Abstract
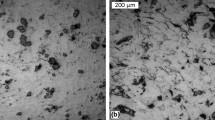
In order to improve the tribological properties of zinc-based alloy, SiC nanoparticles (an average grain size of 100 nm) were reinforced into Zn–38Al–3.5Cu–1.2 Mg alloy through a high-pressure jetting powder and semisolid stirring-assisted ultrasonic vibration process. In the present study, the effects of different SiC contents (0 wt%, 0.07 wt%, 0.13 wt%, and 0.22 wt%) on microstructural properties and wear behavior of the as-cast alloy were investigated in detail. The results indicated that a uniform and dispersive distribution of SiC nanoparticles was observed in the Zn–Al matrix, thus leading to a significant enhancement in wear behavior of Zn–38Al–3.5Cu–1.2 Mg alloy. Further, with the increasing mass fraction of SiC nanoparticles, wear resistance of Zn–38Al–3.5Cu–1.2 Mg alloy was noticeably improved in spite of the increasing friction temperature. The increased wear resistance of Zn–38Al–3.5Cu–1.2 Mg alloy at high friction temperature could be attributed to the presence of uniformly dispersed thermostable SiC nanoparticles, which inhibited the transformation of the abrasion-resistant phase of α + η mixture to the soft phase of α and η on the friction heating interface.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tjong S C, Adv Eng Mater 9 (2007) 81.
Casati R and Vedani M, Metals 4 (2014) 65.
Manikonda R D, Kosaraju S, Arul R K, and Sateesh N, Mater Today Proc 5 (2018) 20104.
Şevik H, Mater Charact. 89 (2014) 81.
Savaşkan T, Maleki R A, and Tan H O, Tribol Int 81 (2015) 105.
Savaşkan T and Azaklı Z, Wear 264 (2008) 920.
Murphy S and Savaskan T, Wear 98 (1984) 151.
Sen S, Dhindaw B K, Stefanescu D M, Catalina A, and Curreri P A, J Cryst Growth 173 (1997) 574.
Tao Y, Sorgenfrei T, Jauß T, Cröll A, Reimann C, Friedrich J, and Derby J, J Cryst Growth 468 (2017) 24.
El-Khaira M T A, Lotfya A, Daouda A, and El-Sheikh A M, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 2353.
Mishra S K, Biswas S, and Satapathy A, Mater Des 55 (2014) 958.
Bobić B, Bajat J, Bobić I, and Jegdić B, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 26 (2016) 1512.
Sajjadi S A, Ezatpour H R, and Parizi M T, Mater Des 34 (2012) 106.
Alaneme K K and Ajayi O J, J King Saud Univ-Eng Sci 29 (2017) 172.
Prabu S B, Karunamoorthy L, Kathiresan S, and Mohan B, J Mater Process Technol 171 (2006) 268.
Kumar A, Kumar S, and Mukhopadhyay N K, J Magn Alloy 6 (2018) 245.
Poddar P, Srivastava V C, De P K, and Sahoo K L, Mater Sci Eng A 460–461 (2007) 357.
Atamanenko T V, Eskin D G, Zhang L, and Katgerman L, Metall Mater Trans A 41A (2010) 2056.
Khalifa W, El-Hadad S, and Tsunekawa Y, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 25 (2015) 3173.
Puga H, Barbosa J, Machado J M, and Vilarinho C, J Mater Process. Technol 263 (2019) 336.
Li Q, Qiu F, Jiang Q C, Dong B X, Geng R, Lv M M, Zhao Q L, and Jiang Q C, Mater Sci Eng A 735 (2018) 310.
Nie K B, Wang X J, Wu K, Hu X S, Zheng M Y, and Xu L, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 8709.
Chen L Y, Peng J Y, Xu J Q, Choi H, and Li X C, Scr Mater 69 (2013) 634.
Srivastava N and Chaudhari G P, Mater Sci Eng A 724 (2018) 199.
Saberi Y, Zebarjad S M, Akbari G H, J Alloys Compd 484 (2009) 637.
Kumar S and Balasubramanian V, Tribol Int 43 (2010) 414.
Kiran T S, Prasannakumar M, Basavarajappa S, Viswanatha B M, Ind Lubr Tribol 67 (2015) 292.
Acknowledgement
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (51874216), The Open-Fund Innovation Program of The Key Laboratory for Ferrous Metallurgy and Resources Utilization of Ministry of Education (FMRU201305), and The Hubei Province Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Project of Undergraduate (201810488058).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Yuan, Q., Gong, Yq. et al. Correlations Between Microstructure and Dry Friction Wear Behavior of Zn–38Al–3.5Cu–1.2 Mg Alloy Reinforced with SiC Nanoparticles. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 2557–2565 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01725-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-019-01725-w