Abstract
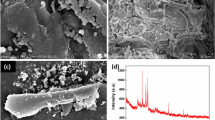
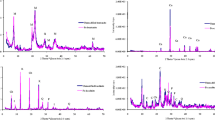
In the present work, pond clay was modified with lanthanum and applied for fluoride uptake from an aqueous environment. The clay soil was treated with a 0.1 M solution of lanthanum oxide and heated at 500 ℃ for 90 min in a muffle furnace. The modified clay was characterized by the following techniques: particle size analysis, zeta potential, Fourier-transform infrared, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, pH at the zero point of charge, X-ray diffraction, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The adsorption experiments revealed that modified clay soil was very effective in removing fluoride with an adsorption capacity of 1.96 mg/g. The fluoride removal was followed well with Langmuir isotherm (R2 = 0.999), pseudo-second-order kinetics (R2 = 1), and the adsorption was an exothermic process. The performance of lanthanum-modified clay (LMC) in a fixed bed column was evaluated using different models, including the Thomas, Adams–Bohart, Yoon–Nelson, and Clark models. A regeneration study was compared with NaOH and NaHCO3 and successfully performed for four adsorption cycles. A probable mechanism is proposed including ligand exchange, electrostatic attraction, and inner complexation for fluoride adsorption on the LMC. The developed adsorbent was also tested for the treatment of natural groundwater.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All the data related to this publication are made available in the manuscript.
References
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2017) Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl Water Sci 7(2):543–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Adimalla N, Venkatayogi S, Das SVG (2019) Assessment of fluoride contamination and distribution: a case study from a rural part of Andhra Pradesh. India Appl Water Sci 9(4):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0968-y
Akafu T, Chimdi A, Gomoro K (2019) Removal of fluoride from drinking water by sorption using diatomite modified with aluminum hydroxide. J Anal Methods Chem 2019:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4831926
Annan E, Nyankson E, Agyei-Tuffour B et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of modified kaolin-bentonite composites for enhanced fluoride removal from drinking water. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2021:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6679422
Atasoy AD, Yesilnacar MI, Sahin MO (2013) Removal of fluoride from contaminated ground water using raw and modified bauxite. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91(5):595–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1099-z
Ayalew AA (2020) Development of kaolin clay as a cost-effective technology for defluoridation of groundwater. Int J Chem Eng 2020:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8820727
Ayawei N, Ebelegi AN, Wankasi D (2017) Modelling and interpretation of adsorption isotherms. J Chem 2017:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3039817
Bharti VK, Giri A, Kumar K (2017) Fluoride sources, toxicity and its amelioration: a review. Peertechz J Environ Sci Toxicol 2(1):021–032. https://doi.org/10.17352/aest.000009
Blott SJ, Pye K (2001) GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf Process Landf 26(11):1237–1248. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.261
Bukalo NN, Ekosse GIE, Odiyo JO, Ogola JS (2017) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of clay size fraction of cretaceous-tertiary kaolins in the Douala sub-basin, Cameroon. Open Geosci 9(1):407–418. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2017-0031
Caponi N, Collazzo GC, Jahn SL, Dotto GL, Mazutti MA, Foletto EL (2017) Use of Brazilian kaolin as a potential low-cost adsorbent for the removal of malachite green from colored effluents. Mater Res 20:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2016-0673
Castro LFD, Brandão VS, Bertolino LC, de Souza WF, Teixeira VG (2019) Phosphate adsorption by montmorillonites modified with lanthanum/iron and a laboratory test using water from the Jacarepaguá Lagoon (RJ, Brazil). J Braz Chem Soc 30(3):641–657. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20180236
Chaudhry SA, Zaidi Z, Siddiqui SI (2017) Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamics of arsenic adsorption onto Iron-zirconium binary oxide-coated sand (IZBOCS): modelling and process optimization. J Mol Liq 229:230–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.12.048
Corral-Capulin NG, Vilchis-Nestor AR, Gutiérrez-Segura E, Solache-Rios M (2019) Comparison of the removal behavior of fluoride by Fe3+ modified geomaterials from water. Appl Clay Sci 173:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.03.003
Dessalegne M, Zewge F, Mammo W, Woldetinsae G, Diaz I (2018) Effective fluoride adsorption by aluminum oxide modified clays: Ethiopian bentonite vs commercial montmorillonite. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop 32(2):199–211. https://doi.org/10.4314/bcse.v32i2.2
Dewage NB, Liyanage AS, Pittman CU Jr, Mohan D, Mlsna T (2018) Fast nitrate and fluoride adsorption and magnetic separation from water on α-Fe2O3 and Fe3O4 dispersed on Douglas fir biochar. Bioresour Technol 263:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.05.001
Djelloul C, Hamdaoui O (2015) Dynamic adsorption of methylene blue by melon peel in fixed-bed columns. Desalin Water Treat 56(11):2966–2975. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.963158
Elgamouz A, Tijani N, Shehadi I, Hasan K, Kawam MAF (2019) Characterization of the firing behaviour of an illite-kaolinite clay mineral and its potential use as membrane support. Heliyon 8(2019):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02281
Enalou HB, Moore F, Keshavarzi B, Zarei M (2018) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of fluoride is water resources, south of Fars province, Iran: stable isotopes (δ18O & δD) and geochemical modeling approaches. Appl Geochem 98:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.09.019
Fito J, Said H, Feleke S, Worku A (2019) Fluoride removal from aqueous solution onto activated carbon of Catha edulis through the adsorption treatment technology. Environ Sys Res 8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-019-0153-1
Garcia-Sanchez JJ, Solache-Rios M, Martinez-Gutierrez JM, Arteaga-Larios NV, Ojeda-Escamilla MC, Rodriguez-Torres I (2016) Modified natural magnetite with Al and La ions for the adsorption of fluoride ions from aqueous solutions. J Fluor Chem 186:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfluchem.2016.05.004
Gautam A, Rawat S, Verma L, Singh J, Sikarwar S, Yadav BC, Kalamdhad AS (2018) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticle from extract of waste tea: an application for phenol red removal from aqueous solution. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 10:377–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2018.08.003
Ghosal PS, Gupta AK, Ayoob S (2015) Effect of formation pH, molar ratio and calcination temperature on the synthesis of an anionic clay based adsorbent targeting defluoridation. Appl Clay Sci 116:120–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.08.026
Hanse A, Chabukdhara M, Baruah SG, Boruah H, Gupta SK (2019) Fluoride contamination in groundwater and associated health risks in Karbi Anglong District, Assam, Northeast India. Environ Monit Assess 191(12):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7970-6
Iriel A, Bruneel SP, Schenone N, Cirelli AF (2018) The removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by a lateritic soil adsorption: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.016
Jagtap S, Yenkie MK, Labhsetwar N, Rayalu S (2012) Fluoride in drinking water and defluoridation of water. Chem Rev 112(4):2454–2466. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2002855
Kadam A, Wagh V, Umrikar B, Sankhua R (2020) An implication of boron and fluoride contamination and its exposure risk in groundwater resources in semi-arid region, western India. Environ Dev Sustain 22(7):7033–7056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00527-w
Karunanidhi D, Aravinthasamy P, Subramani T, Roy PD, Srinivasamoorthy K (2019) Risk of fluoride-rich groundwater on human health: remediation through managed aquifer recharge in a hard rock terrain South India. Nat Resour Res 29(4):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09592-4
Kofa GP, Gomdje VH, Telegang C, Koungou SN (2017) Removal of fluoride from water by adsorption onto fired clay pots: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Appl Chem 2017:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6254683
Lambert JF (2018) Organic pollutant adsorption on clay minerals. In: Bergaya F (ed) Developments in clay science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 195–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102432-4.00007-X
Liu R, Mei X, Zhang J, Zhao DB (2019) Characteristics of clay minerals in sediments of Hemudu area, Zhejiang, China in Holocene and their environmental significance. China Geol 2(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.31035/cg2018069
Ma Z, Zhang Q, Weng X, Mang C, Si L, Guan Z, Cheng L (2018) Fluoride ion adsorption from wastewater using magnesium (II), aluminum (III) and titanium (IV) modified natural zeolite: kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanistic aspects of adsorption. J Water Reuse Desalin 8(4):479–489. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2017.037
Madejova J, Gates WP, Petit S (2017) IR spectra of clay minerals. Dev Clay Sci 8:107–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100355-8.00005-9
Majewska-Nowak K, Grzegorzek M, Kabsch-Korbutowicz MAŁGORZATA (2015) Removal of fluoride ions by batch electrodialysis. Environ Prot Eng 41(1):67–81. https://doi.org/10.5277/epe150106
Mei L, Qiao H, Ke F et al (2020) One-step synthesis of zirconium dioxide-biochar derived from Camellia oleifera seed shell with enhanced removal capacity for fluoride from water. Appl Surf Sci 509:144685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144685
Mobarak M, Selim AQ, Mohamed EA, Seliem MK (2018) Modification of organic matter-rich clay by a solution of cationic surfactant/H2O2: a new product for fluoride adsorption from solutions. J Clean Prod 192:712–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.044
Mudzielwana R, Gitari MW, Akinyemi SA, Msagati TA (2018) Performance of Mn2+-modified bentonite clay for the removal of fluoride from aqueous solution. S Afr J Chem 71:15–23. https://doi.org/10.17159/0379-4350/2018/v71a2
Mukherjee I, Singh UK (2018) Groundwater fluoride contamination, probable release, and containment mechanisms: a review on Indian context. Environ Geochem Health 40(6):2259–2301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0096-x
Mukherjee I, Singh UK (2020) Fluoride abundance and their release mechanisms in ground water along with associated human health risks in a geologically heterogeneous semi-arid region of east India. Microchem J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104304
Mumtaz N, Pandey G, Labhasetwar PK (2015) Global fluoride occurrence, available technologies for fluoride removal and electrolytic defluoridation: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45(21):2357–2389. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1046768
Nabbou N, Belhachemi M, Boumelik M et al (2019) Removal of fluoride from groundwater using natural clay (kaolinite): optimization of adsorption conditions. C R Chim 22(2–3):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2018.09.010
Nagaraj A, Sadasivuni KK, Rajan M (2017) Investigation of lanthanum impregnated cellulose, derived from biomass, as an adsorbent for the removal of fluoride from drinking water. Carbohydr Polym 176:402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.089
Nagaraj A, Pillay K, Kumar SK, Rajan M (2020) Dicarboxylic acid cross-linked metal ion decorated bentonite clay and chitosan for fluoride removal studies. RSC Adv 10(28):16791–16803. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA00598C
Obijole OA, Gitari MW, Ndungu PG, Samie A (2019) Mechanochemically activated Aluminosilicate clay soils and their application for defluoridation and pathogen removal from groundwater. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(4):1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040654
Preethi J, Meenakshi S (2018) Fabrication of La3+ impregnated chitosan/β-cyclodextrin biopolymeric materials for effective utilization of chromate and fluoride adsorption in single systems. J Chem Eng Data 63(3):723–731. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.7b00889
Raghav S, Kumar D (2018) Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies of fluoride adsorbed by tetrametallic oxide adsorbent. J Chem Eng Data 63(5):1682–1697. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b00024
Saadi Z, Saadi R, Fazaeli R (2013) Fixed-bed adsorption dynamics of Pb (II) adsorption from aqueous solution using nanostructured γ-alumina. J Nanostructure Chem 3(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-8865-3-48
Saeed KAH, Kassim KA, Yunus NZM, Nur H (2013) Characterization of hydrated lime-stabilized brown kaolin clay. Int J Eng Res Technol 2(11):3722–3727
Saeed KAH, Kassim KA, Yunus NZM, Nur H (2015) Physico-chemical characterization of lime stabilized tropical kaolin clay. Jurnal Teknologi 72(3):83–90. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v72.4021
Sahu N, Bhan C, Singh J (2020a) Removal of fluoride from an aqueous solution by batch and column process using activated carbon derived from iron infused Pisum sativum peel: characterization, isotherm, kinetics study. Environ Eng Res 26(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.241
Sahu S, Mallik L, Pahi S et al (2020b) Facile synthesis of poly o-toluidine modified lanthanum phosphate nanocomposite as a superior adsorbent for selective fluoride removal: a mechanistic and kinetic study. Chemosphere 252:126551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126551
Saikia P, Bharali RK, Baruah HK (2017) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies for fluoride removal using a novel bio-adsorbent from possotia (Vitex negundo) leaf. J Anal Sci Technol 8(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-017-0132-y
Sengupta P, Saha S, Banerjee S, Dey A, Sarkar P (2020) Removal of fluoride ion from drinking water by a new Fe (OH)3/nano CaO impregnated chitosan composite adsorbent. Polym Plast Technol Mater 59(11):1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2020.1725567
Shen T, Gao M (2019) Gemini surfactant modified organo-clays for removal of organic pollutants from water: a review. Chem Eng J 375:121910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.121910
Singh J, Singh P, Singh A (2016) Fluoride ions vs removal technologies: a study. Arab J Chem 9(6):815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.06.005
Solanki YS, Agarwal M, Gupta S, Shukla P, Gupta AB (2019) Fluoride removal performance of a synthesized adsorbent. J Energy Environ Sustain 7:17–20
Uddin MK, Ahmed SS, Naushad M (2019) A mini update on fluoride adsorption from aqueous medium using clay materials. Desalin Water Treat 145:232–248. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23509
Waghmare SS, Arfin T (2015) Fluoride removal from water by various techniques. Int J Innov Sci Eng Technol 2(3):560–571
Wambu EW, Kurui AJ (2018) Fluoride adsorption onto soil adsorbents: the role of pH and other solution parameters. In: Oshunsanya S (ed) Soil pH for nutrient availability and crop performance. IntechOpen, London, pp 31–44. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.74652
Wendimu G, Zewge F, Mulugeta E (2017) Aluminium-iron-amended activated bamboo charcoal (AIAABC) for fluoride removal from aqueous solutions. J Water Process Eng 16:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.12.012
Yadav KK, Kumar S, Pham QB, Gupta N, Rezania S, Kamyab H, Talaiekhozani A (2019) Fluoride contamination, health problems and remediation methods in Asian groundwater: a comprehensive review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 182:109362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.045
Yang H, Wang Y, Bender J, Xu S (2019) Removal of arsenate and chromate by lanthanum-modified granular ceramic material: the critical role of coating temperature. Sci Rep 9(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44165-8
Zhang S, Lyu Y, Su X, Bian Y, Yu B, Zhang Y (2016) Removal of fluoride ion from groundwater by adsorption on lanthanum and aluminum loaded clay adsorbent. Environ Earth Sci 75(5):401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5205-x
Zhang RL, Xu J, Gao L, Wang Z, Wang B, Qin SY (2020) Performance and mechanism for fluoride removal in groundwater with calcium modified biochar from peanut shell. Sci Adv Mater 12(4):492–501. https://doi.org/10.1166/sam.2020.3620
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the Science and Engineering Research Board, India, Reference no. ECR/2016/001924 is gratefully acknowledged. This study was also supported by Kwangwoon University research grant-2021. We are thankful to Dr. Dhruv Sen Singh, Department of Geology, University of Lucknow for his help in the analysis of grain size of clay soil. One of us (C. Bhan) is highly thankful to the University Grant Commission (UGC), Government of India for providing UGC-NFSC Fellowship.
Funding
No funding received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation. JS: supervision. YCS: writing—reviewing and editing. JRK: reviewing, editing, and finalization.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no any competing interest.
Ethical approval
This manuscript does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Consent to publish
This article has the consent of all the authors and authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhan, C., Singh, J., Sharma, Y.C. et al. Synthesis of lanthanum-modified clay soil-based adsorbent for the fluoride removal from an aqueous solution and groundwater through batch and column process: mechanism and kinetics. Environ Earth Sci 81, 253 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10377-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10377-x