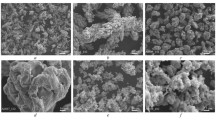
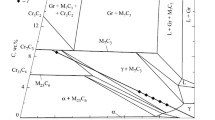
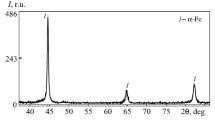
Abstract
Silicon carbide can be used as a source of alloying silicon and carbon elements for making sintered composites. The addition of 4 wt.% silicon carbide to iron or iron-based powders can lead to the formation of ductile iron microstructures in sintered composites, whose matrices can be furthered modified by chemistry manipulation. In this work, copper and nickel powders, as austenite stabilizing alloying elements, were added to sintered Fe-0.85Mo + 4.0 wt.% silicon carbide composite to produce different ductile iron microstructures with different ausferrite features. The reference sintered composite was produced from powder mixture of Fe-0.85Mo + 4.0 wt.% silicon carbide and 4.0 wt.% copper powders. The nickel additions (0.5, 1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 wt.%) to the reference sintered composite led to the decrease of black particle count, the decrease of ferrite halo thickness, the reduction of ausferrite component thickness, and the increase of martensite fraction. This indicates that Ni promotes the reduction of ausferrite component thickness and the martensite transformation. The presence of martensite reduced tensile strength and elongation values. Macrohardness values of sintered nickel-added composites showed less sensitivity to microstructural changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Backhaus-Ricoult M (1990) Interfaces between SiC and metals. Le Journal de Physique Colloques 51:C1-769–C761-774
Schiepers R, Van Beek J, Van Loo F, De With G (1993) The interaction between SiC and Ni, Fe,(Fe, Ni) and steel: morphology and kinetics. J Eur Ceram Soc 11:211–218
Pelleg J (1999) Reactions in the matrix and interface of the Fe-SiC metal matrix composite system. Mater Sci Eng A 269:225–241
Tongsri R, Vetayanugul B (2010) Thermal analysis of Fe-Carbide and Fe-C mixtures. J Met Mater Miner 20
Klein AN, Furlan KP, Schroeder RM, Hammes G, Binder C, Neto JBR, Probst SH, de Mello JDB (2015) Thermodynamic aspects during the processing of sintered materials. Powder Technol 271:193–203
Tang W, Zheng Z, Ding H, ** Z (2003) Control of the interface reaction between silicon carbide and iron. Mater Chem Phys 80:360–365
Binder C, Bendo T, Pereira R, Hammes G, De Mello J, Klein A (2016) Influence of the SiC content and sintering temperature on the microstructure, mechanical properties and friction behaviour of sintered self-lubricating composites. Powder Metall 59:384–393
De Mello JDB, Binder C, Hammes G, Binder R, Klein AN (2017) Tribological behaviour of sintered iron based self-lubricating composites. Friction 5:285–307
Chakthin S, Poolthong N, Tongsri R (2008) Effect of reaction between Fe and carbide particles on mechanical properties of Fe-base composite. Adv Mater Res, Trans Tech Publ 55-57:357–360
Ruangchai K, Wiengmoon A, Morakot**da M, Krataitong R, Tanprayoon D, Yotkaew T, Tosangthum N, Patakham U, Tongsri R (2017) Microstructure, hardness and wear properties of sintered Fe-Mo-Si-C steels with spheroidal graphite iron/compacted graphite iron-like. Key Eng Mater, Trans Tech Publ 751:47–52
Ruangchai K, Wiengmoon A, Morakot**da M, Tosangthum N, Tongsri R (2018) Sintered Fe-Mo-Si-C alloys with ductile cast iron microstructure. J Phys Conf Ser, IOP Publishing 1144:012099
Nithimethakul T, Karin P, Ohtake N, Wila P, Yodkaew T, Vetayanugul B, Morakot**da M, Tongsri R (2021) The effect of molybdenum on the microstructure and mechanical behaviour of the sintered Fe-Mo-Mn-Si-C composite, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing, pp. 012028
Ruangchai K, Wiengmoon A, Krataitong R, Yotkaew T, Tosangthum N, Tongsri R (2018) Pearlitic ductile iron-like sintered Fe-Cr-Mo-Si-C alloys. J Phys Conf Ser, IOP Publishing 1144:012147
Soe A, Wila P, Morakot**da M, Yotkaew T, Karin P, Ohtake N, Tongsri R (2021) Sintered Fe-Cr-Mo-Si-C alloys produced from pre-alloyed Fe-Cr based powders admixed with 4% SiC for high performance applications, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing, pp. 012027
Kaewkam T, Kansuwan P, Ohtake N, Wila P, Krataithong R, Tosangthum N, Yotkaew T, Tongsri R (2021) Sintered Fe-Ni-Si-C alloys, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing, pp. 012035
Morakot**da M, Ruangchai K, Vetayanugul B, Krataitong R, Tosangthum N, Wiengmoon A, Tongsri R (2021) Phase transformation and mechanical properties of sintered Fe-Mo-Si-C-(Cu) alloys, IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing, pp. 012037
Morakot**da M, Fakpan K, Yotkaew T, Tosangthum N, Krataithong R, Daraphan A, Siriphol P, Wila P, Vetayanugul B, Tongsri R (2010) Gas atomization of low melting-point metal powders. Chiang Mai J Sci 37:55–63
De AK, Speer JG, Matlock DK (2003) Color tint-etching for multiphase steels. Adv Mater Process 161:27–31
Stefanescu DM, Alonso G, Larrañaga P, Suarez R (2016) On the stable eutectic solidification of iron carbon silicon alloys. Acta Mater 103:103–114
Srijampan W, Wiengmoon A, Morakot**da M, Krataitong R, Yotkaew T, Tosangthum N, Tongsri R (2015) Microstructure and mechanical property of sintered Fe-Cr-Mo steels due to phase transformations with fast cooling rates. Mater Des 88:693–701
Zhou H, Li Y, Yin Z, Ran M, Liu S, Huang Y, Zhang W, Zheng W, Liu J (2020) Microstructure and mechanical behaviors of grinding balls produced by dual matrix structure two-step austempering process. J Mater Res Technol 9:4672–4681
Gorny M, Gondek Ł, Tyrała E, Angella G, Kawalec M (2021) Structure homogeneity and thermal stability of austempered ductile iron. Metall Mater Trans A 52:2227–2237
Basso A, Caldera M, Chapetti M, Sikora J (2010) Mechanical characterization of dual phase austempered ductile iron. ISIJ Int 50:302–306
Ovali I, Kilicli V, Erdogan M (2013) Effect of microstructure on fatigue strength of intercritically austenitized and austempered ductile irons with dual matrix structures. ISIJ Int 53:375–381
Basso A, Caldera M, Massone J (2015) Development of high silicon dual phase austempered ductile iron. ISIJ Int 55:1106–1113
Colombo DA, Dommarco RC, Basso AD (2019) Rolling contact fatigue behavior of dual-phase austempered ductile iron. Wear 418:208–214
Daber S, Prasad Rao P (2008) Formation of strain-induced martensite in austempered ductile iron. J Mater Sci 43:357–367
Lacaze J, Larrañaga P, Asenjo I, Suarez R, Sertucha J (2012) Influence of 1 wt-% addition of Ni on structural and mechanical properties of ferritic ductile irons. Mater Sci Technol 28:603–608
Colin-García E, Cruz-Ramírez A, Reyes-Castellanos G, Romero-Serrano J, Sánchez-Alvarado R, Hernández-Chávez M (2019) Influence of nickel addition and casting modulus on the properties of hypo-eutectic ductile cast iron. J Min Metall, B: Metall 55:283–293
Martinez V, Ordonez S, Castro F, Olivares L, Marín J (2003) Wetting of silicon carbide by copper alloys. J Mater Sci 38:4047–4054
Schubert T, Brendel A, Schmid K, Koeck T, Zieliński W, Weißgärber T, Kieback B (2007) Interfacial design of Cu/SiC composites prepared by powder metallurgy for heat sink applications. Compos A: Appl Sci Manuf 38:2398–2403
Turchanin M, Agraval P, Abdulov A (2007) Phase equilibria and thermodynamics of binary copper systems with 3d-metals. VI. Copper-nickel system. Powder Metall Met Ceram 46:467–477
Ohno R (1986) Rates of dissolution of solid iron, cobalt, nickel, and silicon in liquid copper and diffusion rate of iron from liquid Cu-Fe alloy into liquid copper. Metall Trans B 17:291–305
Altenberger I, Kuhn H-A, Gholami M, Mhaede M, Wagner L (2015) Ultrafine-grained precipitation hardened copper alloys by swaging or accumulative roll bonding. Metals 5:763–776
Lacaze J, Sertucha J, Åberg LM (2016) Microstructure of as-cast ferritic-pearlitic nodular cast irons. ISIJ Int 56:1606–1615
Putatunda SK (2003) Influence of austempering temperature on microstructure and fracture toughness of a high-carbon, high-silicon and high-manganese cast steel. Mater Des 24:435–443
Sckudlarek W, Krmasha MN, Al-Rubaie KS, Preti O, Milan JC, da Costa CE (2021) Effect of austempering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of ductile cast iron modified by niobium. J Mater Res Technol 12:2414–2425
Bendikiene R, Ciuplys A, Cesnavicius R, Jutas A, Bahdanovich A, Marmysh D, Nasan A, Shemet L, Sherbakov S (2021) Influence of austempering temperatures on the microstructure and mechanical properties of austempered ductile cast iron. Metals 11:967
Saal P, Meier L, Li X, Hofmann M, Hoelzel M, Wagner JN, Volk W (2016) In situ study of the influence of nickel on the phase transformation kinetics in austempered ductile iron. Metall Mater Trans A 47:661–671
Maweja K, Stumpf W, van der Berg N (2009) Characteristics of martensite as a function of the Ms temperature in low-carbon armour steel plates. Mater Sci Eng A 519:121–127
Liu C, Zhao Z, Northwood DO, Liu Y (2001) A new empirical formula for the calculation of MS temperatures in pure iron and super-low carbon alloy steels. J Mater Process Technol 113:556–562
Capdevila C, Caballero FG, De Andrés CG (2002) Determination of Ms temperature in steels: A Bayesian neural network model. ISIJ Int 42:894–902
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported via the project ‘Design and manufacturing of replacement parts for railway applications (P1951261)’ under NSTDA, Pathum Thani, Thailand. Technical supports are obtained from National Metal and Materials Technology Center (MTEC), Pathum Thani, Thailand.
Funding
The authors receive financial support from NSTDA, Thailand for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Monnapas Morakot**da, Panadda Kongmun, Arisara Wanalerkngam, Nattaya Tosangthum, Thanyaporn Yotkaew and Suphakan Kijamnajsuk. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ruangdaj Tongsri and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
“Not applicable”.
Consent for Publication
“Not applicable”.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Morakot**da, M., Kongmun, P., Wanalerkngam, A. et al. Sintered Fe-Mo-Cu-Ni-Si-C Composites Produced by SiC, Nickel, and Copper Additions to Fe-Mo Powder. Silicon 15, 7995–8008 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02641-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02641-x