Abstract
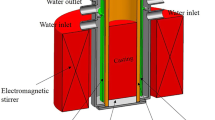
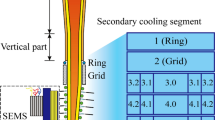
The comparison between the mechanical soft reduction (MSR) and final electromagnetic stirring (FEMS) on center carbon macrosegregation and v-segregation has been investigated in order to improve the inner quality of high carbon 82A steel with a section of size 180 mm × 240 mm. A heat transfer calculation model by using C++ programming language is developed and applied to calculate the appropriate casting speed of continuous casting during the FEMS and MSR processes. The calculated action zone of FEMS and MSR is at the location with a solid fraction of 0.28–0.41 and 0.30–0.90, respectively. The industrial results show that the effects of MSR in improving the center carbon segregation, reducing the shrinkage cavity and suppressing the V-segregation are more effective than FEMS. The mean center carbon segregation degree reduces from 1.19 to 1.15 with FEMS and decreases from 1.19 to 1.07 with MSR. Besides, compared with FEMS, MSR can eliminate shrinkage cavity and V-segregation but may generate center negative segregation and transverse cracks subjected to reduction pressure.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flemings M C, ISIJ Int 40 (2000) p 833.
Choudhary S K, and Ganguly S, ISIJ Int 47 (2007) p 1759.
Raihle C M, and Fredriksson H, Metall Trans B 25 (1994) p 123.
Sung P K, PoirierD R, Yalamanchili B, and Geiger G H,Ironmak Steelmak 17 (1990) p 424.
Ludlow V, Normanton A, Anderson A, Thiele M, Ciriza J, Laraudogoitia J, and Knoop W V, Ironmak Steelmak 32 (2005) p 68.
Fredriksson H, andSvensson I, Metall Trans B 7 (1976) p 599.
Engstrrm G, Fredriksson H, and Rogberg B, Scand J Metall 12 (1983) p 3.
Fredriksson H, Can Metall Q 30 (1991) p 235.
Raihle C M, Sivesson P, Tukiainen M, and Fredriksson H, Ironmak Steelmak 21 (1994) p 487.
Oh K S, Park J K, and Chang S H, Steelmaking in Conf Proc (1995) p 301.
Wang W J, Hu X G, Ning L X, Bulte R, and Bleck W, Int J Miner Metall Mater 13 (2006) p 490.
Oh K S, and Chang Y W, ISIJ Int 35 (1995) p 866.
**ao C, Zhang J M, and Wu L, J Iron Steel Res Int 20 (2013) p 13.
Han Z W, Chen D F, Feng K, and Long M J, ISIJ Int 50 (2010) p 1637.
Sakaki G S, Kwong A T, and Petozzi J J, Steelmaking in Conf Proc (1995) p 295.
Thome R, and Harste K, ISIJ Int 46 (2006) p 1839.
Ogibayashi S, Kobayashi M, Yamada M, and Mukai T, ISIJ Int. 31 (1991) p 1400.
Ji C, Luo S, and Zhu M Y, ISIJ Int 54 (2014) p 504.
Thomas B G, and Zhang L, ISIJ Int 41 (2001) p 1181.
Brimacombe J K, Can Metall Q 15 (1976) p 163.
Choudhary S K, and Mazumdar D, Steel Res Int 66 (1995) pp 199.
Schwerdtfeger K J,The Casting Volume of the 11th ed. of the Making, Sha** and Treating of Steel, The AISE Steel Foundation, Pittsburgh (2003) p 18.
Yim C H , Park J K, Oh K S, and Nam S H, Steelmaking in Conf Proc (1998) p 309.
Mao B, Zhang G F, and Li A W, Theory and Technology of Electromagnetic Stirring for Continuous Casting, Metallurgical industry press, Bei**g (2012) p 162.
Domitner J, Wu M, Kharicha A, Ludwig A, Kaufmann B, Reiter J, and Schaden T, Metall Trans A 45 (2014) p 1415.
Chen Y K, Feng F A, Lin K J, and Sediako D, Steelmaking in Conf Proc (1996) p 505.
Li X B , Ding H, Tang Z Y, and He J C, Int J Miner Metall Mater 19 (2012) p 21.
Cabrera-Marrero J M, Carreno-Galindo V, Morales R D, and Chavez-Alcala F, ISIJ Int 38 (1998) p 812.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, J., Chen, W., Wang, Q. et al. Improving Inner Quality in Continuous Casting Rectangular Billets: Comparison Between Mechanical Soft Reduction and Final Electromagnetic Stirring. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 1623–1632 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0742-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0742-2