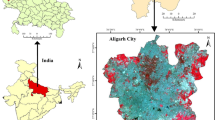
Abstract
Urbanization is a global phenomenon. However, it has been rapid in the develo** world since the late twentieth century. This anthropogenic process is largely responsible for modifying earth’s surface, causing substantial transformations in land use land cover (LULC) and resulting in considerable changes in land surface temperature (LST) and increasing intensity of urban heat islands (UHIs). Aligarh city in Uttar Pradesh is also observing rapid urbanization since the last few decades due to its proximity to the national capital, i.e. (Delhi), and thus experiencing a notable shift in land use land cover and LST. Using Landsat TM and OLI data for the years 2000, 2010 and 2019, this article attempts to assess modifications in land use and land cover and also how they influence land surface temperature in the present study. The results indicate that among all the LULC classes, area under the built-up class has increased dramatically over the span of nineteen years from 1900.8 ha in 2000 to 2680.11 ha in 2019. However, all other classes except vegetation, i.e. open land, agriculture and water bodies, have recorded a reduction in their area by − 9.99%, − 7.17% and − 0.5%, respectively, from 2000 to 2019. LST is extracted for the month of May and December during the same time period and depicts that the maximum temperature for both months is reported around the built-up area and open land. UHIs are also created which reveal a close relationship with LULC and LST. Various statistical techniques like correlation, regression and scatter plots are utilized to show the relationship of each LULC with LST and UHIs and also with three spatial indices, i.e. NDBI, NDVI and NDWI.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abebe, G., Getachew, D., & Ewunetu, A. (2021). Analysing land use/land cover changes and its dynamics using remote sensing and GIS in Gubalafto district, Northeastern Ethiopia. SN Applied Sciences, 4(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04915-8.
Adinna, E., Christian, E. I., & Okolie, A. T. (2009). Assessment of urban heat island and possible adaptations in Enugu urban using landsat-ETM. Journal of Geography and Regional Planning, 2(2), 030–036. http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/oa/wmo/ccl/rural-urban.pdf.
Alawamy, J. S., Balasundram, S. K., Mohd. Hanif, A. H., & Boon Sung, C. T. (2020). Detecting and analyzing land use and land cover changes in the region of Al-Jabal Al-Akhdar, Libya using time-series Landsat data from 1985 to 2017. Sustainability, 12(11), 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114490.
Ali, R. R., & Shalaby, A. (2012). Response of topsoil features to the seasonal changes of land surface temperature in the arid environment. International Journal of Soil Science, 7(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijss.2012.39.50.
Amare, S. (2013). Retrospective analysis of land cover and Use dynamics in Gilgel Abbay watershed by using GIS and remote sensing techniques, North Western Ethiopia. International Journal of Geoscience, 4, 1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2013.47093.
Anderson, J. R., Hardy, E. E., Roach, J. T., & Witmer, R. E. (1976). A land use and land cover classification system for use with remote sensor data. US Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 964, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.3133/pp964.
Annarita, F. (2016). The framework of Urban Built-up Environment. Towards nearly zero energy. Urban Settings in the Mediterranean Climate, 1–63.
Bewket, W., & Teferi, E. (2009). Assessment of soil erosion hazard and prioritization for treatment at the watershed level: Case study in the Chemoga watershed, Blue Nile basin. Ethiopia Land Degradation, 20, 609–622.
Bhagat, R. B. (2011). Emerging pattern of urbanization in India. Economic and Political Weekly, 46(34), 10–12.
Bharath, H. A., Nimish, G., & Lalitha, A. (2020). Exploring temperature indices by deriving relationship between land surface temperature and urban landscape. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 18, 100299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100299.
Brown, D. G., Pijanowski, B. C., & Duh, J. D. (2000). Modeling the relation- ships between land use and land cover on private lands in the Upper Midwest, USA. Journal of Environ Management, 59(4), 247–263. https://doi.org/10.1006/jema.2000.0369.
Buyadi, S. N. A., Mohd, W. M. N. W., & Misni, A. (2013). Impact of land use changes on the surface temperature distribution of area surrounding the National Botanic Garden Shah Alam. Procedia Soc. Behavioral Science, 101, 516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.07.225.
Census of India. (2011). censusindia.gov.in.
Chakraborty, S. D., Kant, Y., & Bharath, B. D. (2014). Study of land surface temperature in Delhi City to managing the thermal effect on urban developments. International journal of advanced scientific and technical research Issue, 4(1), 439–450. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1803_42414258.
Chang, Y., Hou, K., Li, X., Zhang, Y., & Chen, P. (2018). Review of Land use and land cover change research progress. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 113(1), 012087. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/113/1/012087.
Chaudhuri, G., & Mishra, N. (2016). Spatio-temporal dynamics of land cover and land surface temperature in Ganges-Brahmaputra delta: A comparative analysis between India and Bangladesh. Applied Geography, 68, 68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2016.01.002.
Chen, X. L., Zhao, H. M., Li, P. X., & Yin, Z. Y. (2010). Remote sensing image-based analysis of the relationship between urban heat island and land use land cover changes. Remote Sensing of Environment, 104(2), 133–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2005.11.016.
Choudhury, D., Das, K., & Das, A. (2019). Assessment of land use land cover changes and its impact on variations of land surface temperature in Asansol–Durgapur development region. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 22(4), 203–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2018.05.004.
Coates et al. (2014). Reasons to adapt Urban Heat in Netherlands. Urban Climate. 1–25.
Cohen, J. (1960). A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20(1), 37–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316446002000104.
Connors, J. P., Galletti, C. S., & Chow, W. T. L. (2013). Landscape configuration and urban heat island effects: Assessing the relationship between landscape characteristics and land surface temperature in Phoenix Arizona. Landscape Ecology, 28, 271–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-012-9833-1.
Coutts, A., Beringer, J., & Tapper, N. (2010). Changing urban climate and CO2 emissions: Implications for the development of policies for sustainable cities. Urban Policy and Research, 28(1), 27–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/08111140903437716.
Das, T., Jana, A., Mandal, B., & Sutradhar, A. (2021). Spatio-temporal pattern of land use and land cover and its effects on land surface temperature using remote sensing and GIS techniques: A case study of Bhubaneswar city, Eastern India (1991–2021). GeoJournal, 87(Suppl 4), 765–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-021-10541-z.
Demissie, F., Yeshitila, K., Kindu, M., & Schneider, T. (2017). Land use/ land cover changes and their causes in Libokemkem district of south Gonder, Ethiopia. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 8, 224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2017.10.001
Dewan, A. M., & Yamaguchi, Y. (2009). Using remote sensing and GIS to detect and monitor land use and land cover change in Dhaka metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960–2005. Environment Monitoring Assessment, 150(1), 237–249.
Dimyati, M. U., Mizuno, K., Kobayashi, S., & Kitamura, T. (1996). Analysis of land use/cover change in Indonesia. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(5), 931–944. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169608949056.
Ding, H., & Shi, W. (2013). Land use/land cover and its influence on surface temperature: A case study in Bei**g City. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 34(15), 5503–5517.
Erener, A., Düzgün, S., & Yalciner, A. C. (2012). Evaluating land use/cover change with temporal satellite data and information systems. Proceed Technology, 1, 385–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2012.02.079.
Estoque, R. C., Murayama, Y., & Myint, S. W. (2017). Effects of landscape composition and pattern on land surface temperature: An urban heat island study in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Science of the Total Environment, 577, 347–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.19.
Ewunetu, A., Simane, B., & Teferi, E. (2021). Map** and quantifying comprehensive land degradation status using spatial multicriteria evaluation technique in the headwaters area of upper Blue Nile River. Sustainability, 13(4), 2244. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042244.
Fall, S., Niyogi, D., Gluhovsky, A., Pielke, R. A., Kalnay, E., & Rochon, G. (2010). Impacts of land use land cover on temperature trends over the continental United States: Assessment using the North American regional reanalysis. International Journal of Climatology, 30(13), 1980–1993. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1996.
Fehrenbach, et al. (2001). Urban climate under change - A national research programme for develo** a building-resolving atmospheric model for entire city regions. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 28(2), 95-104.
Foley, J. A., DeFries, R., Asner, G. P., Barford, C., Bonan, G., Carpenter, S. R., Chapin, F. S., Coe, M. T., Daily, G. C., Gibbs, H. K., & Helkowski, J. H. (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science, 309(5734), 570–574.
Foody, G. M. (2002). Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sensing Environment, 80(1), 185–201.
Fu, P., & Weng, Q. (2016). A time series analysis of urbanization induced land use and land cover change and its impact on land surface temperature with landsat imagery. Remote Sensing Environment, 175, 205–214.
Gao, Z., Hou, Y., & Chen, W. (2019). Enhanced sensitivity of the urban heat island effect to summer temperatures induced by urban expansion. Environment Research Letters, 14, 094005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab2740
Gondwe, J. F., Li, S., & Munthali, R. M. (2021). Analysis of land use and land cover changes in urban areas using remote sensing: Case of Blantyre city. Hindawi, 2021, 1–17.
Gupta, R. (2014). The pattern of urban land-use changes: A case study of the Indian cities. Environment and Urbanization Asia, 5, 83–104.
Harlan, S. L., Brazel, A. J., Jenerette, G. D., Jones, N. S., Larsen, L., & Prashad, L. (2006). In the shade of affluence: The inequitable distribution of the Urban Heat Island. Research in Social Problems and Public Policy, 15, 173–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0196-1152(07)15005-5.
Hasanlou, M., & Mostofi, N. (2015). Investigating urban heat island estimation and relation between various land cover indices in Tehran city using Landsat 8 imagery. Proceedings of the 1st International Electronic Conference on Remote Sensing, Basel, Switzerland, 22, 1–11.
Hassid, et al. (2000). The effect of the Athens heat island on air conditioning load. Energy and Buildings, 32(2), 131–141.
Hassan, T., Zhang, J., Prodhan, F. A., Pangali Sharma, T. P., & Bashir, B. (2021). Surface urban heat islands dynamics in response to LULC and vegetation across South Asia (2000–2019). Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163177.
Heaviside, C., Macintyre, H., & Vardoulakis, S. (2017). The urban heat island: Implications for health in a changing environment. Current Environmental Health Reports, 4, 296–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-017-0150-3.
Heilig, G. K. (2012). World urbanization prospects: The 2011 revision. United Nations, department of economics and social affairs (DESA), population division, population estimates and projections section, New York.
Herold, M., Scepan, J., & Clarke, K. C. (2002). The use of remote sensing and landscape metrics to describe structures and changes in urban land uses. Environment and Planning A, 34(8), 1443–1458. https://doi.org/10.1068/a3496.
Hussain, A., Bhalla, P., & Palria, S. (2014). Remote sensing based analysis of the role of land use/land cover on surface temperature and temporal changes in temperature; A case study of Ajmer District, Rajasthan. International Archives of Photogrammetry Remote Sensing Spatial Information Science, 8, 1447–1454.
Ibrahim, G. R. (2017). Urban land use land cover changes and their effect on land surface temperature: Case study using Dohuk city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. Climate, 5(1), 13.
Jat, M. K., Garg, P. K., & Khare, D. (2008). Modelling of urban growth using spatial analysis techniques: A case study of Ajmer city (India). International Journal Remote SensIng, 29(2), 543–567. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160701280983.
Ji, W., Ma, J., Twibell, R. W., & Underhill, K. (2006). Characterizing urban sprawl using multi-stage remote sensing images and landscape metrics. Computer Environment Urban System, 30(6), 861–879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2005.09.002.
Kafy, A. A., Dey, N. N., Al Rakib, A., Rahaman, Z. A., Nasher, N. R., & Bhatt, A. (2021). Modeling the relationship between land use/land cover and land surface temperature in Dhaka, Bangladesh using CA-ANN algorithm. Environmental Challenges, 4, 100190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100190.
Kant, Y., Bharath, B. D., Mallick, J., Atzberger, C., & Kerle, N. (2009). Satellite-based analysis of the role of landuse/land cover and vegetation density on surface temperature regime of Delhi, India. Journal Indian Society Remote Sensing, 37(2), 201–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-009-0030-x.
Karakus, et al. (2015). Determination of land use/cover changes and land use potentials of sivas city and its surroundings using geographical information system (GIS) and remote sensing (RS). Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 15, 454–461.
Ketterer, C., Matzarakis, A. (2000). Human-biometeorological assessment of the urban heat island in a city with complex topography—The case of Stuttgart Germany. Urban Climate, 10(3), 573–584.
Khandelwal, S., Goyal, R., Kaul, N., & Mathew, A. (2017). Assessment of land surface temperature variation due to change in elevation of area surrounding Jaipur, India. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 21(1), 87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrs.2017.01.005.
Khorram, S., Biging, G., Chrisman, N., Colby, D., Congalton, R. G., Dobson, J., et al. (1999). Accuracy assessment of remote sensing derived change detection. American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing.
Kumar, K. S., Bhaskar, P. U., & Padmakumari, K. (2012). Estimation of land surface temperature to study urban heat island effect using landsat ETM+ image. International Journal of Engineering ScienceTechnology, 4, 771–778. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1064/1/012023.
Kumar, A., Agarwal, V., Pal, L., Chandniha, S. K., & Mishra, V. (2021). Effect of land surface temperature on urban heat Island in Varanasi City India. Multidisciplinary scientific Journal, 4(3), 420–429.
Lambin, E. F., Turner, B. L., Geist, H. J., Agbola, S. B., Angelsen, A., Bruce, J. W., Coomes, O. T., Dirzo, R., Fischer, G., Folke, C., & George, P. (2001). The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Global Environmental Change, 11(4), 261–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-3780(01)00007-3.
Lambin EF, Geist H (2006) Land-use and land-cover change: local processes and global impacts. Printed in Germany: Springer Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 236 p. ISBN: 1619–2435
Landsat Project Science Office (2000). Landsat 7 Science Data User’s Handbook.
Lillesand, T., Kiefer, R, W., Chipman, J. (2015). Remote sensing and image interpretation. John Wiley & Sons.
Liu, L., & Zhang, Y. (2011). Urban heat island analysis using the Landsat TM data and ASTER Data: A case study in Hong Kong. Remote Sensing, 3(12), 1535–1552.
Lu, D., & Weng, Q. (2007). A survey of image classification methods and techniques for improving classification performance. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(5), 823–870.
Lu, D., Mausel, P., Brondizio, E., & Moran, E. (2004). Change detection techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(12), 2365–2401. https://doi.org/10.1080/0143116031000139863.
Luck, M., & Wu, J. (2002). A gradient analysis of urban landscape pattern: A case study from the Phoenix metropolitan region, Arizona, U.S.A. Landscape Ecology, 17, 327–330.
Lunetta, R. S., Iiames, J., Knight, J., Congalton, R. G., & Mace, T. H. (2001). An assessment of reference data variability using a “virtual field resource database.” Photogrammetric engineering and remote sensing, 67(6), 707–715.
Magar, D. S., Magar, R. K. S., & Chidi, C. L. (2021). Assessment of urban heat island in Kathmandu valley (1999–2017). The Geographical Journal of Nepal, 14, 1–21. https://doi.org/10.3126/gjn.v14i0.35544
McFeeters, S. K. (1996). The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1425–1432.
Mirzaei, P. A., & Haghighat, F. (2010). Approaches to study Urban Heat Island–abilities and limitations. Building and Environment, 45(10), 2192–2201.
Mourya, M., Kumari, B., Tayyab, M., Paarcha, A., & Rahman, A. (2020). Indices based assessment of built-up density and urban expansion of fast growing Surat city using multi-temporal Landsat data sets. Geo Journal, 86(4), 1607–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10148-w.
Mushore, T. D., Odindi, J., Dube, T., & Mutanga, O. (2017). Prediction of future urban surface temperatures using medium resolution satellite data in Harare metropolitan city, Zimbabwe. Building and Environment, 122, 397–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2017.06.033.
Nichol, J. E. (1994). A GIS–based approach to micro-climate monitoring in Singapore’s high rise housing estates. Photogrammetry Engineering Remote Sensing, 60, 1225–1232.
Oke, T. R. (1976). The distinction between canopy and boundary–layer urban heat islands. Atmosphere, 14(4), 268–277.
Oke, T. R., & Maxwell, G. B. (1975). Urban heat island dynamics in Montreal and Vancouver. Atmospheric Environment, 9(2), 191–200.
Othman, A. A., Al-Saady, Y. I., Al-Khafaji, A. K., & Gloaguen, R. (2014). Environmental change detection in the central part of Iraq using remote sensing data and GIS. Arabian Journal of Geoscience, 7(3), 1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0870-0.
Pal, S., & Ziaul, S. (2017). Detection of land use and land cover change and land surface temperature in English Bazar urban centre. The Egypt Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Sciences, 20(1), 125–145.
Patra, S., Sahoo, S., Mishra, P., & Mahapatra, S. (2018). Impacts of Urbanization on land use / cover changes and its probable implications on local climate and ground water level. Journal of Urban Management, 7(2), 70–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jum.2018.04.006.
Pu, et al. (2006). Assessment of multi-resolution and multi-sensor data for urban surface temperature retrieval. Remote Sensing of Environment, 104(2), 211–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2005.09.022.
Ramchandra, T. V., Aithal, B. H., & Durgappa, S. D. (2019). Land surface temperature analysis in an urbanizing landscape through multi-resolution data. Journal Space Science Technology, 1(1), 1–10.
Rawart, J. S., & Kumar, M. (2015). Monitoring land use/cover change using remote sensing and gis techniques: A case study of Hawalbagh block, district Almora, Uttarakhand, India. Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 18(1), 77–84.
Reis,. (2008). Analyzing land use/land cover changes using remote sensing and GIS in Rize, North-East Turkey. Sensors, 8(10), 6188–6202.
Rogan, J., & Chen, D. (2004). Remote sensing technology for map** and monitoring land-cover and land-use change. Progress in Planning, 61(4), 301–325.
Rose, L., Devadas, M. D. (2009). Analysis of land surface temperature and land use/land cover types using remote sensing imagery—A case in Chennai city, India. In: The seventh international conference on urban clim held on, 29.
Roth, M., Oke, T. R., & Emery, W. J. (1989). Satellite-derived urban heat island from three coastal cities and the utilization of such data in urban climatology. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1699–1720. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431168908904002.
Santamouris, et al. (2015). Using reflective pavements to mitigate urban heat island in warm climates-Results from a large-scale urban mitigation project. Urban Climate, 24, 326–339.
Santra, A., Kumar, A., Mitra, S. S., & Mitra, D. (2022). Identification of built-up areas based on the consistently high heat radiating surface in the Kolkata metropolitan area. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 50(28), 1–15.
Smoyer-Tomic, K. E., Kuhn, R., & Hudson, A. (2003). Heat wave hazards: An overview of heat wave impacts in Canada. Natural Hazards, 28(2), 465–485. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022946528157.
Stathopoulou, M., Cartalis, C., Andritsos, A. (2011). Assessing the thermal environment of major cities in Greece.International conference passive and low energy cooling for the built environment, 28, 59–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2005.02.004.
Stewart, I. D., & Oke, T. R. (2012). Local climate zones for urban temperature studies. Bulletins of American Meteorological Society (BAMS), 93(12), 1879–1900. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00019.1
Sui, L. Y., & Ming, C. B. (2002). The study framework of land use/cover change based on sustainable development in China. Geographical Research, 21(3), 324–341.
Sun, T., Sun, R., & Chen, L. (2020). The trend inconsistency between land surface temperature and near surface air temperature in assessing urban heat island effects. Remote Sensing, 12(8), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12081271.
Talukdar, S., Rihan, M., Hang, H. T., Bhaskaran, S., & Rahman, A. (2021). Modelling urban heat island (UHI) and thermal field variation and their relationship with land use indices over Delhi and Mumbai metro cities. Environment Development and Sustainability, 24(3), 3762–3790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01587-7.
Tran, D. X., Pla, F., Latorre-Carmona, P., Myint, S. W., Caetano, M., & Kieu, H. V. (2017). Characterizing the relationship between land use land cover change and land surface temperature. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 124, 119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.01.001.
Turner, B. L., Meyer, W., & Skole, D. (1994). Global land use/land cover change: Towards an integrated study. Ambio, 23(1), 91–95.
Turner,M. G., Gardner, R. H., O’neill,R. V., O’Neill,R. V.(2001). Landscape ecology in theory and practice. Springer, New York.
Turner, B. L., Lambin, E. F., & Reenberg, A. (2007). The emergence of land change science for global environmental change and sustainability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, 104(52), 20666–20671.
Verburg, P. H., VanEck, J. R., deNijsT, C., Dijst, M. J., & Schot, P. (2004). Determinants of land-use change patterns in the Netherlands. Environment and Planning B: Planning Design, 31(1), 125–150. https://doi.org/10.1068/b307.
Weng, Q. (2001). A remote sensing? GIS evaluation of urban expansion and its impact on surface temperature in the Zhujiang Delta, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22, 1999–2014.
Weng, Q., Lu, D., & Schubring, J. (2004). Estimation of LST–Vegetation abundance relationship for urban heat island studies. Remote Sensing of Environment, 89(4), 467–483.
World Bank (2020). Urbanization at a glance, Washington, DC.
**ao, R. B., Ouyang, Z. Y., Zheng, H., Li, W. F., Schienke, E. W., & Wang, X. K. (2007). Spatial pattern of impervious surfaces and their impacts on land surface temperature in Bei**g, China. Journal of Environmental Science, 19(2), 250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(07)60041-2
**e, Q., & Zhou, Z. (2015). Impact of urbanization on urban heat island effect based on TM imagery in Wuhan China. Environment Engineering Management Journal, 14(3), 647–655.
**ong, Y., Huang, S., Chen, F., Ye, H., Wang, C., & Zhu, C. (2012). The impacts of rapid urbanization on the thermal environment: A remote sensing study of Guangzhou, South China. Remote Sensing, 4(7) 2033–2056. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs4072033.
Yang, Li., Qian, F., Song, Z., & K. (2016). Research on urban heat island effect. Procedia Engineering, 169, 11–18.
Yin, Z. Y., Stewart, D. J., Bullard, S., & MacLachlan, J. T. (2005). Changes in urban built-up surface and population distribution patterns during1986–1999 a case study of Cairo Egypt. Computers, Environment Urban Systems, 29(5), 595–616.
Yuan, F., & Bauer, M. E. (2007). Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in land satellite imagery. Remote Sensing Environment, 106(3), 375–386.
Yuan, B., Zhou, L., Dang, X., Sun, D., Hu, F., & Mu, H. (2021). Separate and combined effects of 3D building features and urban green space on land surface temperature. Journal of Environmental Management, 295, 113116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113116.
Yun, H. (2011). A study on land use/cover change the need for a new integrated approach. Geographical Research, 20(6), 645–652.
Zha, Y., Gao, J., & Ni, S. (2003). Use of normalized difference built-up index in automatically map** urban areas from TM imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 24(3), 583–594.
Zhang, X., Estoque, R. C., & Murayama, Y. (2017). An urban heat island study in Nanchang City, China based on land surface temperature and social-ecological variables. Sustainable Cities and Society, 32, 557–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.05.005.
Zhao, Z. Q., He, B. J., Li, L. G., Wang, H. B., & Darko, A. (2017). Profile and concentric zonal analysis of relationships between land use/land cover and land surface temperature: Case study of Shenyang, China. Energy and Buildings, 155, 282–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.09.046.
Zhou, Q., Robson, M., & Pilesjo, P. (1998). On the ground estimation of vegetation cover in Australian rangelands. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(9), 1815–1820.
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly grateful to the USGS /Landsat for providing free data and thankful to the Department of Geography, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India
Funding
No funds, grants or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
First author conceptualized and designed the manuscript, worked on methodology and maps preparation, while the second author wrote and revised the manuscript to get its final shape.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Data and Materials Availability
All the data used in this manuscript are made available.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Vashishtha, D. Spatio-temporal Assessment of Land Use Land Cover Changes and Their Impact on Variations of Land Surface Temperature in Aligarh Municipality. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 51, 799–827 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01652-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01652-2