampling from faeces is a useful method for obtaining DNA samples non-invasively. The quantity and quality of DNA isolated from faecal samples is, however, an important factor affecting the success of downstream analyses. Commercial DNA isolation kits offer an efficient and convenient means for recovering DNA, but the kit methodology can influence the quantity and quality of DNA obtained. Comparisons of kit performance for the isolation of DNA from non-invasive sources for ecological studies based on genetic analysis are uncommon in the literature. This study compared the quantity and quality of DNA isolated from surface washings of fresh koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) faecal pellets (scats) using four commercial DNA isolation kits: Axygen® AxyPrep™ MAG Soil, Stool, and Water DNA Kit (AX), Bioline ISOLATE Fecal DNA Kit (BL), Qiagen QIAamp® Fast DNA Stool Mini Kit (QFS), and Qiagen QIAamp® DNA Stool Mini Kit (QS). DNA quantitation, standard PCR and electrophoresis, real time PCR and replicate genoty** using capillary electrophoresis were used to compare the performance of resultant DNA isolates. The performance of DNA isolated from koala scats varied substantially with the DNA kit utilised. All kits provided accurate genotypes but with differing amounts of missing data. Overall, kit AX performed best, providing DNA isolates of higher quantity and quality compared to kit QS, which has previously been thoroughly assessed for genoty** reliability using DNA from koala scats. Given the high variability noted, assessing kit performance is an important way to maximise data quality from non-invasively sourced DNA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beja-Pereira A, Oliveira R, Alves PC, Schwartz MK, Luikart G (2009) Advancing ecological understandings through technological transformations in noninvasive genetics. Mol Ecol Resour 9:1279–1301. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02699.x
Brinkman TJ, Schwartz MK, Person DK, Pilgrim KL, Hundertmark KJ (2010) Effects of time and rainfall on PCR success using DNA extracted from deer fecal pellets. Conserv Genet 11:1547–1552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-009-9928-7
Broquet T, Ménard N, Petit E (2007) Noninvasive population genetics: a review of sample source, diet, fragment length and microsatellite motif effects on amplification success and genoty** error rates. Conserv Genet 8:249–260
Cristescu R, Cahill V, Sherwin WB, Handasyde K, Carlyon K, Whisson D, Herbert CA, Carlsson BLJ, Wilton AN, Cooper DW (2009) Inbreeding and testicular abnormalities in a bottlenecked population of koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus). Wildl Res 36:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1071/WR08010
Ferrand J, Patron K, Legrand-Frossi C, Frippiat J-P, Merlin C, Alauzet C, Lozniewski A (2014) Comparison of seven methods for extraction of bacterial DNA from fecal and cecal samples of mice. J Microbiol Methods 105:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2014.07.029
Houlden B, England P, Sherwin W (1996a) Paternity exclusion in koalas using hypervariable microsatellites. J Hered 87:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a022972
Houlden BA, England PR, Taylor AC, Greville WD, Sherwin WB (1996b) Low genetic variability of the koala Phascolarctos cinereus in south-eastern Australia following a severe population bottleneck. Mol Ecol 5:269–281. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.1996.00089.x
Kranzfelder P, Ekrem T, Stur E (2016) Trace DNA from insect skins: a comparison of five extraction protocols and direct PCR on chironomid pupal exuviae. Mol Ecol Resour 16:353–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12446
Loebel DA, Johnston PG (1997) Analysis of the intron-exon structure of the G6PD gene of the wallaroo (Macropus robustus) by polymerase chain reaction. Mamm Genome 8:146–147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003359900376
Loebel D, Longhurst T, Johnston P (1995) Full-length cDNA sequence of X-linked G6PD of an Australian marsupial, the wallaroo. Mamm Genome 6:198–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293013
Lonsinger RC, Waits LP (2015) ConGenR: rapid determination of consensus genotypes and estimates of genoty** errors from replicated genetic samples. Conserv Genet Res 7:841–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-015-0506-7
Luikart G, Zundel S, Rioux D, Miquel C, Keating KA, Hogg JT, Steele B, Foresman K, Taberlet P (2008) Low genoty** error rates and noninvasive sampling in bighorn sheep. J Wildl Manag 72:299–304. https://doi.org/10.2193/2006-006
Markey B, Wan C, Hanger J, Phillips C, Timms P (2007) Use of quantitative real-time PCR to monitor the shedding and treatment of chlamydiae in the koala (Phascolarctos cinereus). Vet Microbiol 120:334–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.11.022
Miquel C, Bellemain E, Poillot C, Bessiere J, Durand A, Taberlet P (2006) Quality indexes to assess the reliability of genotypes in studies using noninvasive sampling and multiple-tube approach. Mol Ecol Notes 6:985–988. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01413.x
Pearson SK, Tobe SS, Fusco DA, Bull CM, Gardner MG (2015) Piles of scats for piles of DNA: deriving DNA of lizards from their faeces. Aust J Zool 62:507–514. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO14059
Piggott MP, Taylor AC (2003a) Extensive evaluation of faecal preservation and DNA extraction methods in Australian native and introduced species. Aust J Zool 51:341–355. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO03012
Piggott MP, Taylor AC (2003b) Remote collection of animal DNA and its applications in conservation management and understanding the population biology of rare and cryptic species. Wildl Res 30:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1071/WR02077
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E, Taberlet P (2005) Genoty** errors: causes, consequences and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 6:846–847. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1707
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. 3–36
Ruiz-Rodriguez CT, Ishida Y, Greenwood AD, Roca AL (2014) Development of 14 microsatellite markers in the Queensland koala (Phascolarctos cinereus adustus) using next generation sequencing technology. Conserv Genet Resour 6:429–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-013-0115-2
Stenglein J, De Barba M, Ausband D, Waits L (2010) Impacts of sampling location within a faeces on DNA quality in two carnivore species. Mol Ecol Resour 10:109–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02670.x
Taberlet P, Griffin S, Goossens B, Questiau S, Manceau V, Escaravage N, Waits LP, Bouvet J (1996) Reliable genoty** of samples with very low DNA quantities using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 24:3189–3194. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.16.3189
Valière N (2002) GIMLET: a computer program for analysing genetic individual identification data. Mol Ecol Notes 2:377–379. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00228.x-i2
Valière N, Berthier P, Mouchiroud D, Pontier D (2002) GEMINI: software for testing the effects of genoty** errors and multitubes approach for individual identification. Mol Ecol Notes 2:83–86. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-8286.2002.00134.x
Valière N, Bonenfant C, Toïgo C, Luikart G, Gaillard J-M, Klein F (2007) Importance of a pilot study for non-invasive genetic sampling: genoty** errors and population size estimation in red deer. Conserv Genet 8:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-006-9149-2
Walker FM, Taylor AC, Sunnucks P (2008) Female dispersal and male kinship-based association in southern hairy-nosed wombats (Lasiorhinus latifrons). Mol Ecol 17:1361–1374. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03670.x
Walker FM, Horsup A, Taylor AC (2009) Leader of the pack: faecal pellet deposition order impacts PCR amplification in wombats. Mol Ecol Resour 9:720–724. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02582.x
Watson C, Margan S, Johnston P (1998) Sex-chromosome elimination in the bandicoot Isoodon macrourus using Y-linked markers. Cytogenet Genome Res 81:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1159/000015008
Wedrowicz F, Karsa M, Mosse J, Hogan FE (2013) Reliable genoty** of the koala (Phascolarctos cinereus) using DNA isolated from a single faecal pellet. Mol Ecol Resour 13:634–641. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12101
Yu Z, Morrison M (2004) Improved extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from digesta and fecal samples. Biotechniques 36:808–813. https://doi.org/10.2144/3605A0808
Acknowledgements
Thank-you to Grand Ridge Plantations Pty. Ltd. (HVP Plantations) and the Holsworth Wildlife Research Endowment—Equity Trustees Charitable Foundation for funding this research. The Southern Ash Wildlife Shelter (SAWS) are also thanked for providing access to koala scats for this study. We also thank the reviewers of this manuscript for their helpful comments.
Funding
This project was funded by Grand Ridge Plantations Pty. Ltd. (HVP Plantations) and the Holsworth Wildlife Research Endowment—Equity Trustees Charitable Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Sampling was performed after obtaining a research permit under the provisions of the Wildlife Act 1975 and National Parks Acts 1975 from the Department of Environment and Primary Industries (Permit No. 10007130), and approval from Monash University Biological Sciences Animal Ethics Committee (AEC No. GIPP/2011/03).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wedrowicz, F., Mosse, J., Wright, W. et al. Isolating DNA sourced non-invasively from koala scats: a comparison of four commercial DNA stool kits. Conservation Genet Resour 11, 219–229 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-018-0994-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-018-0994-3