Abstract
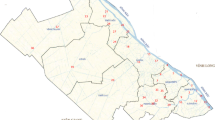
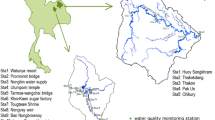
The evaluation and interpretation of the spatio-temporal pattern of surface water quality is crucial for the assessment, restoration and protection of drinking water sources. This case study reports different multivariate statistical techniques such as cluster analysis, factor analysis/principal component analysis (FA/PCA) and discriminant analysis, which had been applied for 6 years (2005–2010) water quality data set generated from 19 parameters at 14 different sites within the Fei-Tsui Reservoir basin. Hierarchical cluster analysis grouped 14 sampling sites into three clusters: high-, moderate- and low-pollution regions. This study revealed that water release from the dam outlet will further increase the concentrations of pollutants in the downstream river. PCA/FA did not result in considerable data reduction, as it points to 13 parameters (68 % of original 19) required to explain the 72.8 % of the total variance in the water quality data set. The varifactors obtained from PCA suggested that parameters responsible for water quality variation were mainly related to mineral-related parameters (natural), nutrient group (non-point sources pollution), physical parameters (natural) and organic pollutants (anthropogenic sources). Discriminant analysis used only five parameters: water temperature, dissolved oxygen (DO), calcium, total dissolved solids (TDS) and turbidity; and seven parameters: BOD, DO, nitrate nitrogen, TDS, total alkalinity, turbidity and WT, to discriminate between temporal and spatial with 88 and 90 % correct assignation, respectively. This study illustrated the usefulness of multivariate statistical techniques for designing the sampling and analytical protocol, analysis and interpretation of complex data sets, identification of pollution sources/factors, and provides a reliable guideline for selecting the priorities of possible controlling measures in the sustainable management of Fei-Tsui Reservoir basin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbulut NE, Bayari S, Akbulut A, Sahin Y (2009) Rivers of Turkey. In: Tockner K, Robinson CT, Uehlinger U (eds) Rivers of Europa. Academic Press, New York, pp 643–672
Akin BS, Atici T, Katircioglu H, Keskin F (2011) Investigation of water quality on Gokcekaya dam lake using multivariate statistical analysis, in Eskisehir, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 63(6):1251–1261
APHA (1985) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, D. C., p 1268
Bengraine K, Marthaba TF (2003) Using Principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. J Hazard Mater B100:179–195
Beutel MW (2006) Inhibition of ammonia release from anoxic profundal sediments in lakes using hypolimnetic oxygenation. Ecol Eng 28:271–279
Chung SW, Ko IH, Kim YK (2008) Effect of reservoir flushing on downstream river water quality. J Environ Manage 86(1):139–147
Guo H, Wang Y (2004) Hydro geochemical processes in shallow quaternary aquifers from the northern part of the Datong Basin, China. Appl Geochem 19:19–27
Huang F, Wang XQ, Lou LP, Zhou ZQ, Wu JP (2010) Spatial variation and source apportionment of water pollution in Qiantang River (China) using statistical techniques. Water Res 44:1562–1572
Hussain M, Ahmed SM, Abder rahman W (2008) Cluster analysis and quality assessment of logged water at an irrigation project, eastern Saudi Arabia. J Environ Manage 86:279–307
Jarvie HP, Whitton BA, Neal C (1998) Nitrogen and phosphorus in east-coast British rivers: speciation, sources and biological significance. Sci Total Environ 210(211):79–109
Koklu R, Sengorur B, Topal B (2010) Water quality assessment using multivariate statistical methods—a case study: Melen River system (Turkey). Water Resour Manag 24:959–978
Kowalkowski T, Zbytniewski R, Szpejna J, Buszewski B (2006) Application of chemometrics in river water classification. Water Res 40:744–752
Krishna AK, Satyanarayanan M, Govil PK (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: a case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Hazard Mater 167:366–373
Kumarasamy P, James RA, Dahms H-U, Buyon CW, Ramesh R (2013) Multivariate water quality assessment from the Tamiraparani river basin. Environ Earth Sci, South India. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2644-0
Li S, Zhang QF (2010) Spatial characterization of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the upper Han River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 176:579–588
Liu CW, Lin KH, Kuo YM (2003) Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 313:77–89
McKenna JE Jr (2003) An enhanced cluster analysis program with bootstrap significance testing for ecological community analysis. Environ Model Softw 18(3):205–220
Najar IA, Khan AB (2012) Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of three lakes in Kashmir, India, using multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 66(8):2367–2378
Noh J, Kim JC, Park J (2014) Turbidity control in downstream of the reservoir: the Nakdong River in Korea. Environ Earth Sci 71(4):1871–1880
Noori R, Sabahi MS, Karbassi AR, Baghvand A, Taati Zadeh H (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of surface water quality based on correlations and variations in the data sets. Desalination 260:129–136
Ouyang Y, Nkedi-kizza P, Wu QT, Shinde D, Huang CH (2006) Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality. Water Res 40:3800–3810
Parizi HS, Samani N (2013) Geochemical evolution and quality assessment of water resources in the Sarcheshmeh copper mine area (Iran) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ Earth Sci 69(5):1699–1718
Peter DH, Castella E, Slaveykova VI (2014). Effects of a reservoir flushing on trace metal partitioning, speciation and benthic invertebrates in the floodplain. Environ Sci Proces Impacts 16(12):2692–2702
Qadir A, Malik RN, Husain SZ (2007) Spatio–temporal variations in water quality of Nullah Aik-tributary of the river Chenab, Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 140:43–59
Razmkhah H, Abrishamchi A, Torkian A (2010) Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality by pattern recognition techniques: a case study on Jajrood River (Tehran, Iran). J Environ Manage 91:852–860
Sarbu C, Pop HF (2005) Principal component analysis versus fuzzy principal component analysis. A case study: the quality of Danube water (1985–1996). Talanta 65:1215–1220
Shrestha S, Kazama F (2007) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ Model Softw 22:464–475
Simeonov V, Stratis JA, Samara C, Zachariadis G, Voutsa D, Anthemidis A, Sofoniou M, Kouimtzis T (2003) Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Res 37:4119–4124
Singh KP, Malik A, Mohan D, Sinha S (2004) Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India): a case study. Water Res 38:3980–3992
Su S, Zhi J, Lou L, Huang F, Chen X, Wua J (2011) Spatio-temporal patterns and source apportionment of pollution in Qiantang River (China) using neural-based modeling and multivariate statistical techniques. Phys Chem Earth 36:379–386
Varol M, Sen B (2009) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Behrimaz Stream, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 159:543–553
Varol M, Gokot B, Bekleyen A, Sen B (2012) Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Catena 92:11–21
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrado E, Deban L (1998) Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 32:3581–3592
Wang X, Cai Q, Ye L, Qu X (2012) Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in stream water quality by multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the **angxi River basin, China. Quat Int 282:137–144
Wu B, Zhao DY, Zhang Y, Zhang XX, Cheng S (2009) Multivariate statistical study of organic organic pollutants in Nan**g reaches of Yangtze River. J Hazard Mater 169:1093–1098
Wunderlin DA, Diaz MP, Ame MV, Pesce SF, Hued AC, Bistoni MA (2001) Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Suquia river basin (Cordoba, Argentina). Water Res 35:2881–2894
Ye L, Cai Q, Liu R, Cao M (2009) The influence of topography and land use on water quality of **angxi River in three Gorges Reservoir region. Environ Geol 58(5):937–942
Zhang Y, Guo F, Meng W, Wang XQ (2009) Water quality assessment and source identification of Daliao river basin using multivariate statistical methods. Environ Monit Assess 152:105–121
Zhao J, Fu G, Lei K, Li Y (2011) Multivariate analysis of surface water quality in the Three Gorges area of China and implications for water management. J Environ Sci 23(9):1460–1471
Zhou F, Huang GH, Guo HC, Zhang W, Hao ZJ (2007) Spatio-temporal patterns and source apportionment of coastal water pollution in eastern Hong Kong. Water Res 41:3429–3439
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Taipei Fei-Tsui Reservoir Administration Office for providing the valuable water quality data sets. We sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for giving comments and suggestions which improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chow, M.F., Shiah, F.K., Lai, C.C. et al. Evaluation of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Fei-Tsui Reservoir basin, Taiwan. Environ Earth Sci 75, 6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4922-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4922-5