Abstract
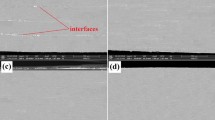
An Al–0.2 wt%Zr alloy was subjected to an accumulative roll bonding (ARB) process up to a strain of 8.0. The process led to ultrafine-grained materials with a mean grain size of 400 nm by 10-cycle ARB process, which was studied by atomic force microscopy (AFM). The Vickers microhardness measurements showed that the hardness value monotonously increased the number of ARB cycles and then reached a constant value of about 45 HV. Yield strength and tensile strength increased during the ARB process and reached to 125 and 158 MPa, respectively, after 10-cycles ARB process. The total elongation and uniform elongation were 65 and 48% before the ARB process and decreased after 10-cycle ARB to 17.5 and 6.5%, respectively. Also, after the tensile test, the fracture surfaces were studied by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and the result showed that the fracture mode in the 0 cycle (before ARB) and 1 cycle was ductile and changed to brittle with further ARB processing from 3 up to 10 cycles.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borhani E, Jafarian H, Shibata A, and Tsuji N, Mater Trans 53 (2012) 1863.
Valiev R Z, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon T G, Zehetbauer M J, and Zhu Y T, JOM 58 (2006) 33.
Valiev R Z. and Langdon T G, Prog Mater Sci 51 (2006) 881.
Borhani E, Jafarian H, Terada D, Adachi H, and Tsuji N, Mater Trans 54 (2012) 72.
Schafler E, and Kerber M B, Mater Sci Eng A 462 (2007) 139.
Huang J Y, Zhu Y T, Jiang H, and Lowe T C, Acta Mater 49 (2001) 1497.
Korbel A, Richert M, and Richert J, In Proceedings of the 2nd RISO International Symposium on Metallurgy and Material Science (1981), p 445. (in Denmark).
Mizunuma S, Mater Sci Forum (2006) 185.
Nakamura K, Neishi K, Kaneko K, Nakagaki M, and Horita Z, Mater Trans 45 (2004) 3338.
Saito Y, Tsuji N, Utsunomiya H, Sakai T, and Hong R G, Scr Mater 39 (1998) 1221.
Tsuji N, Saito Y, Lee S H, and Minamino Y, Adv Eng Mater 5 (2003) 338.
Knipling K E, Dunand D C, and Seidman D N, Acta Mater 56 (2008) 1182.
Humphreys F J, and Hatherly M, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, 2nd ed, Elsevier, Amsterdam (2004).
Knipling K E, Dunand D C, and Seidman D N, Acta Mater 56 (2008) 114.
Pirgazi H, Akbarzadeh A, Petrov R, and Kestens L, Mater Sci Eng A 497 (2008) 132.
Saito Y, Utsunomiya H, Tsuji N, and Sakai T, Acta Mater 47 (1999) 579.
Lee S H, Saito Y, Sakai T, and Utsunomiya H, Mater Sci Eng A 325 (2002) 228.
Smirnova N A, Levit V I, Pilyugin V I, Kuznetsov R I, Davydova L S, and Sazonova V A, Fiz Met Metalloved 61 (1986) 1170.
Borhani E, Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Heavily Deformed Al–Sc Alloy Having Different Starting Microstructures, Ph.D. thesis, Kyto University, Japan (2011).
Lee S H, Sakai T, Saito Y, Utsunomiya H, and Tsuji N, Mater Trans 40 (1999) 1422.
Tohidi A A, Ketabchi M, and Hasannia A, Mater Sci Eng A 577 (2013) 43.
Hansen N, Acta Metallurgica 25 (1977) 863.
Totten G E, **e L, and Funatani K Handbook of Mechanical Design Alloy vol 164, p 627, CRC Press.
May J, Amberger D, Dinkel M, Hoppel H W, and Goken M, Mater Sci Eng A 483–484 (2008) 481.
Rezaei M R, Toroghinejad M R, and Ashrafzadeh F, Mater Process Tech 211 (2011) 1184.
ASM handbooks, Fractography, vol 12.
Azad B, Borhani E, and Mohammadian Semnani H R, Kovove Mater 54 (2016) 9.
Azad B, and Borhani E, J Min Metall Sect B 52 (2016) 93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azad, B., Semnani, H.M. & Borhani, E. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Nano-structured Al–0.2 wt%Zr Alloy Fabricated by Accumulative Roll Bonding (ARB) Process. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 2725–2732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1133-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1133-7