Abstract
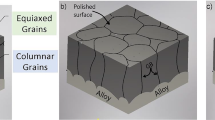
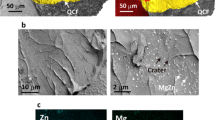
The cyclic oxidation behavior of Hf/Y-doped B2 FeAl intermetallics at 1373 K was investigated. For an undoped FeAl alloy, premature spallation of the alumina film occurs due to the formation of numerous voids at the film/alloy interface and apparent shrinkage in the film. In contrast to this, do** with either Hf or Y significantly improves the interfacial adhesion between the alumina film and the alloy substrate, particularly with Hf-do**. Microstructural observation in combination with Auger electron spectroscopic analysis suggests that in addition to prohibiting interfacial void formation and alleviating film shrinkage, the addition of Hf in the FeAl alloy could consolidate the film/alloy interface by directly participating in chemical bonding across the interface as a Hf ion. This causes the spallation of alumina film from the equiaxed grains/columnar grains interface rather than the bottom of the film.
Graphic abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viguier B, Martinez M, Lacaze J. Characterization of complex planar faults in FeAl(B) alloys. Intermetallics. 2017;83:64.
Ruan Y, Yan N, Zhu HZ, Zhou K, Wei B. Thermal performance determination of binary Fe-Al alloys at elevated temperatures. J Alloys Compd. 2017;701:676.
Zhang ZX, Li XY, Dong HS. Plasma-nitriding and characterization of FeAl40 iron aluminide. Acta Mater. 2015;86:341.
Airiskallio E, Nurmi E, Heinonen MH, Väyrynen IJ, Kokko K, Ropo M, Punkkinen MPJ, Pitkänen H, Alatalo M, Kollár J, Johansson B, Vitos L. High temperature oxidation of Fe–Al and Fe–Cr–Al alloys: the role of Cr as a chemically active element. Corros Sci. 2010;52:3394.
Li DQ, Zhou LX, Zhu KJ, Gu J, Zheng SH. Isothermal oxidation behavior of scandium and yttrium co-doped B2-type iron–aluminum intermetallics at elevated temperature. Rare Met. 2018;37(8):690.
Brito P, Pinto H, Kostka A. The crystallographic template effect assisting the formation of stable α-Al2O3 during low temperature oxidation of Fe–Al alloys. Corros Sci. 2016;105:100.
Nowak K, Kupka M, Maszybrocka J, Barylski A. Effect of thermal oxidation process on wear resistance of B2 iron aluminide. Vacuum. 2015;114:221.
Lang FQ, Yu ZM, Gedevanishvili S, Deevi SC, Narita T. Cyclic oxidation behavior of Fe-40Al sheet. Intermetallics. 2004;12:451.
Zhang Y, Pint BA, Garner GW, Cooley KM, Haynes JA. Effect of cycle length on the oxidation performance of iron aluminide coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 2004;188–189:35.
DeVan JH, Tortorelli PF. The oxidation–sulfidation behavior of iron alloys containing 16–40 at% aluminum. Corros Sci. 1993;35:1065.
Hou PY, Moskito J. Sulfur segregation to Al2O3–FeAl interfaces studied by field emission-Auger electron spectroscopy. Oxid Met. 2003;59(5):559.
Xu CH, Gao W, He YD. High temperature oxidation behaviour of FeAl intermetallics–oxide scales formed in ambient atmosphere. Scr Mater. 2000;42(10):975.
He YS, Hu R, Luo WZ, He T, Liu XH. Oxidation behavior of a novel multi-element alloyed Ti2AlNb-based alloy in temperature range of 650–850 °C. Rare Met. 2018;37(10):838.
Han T, Xu XJ, Ge XL, Zhong YY, Liu QH, Chen TZ. High temperature oxidation behavior of Ti–8Si–1.4Zr–xY2O3 alloy. Chin J Rare Met. 2018;42(2):130.
Xu CH, Gao W, Li S. Oxidation behaviour of FeAl intermetallics–the effect of Y on the scale spallation resistance. Corros Sci. 2001;43:671.
Li DQ, Lin DL, Xu Y. Oxidation behavior of FeAl alloys with and without titanium. J Mater Sci. 2001;36(4):979.
Montealegre MA, Gonzalez-Carrasco JL. Influence of the yttria content on the oxidation behaviour of the intermetallic Fe40Al alloy. Intermetallics. 2003;11:169.
Liu ZY, Gao W, Wang FH. Oxidation resistance of magnetron sputter deposited beta-FeAl + Zr coatings. High Temp Mater Process. 2000;19(6):419.
Pint BA. Progress in understanding the reactive element effect since the Whittle and Stringer literature review. In: Proceedings of John Stringer Symposium on High Temperature Corrosion. Novelty, Ohio, USA: ASM International; 2003, 9.
Whittle DP, Stringer J. Improvements in high temperature oxidation resistance by additions of reactive elements or oxide dispersions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A. 1980;295:309.
Gesmundo F, Hou PY. Analysis of pore formation at oxide-alloy Interfaces–II: theoretical treatment of vacancy condensation for immobile interfaces. Oxid Metals. 2003;59(1):63.
Christensen RJ, Tolpygo VK, Clarke DR. The influence of the reactive element yttrium on the stress in alumina scales formed by oxidation. Acta Mater. 1997;45(4):1761.
Xu CH, Gao W. Oxidation behaviour of FeAl intermetallics: effects of reactive elements on cyclic oxidation properties. Mater Sci Technol. 2001;17(3):324.
Xu CH, Gao W, Gong H. Oxidation behaviour of FeAl intermetallics. The effects of Y and/or Zr on isothermal oxidation kinetics. Intermetallics. 2000;8:769.
Liu T, Wang CX, Shen HL, Chou WS, Iwata NY, Kimura A. The effects of Cr and Al concentrations on the oxidation behavior of oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic alloys. Corros Sci. 2013;76:310.
Pint BA, More KL, Wright IG. The use of two reactive elements to optimize oxidation performance of alumina-forming alloys. Mater High Temp. 2003;20(3):375.
Sato A, Chiu YL, Reed RC. Oxidation of nickel-based single-crystal superalloys for industrial gas turbine applications. Acta Mater. 2011;59:225.
Prajitno D, Gleeson B, Young DJ. The cyclic oxidation behaviour of α-Cr + β-NiAl alloys with and without trace Zr addition. Corros Sci. 1997;39(4):639.
Tan X, Peng X, Wang F. The effect of grain refinement on the adhesion of an alumina scale on an aluminide coating. Corros Sci. 2014;85:280.
Douglass DL, Kuenzly JD. Oxidation mechanism of Ni3Al containing yttrium. Oxid Metals. 1974;8(3):139.
Pint BA, Martin JR, Hobbs LW. 18O/SIMS characterization of the growth mechanism of doped and undoped α-Al2O3. Oxid Metals. 1993;39(3/4):167.
Pint BA, Alexander KB. Grain boundary segregation of cation dopants in α-Al2O3 scales. J Electrochem Soc. 1998;145(6):1819.
Pint BA. Experimental observations in support of the dynamic-segregation theory to explain the reactive-element effect. Oxid Metals. 1996;45(1/2):1.
Li DQ, Guo HB, Wang D, Zhang T, Gong SK, Xu HB. Cyclic oxidation of β-NiAl with various reactive element dopants at 1200 °C. Corros Sci. 2013;66:125.
Hou PY, Niu Y, Van Lienden C. Analysis of pore formation at oxide-alloy interfaces–I: experimental results on FeAl. Oxid Metals. 2003;59(1):41.
Guo HB, Li DQ, Peng H, Cui YJ, Gong SK. High-temperature oxidation and hot-corrosion behaviour of EB-PVD β-NiAlDy coatings. Corros Sci. 2011;53:1050.
Zheng YB, Wang F, Ai TT, Li C. Structural, elastic and electronic properties of B2-type modified by ternary additions FeAl-based intermetallics: first-principles study. J Alloys Compd. 2017;710:581.
Pint BA, Schneibel JH. The effect of carbon and reactive element dopants on oxidation lifetime of FeAl. Scr Mater. 2005;52:1199.
Pint BA, More KL, Tortorelli PF. Optimizing the imperfect oxidation performance of iron aluminides. Mater Sci Forum. 2001;369–372(1):411.
Carling KM, Carter EA. Effects of segregating elements on the adhesive strength and structure of the α-Al2O3/β-NiAl interface. Acta Mater. 2007;55:2791.
Guo HB, Zhang T, Wang SX, Gong SK. Effect of Dy on oxide scale adhesion of NiAl coatings at 1200 °C. Corros Sci. 2011;53:2228.
Heuer AH, Hovis DB, Smialek JL, Gleeson B. Alumina scale formation: a new perspective. J Am Ceram Soc. 2011;94(S1):146.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Basic Research Program of State Grid (No. GCB17201600179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, DQ., Zhou, LX., Zhang, J. et al. Enhanced alumina film adhesion of Hf/Y-doped iron–aluminum alloys during high-temperature oxidation: a new observation. Rare Met. 38, 877–884 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01308-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01308-0